Carbon Export in the Seasonal Sea Ice Zone North of Svalbard From Winter to Late Summer
- 1Institute of Arctic and Marine Biology, UiT–The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway
- 2Fram Centre, Norwegian Polar Institute, Tromsø, Norway
- 3Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Center for Polar and Marine Research, Bremerhaven, Germany
- 4Department of Oceanography and Climate, Institute of Marine Research, Bergen, Norway
- 5Département de Biologie, Québec-Océan and Takuvik, Université Laval, Quebec City, QC, Canada
- 6Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot, Poland
Phytoplankton blooms in the Arctic Ocean's seasonal sea ice zone are expected to start earlier and occur further north with retreating and thinning sea ice cover. The current study is the first compilation of phytoplankton bloom development and fate in the seasonally variable sea ice zone north of Svalbard from winter to late summer, using short-term sediment trap deployments. Clear seasonal patterns were discovered, with low winter and pre-bloom phytoplankton standing stocks and export fluxes, a short and intense productive season in May and June, and low Chl a standing stocks but moderate carbon export fluxes in the autumn post-bloom conditions. We observed intense phytoplankton blooms with Chl a standing stocks of >350 mg m−2 below consolidated sea ice cover, dominated by the prymnesiophyte Phaeocystis pouchetii. The largest vertical organic carbon export fluxes to 100 m, of up to 513 mg C m−2 day−1, were recorded at stations dominated by diatoms, while those dominated by P. pouchetii recorded carbon export fluxes up to 310 mg C m−2 day−1. Fecal pellets from krill and copepods contributed a substantial fraction to carbon export in certain areas, especially where blooms of P. pouchetii dominated and Atlantic water advection was prominent. The interplay between the taxonomic composition of protist assemblages, large grazers, distance to open water, and Atlantic water advection was found to be crucial in determining the fate of the blooms and the magnitude of organic carbon exported out of the surface water column. Previously, the marginal ice zone was considered the most productive region in the area, but our study reveals intense blooms and high export events in ice-covered waters. This is the first comprehensive study on carbon export fluxes for under-ice phytoplankton blooms, a phenomenon suggested to have increased in importance under the new Arctic sea ice regime.
Introduction
Vertical carbon export plays a key role in the biological carbon pump by contributing to the sequestration of CO2 from the surface to the deep ocean, as well as providing a food source for mesopelagic, deep-sea and benthic ecosystems (Ducklow et al., 2001; Boyd and Trull, 2007). In the Arctic Ocean, primary productivity and pelagic–benthic coupling are primarily driven by the distribution, thickness, and melting of sea ice, controlling the light transmittance and stratification in the waters below (Wassmann and Reigstad, 2011; Lalande et al., 2014). The proportion of multiyear ice (MYI) has declined by 90% since 1979 (Stroeve and Notz, 2018; IPCC report, 2019), and the Arctic Ocean is expected to be ice free in summer by the end of the century or earlier (Massonnet et al., 2012; Wang and Overland, 2012). Thus, the whole Arctic Ocean may eventually transition into a seasonally ice-covered ocean. As a result of the shorter, more transparent, and dynamic sea ice cover, large under-ice phytoplankton blooms in the Arctic have been reported (Fortier et al., 2002; Arrigo et al., 2012; Mundy et al., 2014; Assmy et al., 2017; Johnsen et al., 2018; Ardyna and Arrigo, 2020; Ardyna et al., 2020). Recent studies have described the phytoplankton dynamics and environmental drivers of these under-ice blooms (Ardyna et al., 2020), but the fate of the carbon produced by these blooms is yet to be explored (Ardyna and Arrigo, 2020).
As a consequence of the changing Arctic sea ice regime, blooms of phytoplankton are now beginning earlier in the seasonal sea ice zone (SIZ) (Kahru et al., 2011). The SIZ is defined as the area that encompasses the annual minimum and maximum sea ice extents as well as the ice margin significantly influenced by ocean (Wadhams, 1986). It has been predicted that the northern portions of the SIZ will experience the largest changes and that the earlier phytoplankton blooms would result in earlier and an overall increase in carbon export (Wassmann and Reigstad, 2011). Additionally, Wassmann and Reigstad (2011) predicted an extended ice-free period that would lead to a longer productive season, especially in the form of regenerated production dominated by heterotrophic processes once nutrients are limiting. However, little quantitative information exists from the northernmost regions of today's SIZ. Contrary to the Barents Sea, the areas further north have previously been logistically challenging to access, and thus, the current SIZ of the Eurasian Arctic has been understudied, especially across seasons.
Daily measurements of vertical export can reveal central processes occurring in the upper water column, including the timing and synchrony between phytoplankton blooms and zooplankton grazers, giving us insight into the partitioning of organic carbon between pelagic and benthic ecosystems. Since a large portion of pelagic–benthic coupling is determined by the gravitational flux of particles [but see Boyd et al. (2019) for other mechanisms], the protist community composition plays an important role. Protists are unicellular or unicellular-colonial eukaryotes, including heterotrophic, phototrophic, and mixotrophic organisms. Diatoms, large (generally >10 μm) unicellular phytoplankton encased in silicified shells, are considered to be important contributors to vertical carbon export under certain conditions. Once diatom blooms terminate their growth phase and nutrients become limited, mass sedimentation events of ungrazed cells are often observed (Kiørboe et al., 1996; Olli et al., 2002; Wassmann et al., 2006b; Bauerfeind et al., 2009; Juul-Pedersen et al., 2010; Lalande et al., 2014; Roca-Martí et al., 2017; 2019). Some diatom species form large chains that can aggregate or entrap other cells in sticky mucilage and sometimes spines, producing rapidly sinking flocs of cells (Assmy et al., 2019). On the other hand, several studies revealed limited export of Phaeocystis spp.-dominated blooms (Riebesell et al., 1995; Reigstad and Wassmann, 2007; Wolf et al., 2016), while others have reported significant contribution of this prymnesiophyte to export (Lalande et al., 2011; Moigne et al., 2015; Wollenburg et al., 2018), mainly as a consequence of deep mixing, aggregation, ballasting, or heavy grazing by large zooplankton who mediate export through the production of fast-sinking fecal pellets (Hamm et al., 2001; Reigstad and Wassmann, 2007; Boyd et al., 2019). This is consistent with a recent study, partly based on vertical export data presented herein, showing that the carbon flux attenuation coefficient is negatively correlated with the dominance of diatoms compared to non-ballasted Phaeocystis, and therefore, the relative contribution of diatoms is a good predictor for carbon flux attenuation in the upper 200 m of the water column, especially in the cold waters of the Arctic (Wiedmann et al., 2020).
As the Arctic is warming and stratification is strengthening as a result of freshening, generally reducing nutrient supply, the flagellated species, such as Phaeocystis spp., have been predicted to become more dominant, because their high surface-area-to-volume ratio makes them more efficient at acquiring nutrients, and their size and colonies embedded in polysaccharide gel matrixes make them hydrodynamically resistant to sinking (Li et al., 2009; Peter and Sommer, 2012; Metfies et al., 2016). A recent study has found bio-optical evidence for increasing dominance of Phaeocystis pouchetii in the Barents Sea (Orkney et al., 2020). This shift toward smaller cells has further been modeled to increase the length of the food web and, consequently, retain phytoplankton carbon and to be respired in the upper water column (Vernet et al., 2017). In addition, the decline in silicic acid concentrations, an essential nutrient for diatom growth, in the Nordic seas and Barents Sea (Hátún et al., 2017) seems to have led to the increased dominance of Phaeocystis in the Barents Sea (Orkney et al., 2020). Shifts in bloom-forming protists' composition, as well as their seasonal timing in relation to heterotrophic consumers, will greatly influence vertical export.
In order to measure the pelagic processes and associated export fluxes, synchronized and daily sampling is necessary. In our study, we investigate these processes seasonally under generally dense sea ice cover, from a collection of 22 short-term sediment trap deployments in the SIZ north of Svalbard. The study focuses on how the magnitude and attenuation of vertical export in the epipelagic zone is determined by seasonal variability in sea ice cover, protist community composition, and the composition of the exported organic material. With a seasonal coverage from late January to August in a region previously hard to access, this study provides new insight to the export efficiencies in the changing Arctic Ocean, including under-ice blooms.
Materials and Methods
Study Area
Vertical carbon export was studied during three field campaigns in the SIZ north of Svalbard: CarbonBridge (Bridging productivity regimes in the Arctic Ocean, with R/V Helmer Hanssen), N-ICE2015 (Norwegian young sea ICE Cruise, with R/V Lance), and TRANSSIZ (Transitions in the Arctic Seasonal Sea Ice Zone, PS92, ARK XXIX/1, with R/V Polarstern). In total, areas represented by 22 stations were sampled in May and August 2014 and from late January to late June 2015. The ice cover in the visited areas ranged from 0 to 100% in sea ice cover and was influenced to various degrees by Atlantic water transported by the West Spitsbergen Current (WSC) and by overlaying Arctic surface waters (ArSW) advected in the opposite direction (Rudels et al., 2000; Fer et al., 2017; Meyer et al., 2017; Crews et al., 2018; Menze et al., 2019) (Figure 1).
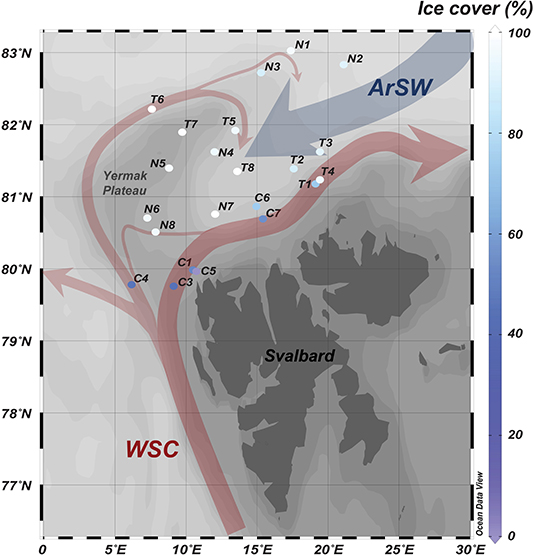
Figure 1. Map of the sampling stations, with rough visualization of the pathways of inflowing Atlantic water with the West Spitsbergen Current (WSC), subsequently splitting up in the Svalbard and Yermak AW Branches, respectively, while the blue arrow depicts the overlaying Arctic surface waters (ArSW) advected in the opposite direction. Station names refer to field campaign and order of sampling, where “C” is CarbonBridge (2014), “T” is TRANSSIZ (2015), and “N” is N-ICE2015 (2015), and the color of station symbols represents the sea ice cover at the stations upon sampling.
Sampling and Vertical Export Measurements
Short-term sediment trap arrays [KC Demark, parallel cylinders mounted on a gimbaled frame, with an aspect ratio (height:diameter) of 6.25 to avoid turbulent mixing in the cylinders during sampling] were deployed at the edge of or through a hole in a floe of drifting sea ice, at depths ranging from 5 to 200 m for 21 to 71.5 h, with longer deployments during periods of low flux (Table 1). The trap cylinders are weighted and mounted on a gimbaled frame equipped with a vane and will remain vertical and perpendicular to the current directions. No fixatives or poisons were added to the traps during deployment, but the trap cylinders were filled with a saturated NaCl solution to reduce microbial activity during the deployments of N-ICE2015, which were longer.
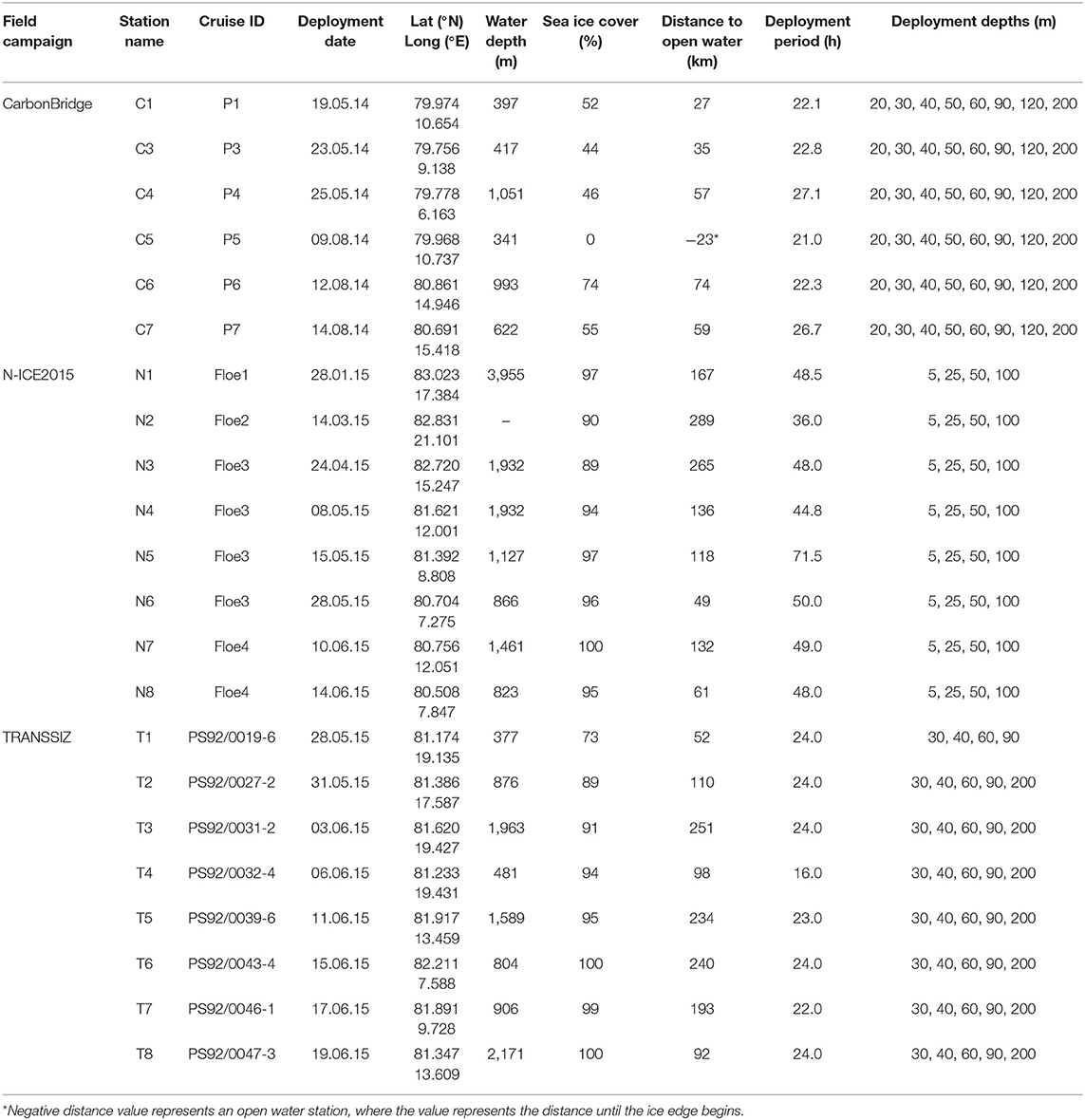
Table 1. Sampling station, cruise ID, sediment trap deployment date, location, water depth, sea ice cover, distance to open water, deployment period, and deployment depths.
Upon retrieval, the contents of the two trap cylinders from each depth were pooled, homogenized carefully, and subsampled for measurements of particulate organic carbon (POC) and nitrogen (PON) and chlorophyll a (Chl a) and for counts of protists and fecal pellets (FP) from large zooplankton. The 100-ml protist samples for CarbonBridge and TRANSSIZ were fixed with glutaraldehyde–Lugol mixture (2% final concentration), and the 200-ml fecal pellet samples with formaldehyde (2% final concentration). For N-ICE2015, samples for protist cell counts (100 ml) were fixed with an aldehyde mixture (0.1% glutaraldehyde and 1% hexamethylentetramine-buffered formaldehyde final concentrations). All samples were stored refrigerated (4°C) until microscopy analyses were performed.
Water samples for concentrations of suspended POC, PON, and Chl a, as well as for protists (during CarbonBridge and N-ICE2015), algal marker pigments determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (during TRANSSIZ), and inorganic nutrients [nitrates (nitrate and nitrite combined), phosphate, and silicic acid] analyses, were collected from discrete depths between 0 and 200 m, with Niskin bottles mounted on a Sea-Bird rosette water sampler equipped with a conductivity, temperature, and depth (CTD) probe (SBE911+). During CarbonBridge and TRANSSIZ, the inorganic nutrient samples were collected in acid-washed 100 ml plastic bottles and immediately frozen at −20°C, while during N-ICE2015, the samples were immediately fixed with 0.2 ml chloroform and refrigerated, until analysis could be performed in a land-based lab.
The POC, PON, and Chl a samples from both the suspended and exported profiles were filtered (300–500 ml) onto GF/F filters (Whatman), precombusted at 500°C for the POC/PON samples, and immediately frozen at −20°C, or immediately dried (at 60°C) and stored on PALL filter slides (N-ICE2015 samples), and analyzed later. For HPLC pigment analyses, water samples (1–2 L) were filtered on GFF filters and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Samples were thereafter stored at −80°C until analyses. The samples were then processed according to the procedures described in Kilias et al. (2013).
Chl a, POC/PON, and Nutrient Analyses
The frozen POC/PON filters were dried at 60°C for 24 h and subsequently placed in an acid fume bath (concentrated HCl) for 24 h to remove all inorganic carbon. The filters were then replaced into the 60°C drying oven for an additional 24 h and finally packed into nickel capsules. The samples were analyzed using an Exeter Analytical CE440 CHN elemental analyzer. Samples for POC/PON from N-ICE2015 were analyzed with continuous-flow mass spectrometry (CF-IMRS) carried out with a RoboPrep/Tracermass mass spectrometer (Europa Scientific, UK). Chl a was extracted from filters for roughly 12 h in the dark, in 100% methanol at 4–5°C, and measured fluorometrically using a pre-calibrated (Sigma, C6144) Turner Design AU-10 fluorometer. The samples were also measured fluorometrically for the degradation product phaeopigment by the addition of HCl (5% concentration) following Holm-Hansen and Riemann (1978).
The CarbonBridge and TRANSSIZ inorganic nutrient samples were analyzed for nitrate, nitrite, phosphate, and silicic acid following standard seawater methods, using a Flow Solution IV analyzer from O.I. Analytical, USA. The analyzer was calibrated using reference seawater from Oceanic Scientific International Ltd., UK. The N-ICE2015 samples were measured spectrometrically in a modified Skalar Autoanalyzer. The measurement uncertainty for nitrite is 0.06 mmol m−3 and 10% or less for nitrate, phosphate, and silicic acid.
Protist and Fecal Pellet Analyses
For N-ICE2015 and CarbonBridge, samples for protist cell counts were settled in Utermöhl sedimentation chambers (HYDRO-BIOS©, Kiel, Germany) for 48 h. Protists, here including phototrophic, heterotrophic, and mixotrophic unicellular eukaryotes, were identified and enumerated at 100–600× magnification using an inverted Nikon Ti-S light and epifluorescence microscope. The organisms were identified to the lowest possible taxonomic level, ideally to the species level, otherwise to the genus level or grouped into size classes. Cell carbon was estimated according to Menden-Deuer and Lessard (2000). For TRANSSIZ, the taxonomic structure of the protist community was deduced from the marker pigments measured by HPLC and applying the CHEMTAX program (Mackey et al., 1996), which takes into account that several marker pigments are not unique to one phytoplankton group. Pigment ratios used in the CHEMTAX program were constrained as suggested by Higgins et al. (2011) based on microscopic examination of representative samples during the cruise and applying the input matrix published by Fragoso et al. (2017). The resulting protist group composition was adjusted according to Chl a concentrations. For comparability between field campaigns, the relative biomass of protist groups in the upper water column (0–30 m) was used. Comparable protist data between field campaigns were not available from the sediment traps.
Depending on the concentration of pellets, 25–100 ml of the zooplankton fecal pellet subsamples were left for 24 h to settle in an Utermöhl sedimentation column and, subsequently, enumerated using a Leica inverted microscope. The length and width of each fecal pellet was measured, and its condition noted (intact, end-pieces or mid-pieces), and pellet volumes were calculated according to the shape of the pellets. Long cylindrical pellets were classified as calanoid copepod pellets, larger fecal strings with cut ends (filiform) were classified as euphausiid/krill pellets, and ellipsoid pellets were attributed to appendicularians and amphipods depending on their size (González, 2000; Wexels Riser et al., 2006). Fecal pellet volumes were converted into fecal pellet carbon (FPC) using a volumetric carbon conversion factor of 0.0943 mg C mm−3 for copepod pellets, 0.1861 mg C mm−3 for carnivorous amphipod pellets, 0.0451 mg C mm−3 for krill pellets, and 0.025 mg C mm−3 for appendicularians pellets (Wexels Riser et al., 2006).
Calculations: Depth-Integrated Standing Stocks, Loss Rate, and Phytoplankton Carbon
Standing stock was calculated for the upper 100 m of the water column by integrating the suspended Chl a or POC biomass samples. The 100-m depth horizon was chosen as previous studies have found that vertical flux at around 100 m explains >85% of the variation in biogenic matter on the surface sediment of the sea floor (Renaud et al., 2008). The fraction of the standing stock exported daily to 100 m is termed the loss rate and measured in % per day (Reigstad et al., 2008). For the stations where sediment traps were positioned at 90 m, the export flux was extrapolated to 100 m based on the flux curve (Boyd and Trull, 2007).
Estimates of the contribution of phytoplankton-derived POC (PPC) were derived from an estimation of the C:Chl a ratio, using the slope of the linear regression of POC against Chl a taken from the measurements of all the suspended samples at all stations, here 40.4 (w:w). The slope of the relationship will be the average C:Chl a of that organic matter which is statistically associated to the Chl a pigment (Banse, 1977), and the ratio of 40.4 found by the current study is in the range provided by previous literature, especially for biomasses including diatoms and prymnesiophytes (Sathyendranath et al., 2009).
The detritus fraction of the exported organic carbon was estimated by subtracting the PPC and FPC fractions from the total POC in the sediment trap samples.
Seasonal and Bloom Stage Categorization
The stations were separated according to the stage of the bloom they were in, based on the following parameters: sea ice cover, hydrographical characteristics and mixed layer depth, nutrient profiles, distinction and depth of the Chl a maximum, Chl a standing stocks, and protist community composition (Table 2). These parameters were chosen according to Hodal and Kristiansen (2008), Kubiszyn et al. (2017), Leu et al. (2015), Reigstad et al. (2002, 2008), Sundfjord et al. (2008), Tremblay et al. (2006), and Wassmann et al. (1999). Assessment of categorization was further supported by other studies from the field campaigns (Peeken, 2016; Assmy et al., 2017; Olsen et al., 2017; Massicotte et al., 2019; Sanz-Martín et al., 2019; Svensen et al., 2019). Depending on the focus of the study, the parameters may vary. Winter stations, ranging from late January to late April, were further separated from the pre-bloom stage according to sea ice cover and thicknesses (data found in Kowalczuk et al., 2017), nutrient profiles, and especially the standing stocks of Chl a and protist biomass. For further details, see Table 3.
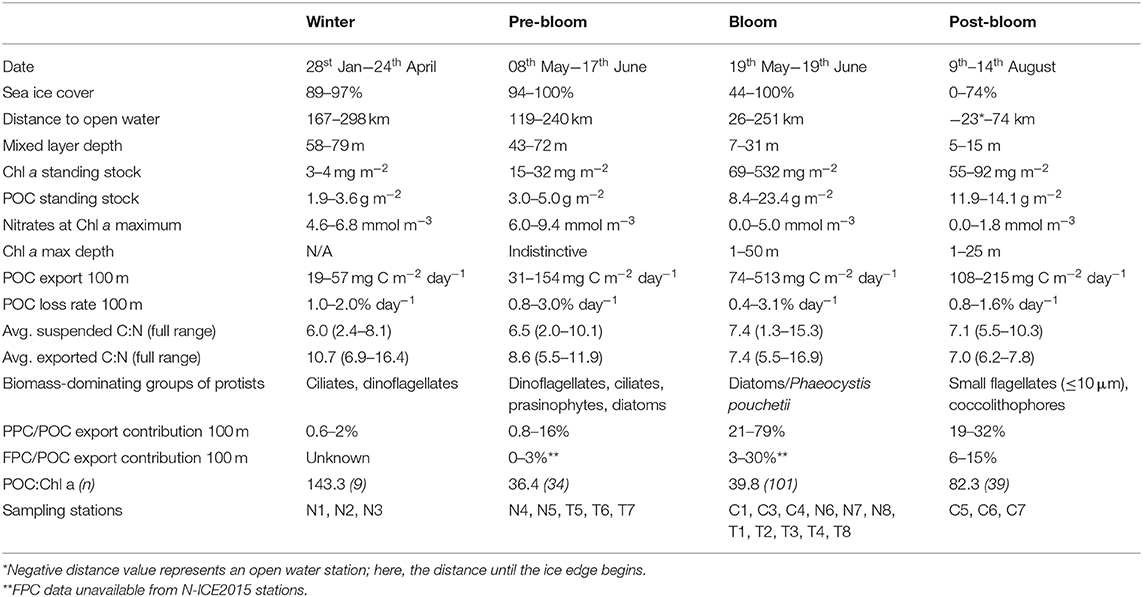
Table 3. Physical and biological properties during the different bloom stages at the 22 sampling stations in 2014 and 2015.
Sea Ice Cover, Distance to Open Water, and Water Mass Characteristics
Sea ice cover for all stations were derived from satellite data provided by the Center for Satellite Exploitation and Research [CERSAT, Ezraty et al. (2007)]. The product is available on a 12.5 × 12.5-km grid based on 85-GHz SSM/I brightness temperatures, using the ARTIST Sea Ice (ASI) algorithm. The distance to open water was calculated by measuring the distance to the closest area with ice areal cover of <15% as an ice edge indicator.
Mixed layer depths (MLD) were taken as the average depth of the mixed layer during the duration of the sediment trap deployment, based on existing datasets from the field campaigns. During CarbonBridge and TRANSSIZ, the MLD is defined as the depth where the potential density crosses 20% of the density difference between a surface layer density (3–5 m) and deeper (50–60 m) values (Nikolopoulos et al., 2016; Randelhoff et al., 2018). For N-ICE2015, the MLD was defined as the depth in each profile where the potential density first exceeded the density at 20 m depth by 0.01 kg m−3 in winter and the near-surface value by 0.003 kg m−3 in spring (Meyer et al., 2017).
Statistical Analyses
To assess the strength of trends in the data, linear regressions were performed on log-transformed Chl a standing stocks against the stations' distances to open water and against the mixed layer depth of each station. Standing stocks for the stations were log-transformed as they increased in an exponential manner as blooms developed.
Results
Environmental and Bloom Settings
All stations were located in ice-covered waters (44–100%), apart from one open water station (C5) sampled in August (Figure 1, Table 1). During N-ICE2015 and TRANSSIZ, ice thickness ranged from 0.90 to 1.45 m and snow thickness from 0.10 to 0.54 m, with the thickest snow and ice in early May over the northern part of the Yermak Plateau and thinnest in mid-June over the Sofia Basin and southern Yermak Plateau [for full details, see Kowalczuk et al. (2017) and Massicotte et al. (2019)]. Ice and snow thickness were not measured during the CarbonBridge campaign. Unfortunately, light measurements were not available for all campaigns, but see Pavlov et al. (2017) and Katlein et al. (2019) for the N-ICE2015 and TRANSSIZ/PS92 stations, respectively.
Winter and Pre-bloom
Typical winter conditions were found at the deep Nansen Basin stations sampled from late January to late April and characterized by dense ice cover and large distance (>160 km) to open water. The mixed layer depth at these stations ranged between 58 and 79 m within which water temperatures were close to the freezing point (on average −1.7°C) and salinities around 34.3 psu (Figures 2, 3B). In the upper 50 m, Chl a and POC standing stocks were very low (3–4 mg m−2, the lowest observed during the study), and nitrates (nitrate+nitrite) and silicic acid concentrations were between 5 and 7 mmol m−3 and between 2 and 3 mmol m−3, respectively (see Table 3, Figures 2, 3A).
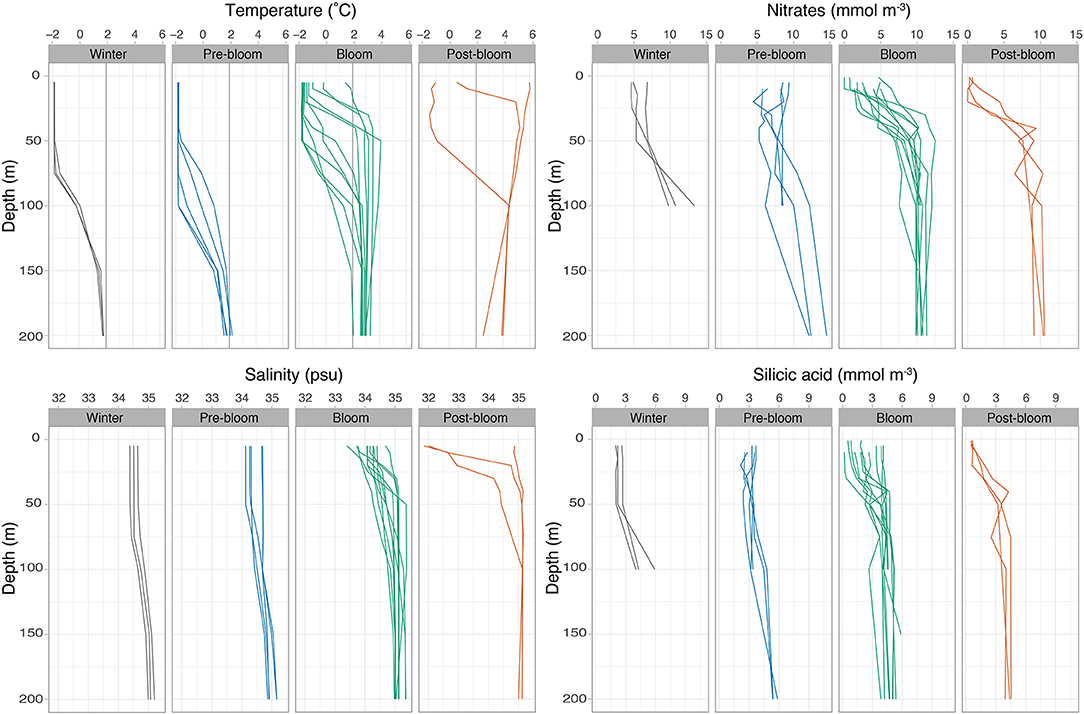
Figure 2. Physical and chemical setting of all the sampling stations, sorted into winter, prebloom, bloom, and post-bloom stages. Temperature (with 2°C Atlantic water reference line), salinity, nitrates, and silicic acid concentrations are shown for the upper 100–200 m of the water column.
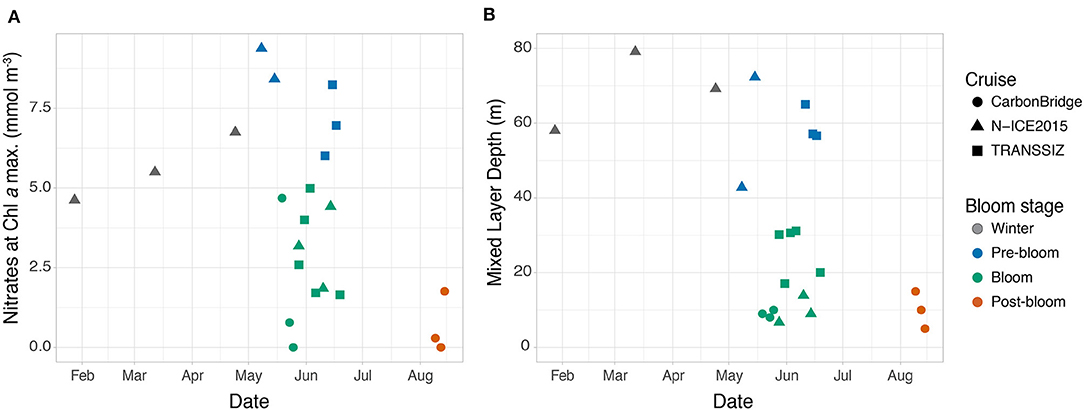
Figure 3. Seasonal development of (A) nitrate concentrations at the Chl a maximum depth or the average of the upper 10 m of the water column (when no Chl a maximum was present), and (B) of the depth of the mixed layer. Note that for N-ICE2015 and TRANSSIZ, the dates are from 2015, while for CarbonBridge, the dates are from 2014.
Five stations over the northern Yermak Plateau sampled in May and June were categorized as pre-bloom stations based on the dense sea ice cover, cold and saline surface conditions (Figure 2), low but increasing Chl a standing stocks, and high nutrient concentrations (6–9 mmol m−3 for nitrates and 2.5–4 mmol m−3 for silicic acid, Figure 3A) in the upper 100 m (Table 3). The pre-bloom stations had mixed layer depths between 43 and 72 m (Figure 3B).
Bloom
The highest Chl a standing stocks and low nutrient concentrations were recorded at 11 stations sampled in May and June (in 2014 and 2015). They were classified as bloom stations. In surface waters, the concentrations of nitrates ranged from 0 to 5 mmol m−3 (Figure 3A) and silicic acid from 0.2 to 4 mmol m−3 (Figure 2). For additional profiles of nitrates, silicic acid, and phosphate during the diatom and Phaeocystis blooms, see the Supplementary Materials. The areas over the Yermak Plateau (sampling stations N6–N8 and T8) and the shelf break (stations T1–T4) showed cold Arctic surface waters (<0°C) above the warmer modified or core Atlantic waters (Rudels et al., 2000), while the areas further south (stations C1–C4) showed warmer and more saline water masses throughout the water column (Figure 2). All stations had core Atlantic water (>2°C) below 100 m depth (with the exception of station T1) and mixed layer depths between 7 and 31 m (Figure 3B). For further details of water mass characteristics for these areas, see Meyer et al. (2017), Peeken (2016), and Randelhoff et al. (2018).
Post-bloom
The areas sampled in August were in a post-bloom stage (stations C5–C7), and nutrient concentrations in surface waters were very low (0–2 mmol m−3 for nitrates and 0.5–1 mmol m−3 for silicic acid), displaying warm and saline unstratified water column at station C5 and an advanced state of sea ice melt with a cold and fresh surface layer overlayering the warm and saline waters at depth at stations C6 and C7 (Figures 2, 3). These stations had lowered Chl a standing stocks (55–92 mg m−2) and mixed layer depths between 5 and 15 m (Figure 3B).
Seasonal Patterns
Standing Stocks
The standing stocks of Chl a and POC displayed large seasonal variation, with the broadest variation in May and June (Figure 4). During winter, standing stocks remained below ~3 mg Chl a m−2 and 5 g C m−2 (Table 3). Pre-bloom POC standing stocks were similar to winter conditions, but Chl a standing stocks were 10-fold higher (32 mg m−2).
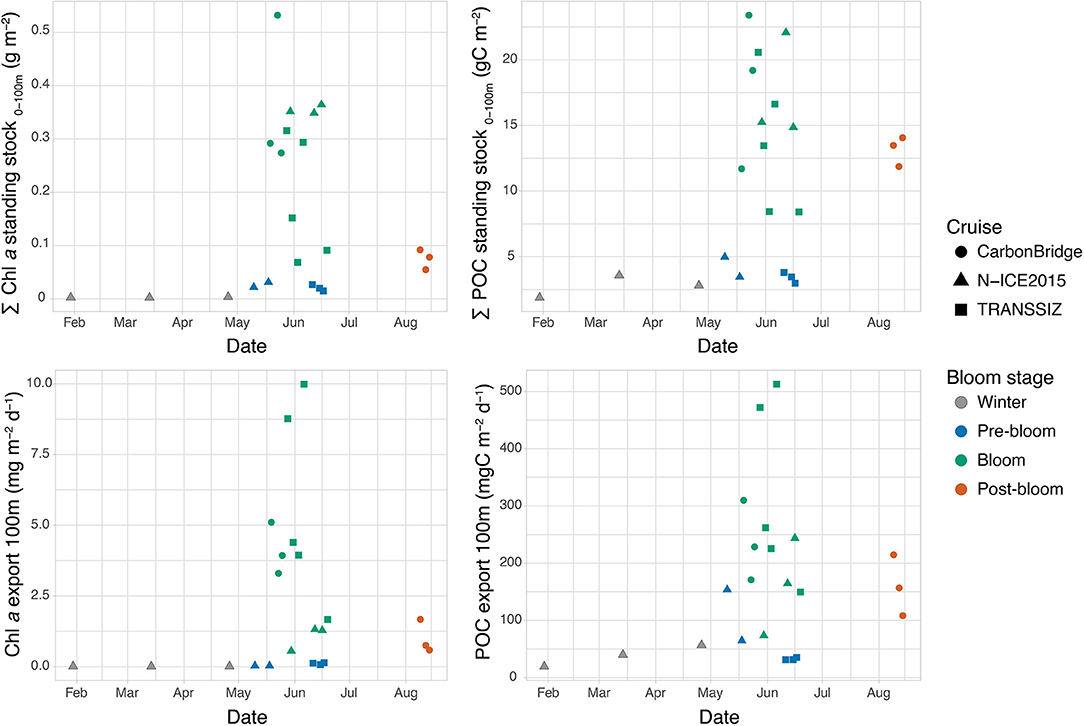
Figure 4. Seasonal development of depth-integrated Chl a and POC standing stock and vertical export flux of Chl a and POC. Note that for CarbonBridge, the dates are from 2014, while for N-ICE2015 and TRANSSIZ, the dates are from 2015.
During the bloom stage in May and June, Chl a and POC standing stocks ranged between 69 and 532 mg m−2 and between 8 and 23 g m−2, respectively. In August, the post-bloom stage, Chl a standing stocks had decreased to 55–92 mg m−2, while those of POC remained at intermediate levels of 12–14 g C m−2, twice as high as during the pre-bloom stages (Figure 4).
Relationships Between Chl a Standing Stock and Sea Ice Conditions
Strong negative correlations were found between the standing stock of Chl a and the distance to open water (r2 = 0.54, P = 0.00006; Figure 5A) and between Chl a standing stock and the mixed layer depth (r2 = 0.69, P = 0.000001; Supplementary Material). The sampling areas located closest to open water (<15% sea ice cover) were generally characterized by the highest standing stocks of Chl a, while those farthest into the ice had lower stocks. Notably, the sampling station in open water had lower Chl a standing stock than those situated between 27 and 109 km into the ice pack. The highest standing stock (532 mg Chl a m−2) was recorded at a station located 35 km into the ice. The sampling stations with the shallowest mixed layer depth (<25 m) generally had the highest Chl a standing stock, while areas with deeper mixed layers were mainly associated with lower standing stocks. No significant correlation was found between Chl a standing stock and ice cover (r2 = 0.06, P = 0.142) as the 15 stations where ice cover ≥89% showed almost the full range of integrated standing stocks (Figure 5B). It is important to note that these linear models span over many seasons and were not weighted accordingly.
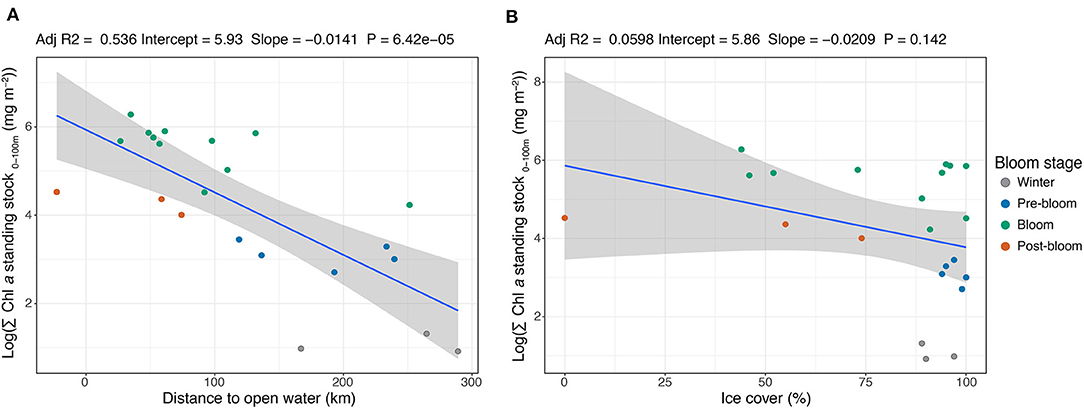
Figure 5. Linear regression between the stations' (n = 22) depth-integrated Chl a standing stock in the upper 100 m of the water column (on a logarithmic scale) and (A) the distances to open water (classified as <15% sea ice cover) and (B) sea ice cover. The regression fit (r2), intercept, slope, and P-value are shown above the respective figures. Note that the negative value for distance to open water refers to a station in open water and its distance from the ice edge, while the other positive values were all stations with sea ice cover >40%.
Surface Water Protist Community
During the winter over the Nansen Basin, ciliates and dinoflagellates dominated in terms of biomass in the upper 30 m of the water column (Figure 6). Ciliates, which accounted for 32–84% of the total biomass, were mainly composed of Mesodinium rubrum, Uronema marinum, and unidentified cysts, while dinoflagellates, accounting for 12–69% of the biomass, were mainly of Gymnodinium spp. and also Alexandrium sp. at station N2.
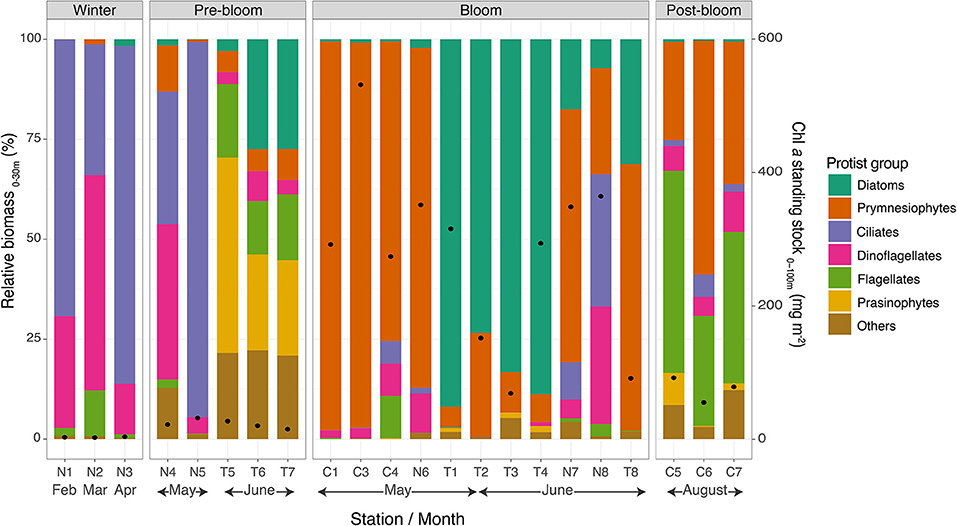
Figure 6. Relative biomass of dominant protist groups in the upper 30 m of the water column (bars) and Chl a standing stocks in the upper 100 m. Note that “C” stations were sampled in 2014 and “N” and “T” stations in 2015.
For the stations in a pre-bloom state over northern Yermak Plateau, the composition of the protist community in the upper 30 m differed between the N-ICE2015 and TRANSSIZ campaigns, which can be largely attributed to differences in timing. The N-ICE2015 stations in mid-May (N4–N5) had a 33–93% dominance of ciliates (mainly Mesodinium rubrum) and at station N4 of dinoflagellates (38%, Gymnodinium spp.) (Figure 6). The TRANSSIZ stations in mid-June 2015 (T5–T7) were dominated by prasinophytes and diatoms (24–48% and 3–27%, respectively). The relative biomass contributions from TRANSSIZ were based on HPLC analyses, and thus, further taxonomic resolution was not possible.
During the blooms when Chl a standing stocks were high, protist biomass in the upper water column was either dominated by diatoms or the prymnesiophyte P. pouchetii (Figure 6). The exception was N-ICE2015 station N8, sampled over the southern Yermak Plateau in June, where ciliates accounted for 33% (Leegaardiella sol and several unidentified species), dinoflagellates for 29% (Gynodinium spp.), and prymnesiophytes for 27%, which were mainly unidentified coccolithophores, in the upper 30 m. However, for station N8, at 50 m and below, the prymnesiophyte P. pouchetii dominated in terms of biomass (data not shown). The stations sampled over the shelf break north of Svalbard (T1–T4) were dominated by diatoms, 73–91% (Figure 6), mainly Thalassiosira antarctica var. borealis and Thalassiosira hyalina (pers. comm. Eva-Maria Nöthig). In the southernmost stations (C1–C4), the southern Yermak Plateau station N6, and the deeper Sofia Basin stations (N7 and T8), the relative protist biomass in the upper 30 m was dominated by P. pouchetii, 63–97% (Figure 6), mainly in the form of colonies.
The southernmost stations in August in post-bloom states (C5–C7) were found to be dominated by small unidentified flagellates (28–51%, mainly <10 μm in size) and by unidentified coccolithophores (24–59%) (Figure 6).
Vertical Export Fluxes
Similar seasonal patterns in Chl a and POC export fluxes were observed at 100 m depth (Figure 4). Export fluxes of Chl a were low during winter and the pre-bloom stage, between 0.005 and 0.14 mg m−2 day−1, and generally low for POC, between 19 and 65 mg C m−2 day−1, with the exception of the N-ICE2015 station N4 in May, which had a distinctly higher export flux of 154 mg C m−2 day−1 despite its low POC standing stock (4.9 g C m−2). During the blooms, the export fluxes varied greatly, with fluxes generally 10-fold higher than during the pre-bloom period, ranging from 1.3 to 10 mg m−2 day−1 and from 150 to 513 mg C m−2 day−1 for Chl a and POC, respectively. The exception was N-ICE2015 station N6, where export fluxes remained low (0.5 mg Chl a m−2 day−1 and 74 mg C m−2 day−1) while standing stocks were high (351 mg Chl a m−2 and 15 g C m−2). The post-bloom August conditions had relatively low Chl a export flux (0.6–1.7 mg m−2 day−1) but elevated POC export flux (108–215 mg C m−2 day−1), consistent with the higher POC standing stocks relative to Chl a standing stocks at those stations in August. Notably, the highest Chl a and POC standing stocks were found at the southernmost stations and over the southern Yermak Plateau (CarbonBridge and N-ICE2015 stations), but the highest export fluxes were measured over the shelf break north of Svalbard (TRANSSIZ stations) (Figure 4).
Vertical Depth Profiles of POC Export
Vertical depth resolution of POC export fluxes revealed that not only the magnitude of the exported material but also the vertical profiles changed over the seasons sampled. During winter, pre-bloom, and post-bloom conditions, the vertical profiles of POC fluxes remained low and relatively constant from the surface down to 100–200 m depth (Figure 7). For the bloom stations, the vertical export flux profiles showed a sharp decrease from the upper water column to depths of 100–200 m (Figure 7). The strongest attenuation of POC export was observed at bloom stations T1, T4, and N7, with very high export fluxes of 964–1,165 mg C m−2 day−1 at 25–30 m decreasing to 165–513 mg C m−2 day−1 at 100 m.
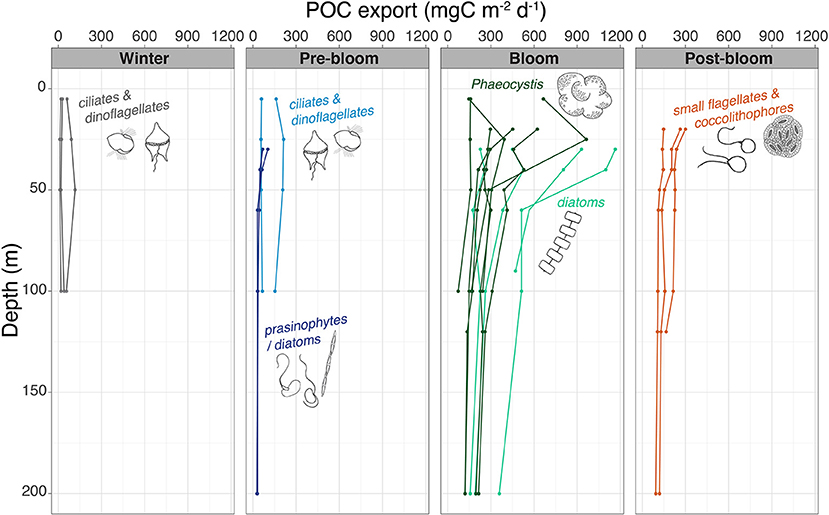
Figure 7. Vertical export flux of POC with depth. The dominant groups of protists in the surface waters are shown alongside their respective profiles or stations.
Loss Rates
During winter, vertical POC export fluxes were low (19–57 mg C m−2 day−1), equivalent to a loss of 0.6–2% day−1 of the POC standing stock, but increased with time (Figure 8). During the pre-bloom phase, POC fluxes were generally lower, but noteworthy differences were observed between the N-ICE2015 and TRANSSIZ stations, all of which were sampled over the Yermak Plateau (Figure 8). The TRANSSIZ sampling stations (T5, T6, and T7), located in dense ice cover in June, had low vertical export fluxes at 100 m (~30 mg C m−2 day−1), representing a daily loss of 0.5–0.9% day−1 of the POC standing stock. The N-ICE2015 stations (N4, N5), sampled in mid-May, had higher 100 m export fluxes. At station N4, these fluxes translated into a high daily POC loss rate of 3% day−1.
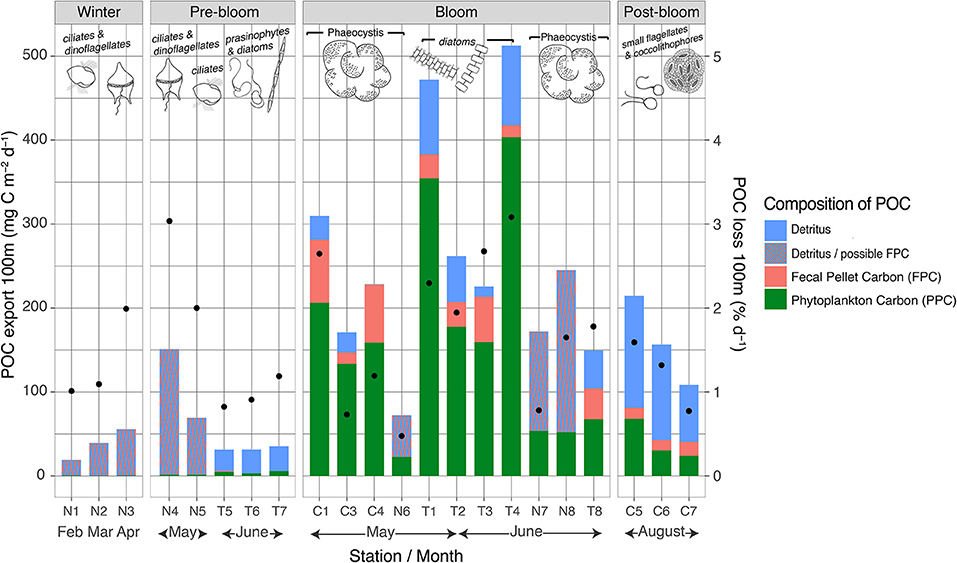
Figure 8. Vertical POC export at 100 m depth including composition (bars, absolute values stacked) and the daily POC loss rates for each station (black dots). Note that “detritus/possible FPC” represents those stations where FPC samples were unavailable for analyses and that the “C” stations were sampled in 2014 and the “N” and “T” stations in 2015. The drawings over the bars represent the dominant protist groups in the upper water column at each station.
A large variation was found within and between the stations sampled during blooms, with POC fluxes at 100 m ranging from 74 to 513 mg C m−2 day−1, translating into daily loss rates of 0.4–3% day−1 at 100 m (Figure 8). Furthermore, the strongest attenuation was at station N7 (Figure 7). At this station, vertical export rate at 100 m was only 17% of the flux at 25 m, while at stations T1–T4, 100 m export fluxes were 44–51% of that at 30 m (Figure 7). The highest 100-m vertical export was found at sampling stations T1 and T4, sampled in late May and early June over the shelf break north of Svalbard (Figure 1). Here, the POC loss rates were 2–3% of the standing stock (Figure 8). Notably, the four shelf-break stations had consistently higher 100 m loss rates for Chl a than for POC (3–6% day−1 compared to 2–3% day−1). For the southernmost stations sampled in May (C1–C4, Figure 1), the POC export and loss rates at 100 m varied greatly (Figure 7), between 74 and 310 mg C m−2 day−1 and between 0.4 and 2.6% day−1, respectively (Figure 8). Station C1 had a higher loss rate of POC (2.6% day−1) than for Chl a (1.7% day−1). Notably, the highest depth-integrated standing stocks of Chl a and POC (532 mg m−2 and 23.4 g m−2, respectively) were found at station C3, yet with low loss rates (0.6 and 0.7% day−1, respectively), and POC fluxes of 171 mg C m−2 day−1 at 100 m. Likewise, at sampling stations over the Yermak Plateau (N6, N7, and N8), Chl a standing stocks of ~350 mg m−2 were recorded, which were some of the highest values observed in the study, yet had Chl a loss rates of <0.4% day−1 at 100 m.
Finally, the stations in a post-bloom stage (C5, C6, and C7), sampled in August on the shelf north of Svalbard, found POC export fluxes of 108–215 mg C m−2 day−1 and POC loss rates of 0.8–1.6% day−1 (Figure 8).
Vertical Export Composition
During winter, the composition of the material exported at 100 m was largely unidentifiable particles classified as detritus (Figure 8). The calculated contribution of PPC to POC flux was ≤2%.
During the pre-bloom stage, the exported material was mainly comprised of detritus, 0–3% being FPC, and with a PPC contribution of 9–16% (Figure 8). The N-ICE2015 stations (N4 and N5), sampled in mid-May over the Yermak Plateau, had higher POC fluxes (64–153 mg C m−2 day−1) but with a lower contribution of PPC (<2%) (FPC contribution was unknown).
At the bloom-classified stations T1, T2, T3, and T4, sampled in late May and early June over the shelf break north of Svalbard (Figure 1), the highest 100-m vertical export fluxes were found and were composed of 75–79% PPC and 2.8–6.0% FPC (calanoid copepod and euphausiid pellets) (Figure 8). Of the southernmost stations in bloom (C1, C3, and C4) and those over the Yermak Plateau or Sofia Basin (N6, N7, N8, and T8), the highest fluxes were found where the exported POC had a larger contribution of FPC and/or detrital material (stations C1, C4, N8, and T8). For example, station C1, sampled in May at the southernmost area (Figure 1), had a 24% FPC contribution to the POC exported at 100 m, mainly produced by large calanoid copepods and euphausiids. Stations N6, N7, and N8 had Chl a standing stocks of ~350 mg m−2, some of the highest values observed in the current study, yet the contribution of PPC to exported POC was only 21–32% (Figure 8). FPC data were unavailable for analysis for these N-ICE2015 stations.
Of the POC exported during the post-bloom stages, 19.4–31.6% was found to be PPC derived and 6.1–15.4% to be FPC derived (calanoid copepod and euphausiid pellets) (Figure 8). Similar to winter and pre-bloom conditions, most of the exported POC was of detrital origin.
Discussion
The current study is the first seasonal compilation of the fate of phytoplankton blooms in the SIZ north of Svalbard, including under-ice blooms. Despite the relatively large area covered during this study, clear seasonal patterns were found: low winter, pre-bloom, and post-bloom biogenic standing stocks and export fluxes and a short and intense productive season in May and June, with the exception of the northern Yermak Plateau. The results revealed how high export fluxes, up to 513 mg C m−2 day−1 at 100 m, can occur even in areas densely covered by thinning sea ice. These under-ice blooms were aided by favorable environmental conditions including stratification, winter-accumulated nutrients, a sufficient phytoplankton inoculum, and light transmission to the surface water column through melt ponds or leads (Assmy et al., 2017; Randelhoff et al., 2018; Katlein et al., 2019; Kauko et al., 2019). The distance to open water was a better predictor of standing stocks and carbon export than sea ice cover at the stations. Furthermore, despite spatial and temporal heterogeneity, two types of blooms could be distinguished: one dominated by the prymnesiophyte P. pouchetii and one dominated by diatoms. The largest vertical export fluxes of POC and Chl a were found at bloom stations dominated by diatoms, while the largest standing stocks were found at stations dominated by P. pouchetii. Previously, the ice edge (marginal ice zone) was considered the most productive region in the area, but our study recorded intense blooms and high export events under ice-covered waters. The results reveal large variations in carbon export fluxes during different blooms and highlight the roles of phytoplankton community composition, the synchrony with zooplankton grazers, and the impact of advection in determining the fate of blooms in ice-covered waters.
Earlier Phytoplankton Blooms Trigger Earlier Vertical Export Pulses
As the sea ice cover in the Arctic Ocean is shrinking and thinning, blooms of phytoplankton are now beginning earlier and already partly below the consolidated ice cover (Kahru et al., 2011; Ardyna and Arrigo, 2020). Through a series of conceptual models, Wassmann and Reigstad (2011) suggested that the earlier onset of blooms would be reflected in the export of carbon, with the largest changes occurring in the northern portions of the SIZ. The study area north of Svalbard has experienced dramatic changes in sea ice conditions in the last decade with increased fragmentation of sea ice. No study has yet been able to quantify the vertical export rates under the new sea ice regime. During the current study, early and intense phytoplankton blooms were recorded in May and June in both 2014 and 2015, with Chl a and POC standing stocks reaching up to 0.5 and 23 g m−2, respectively, and POC fluxes exceeding 500 mg C m−2 day−1 at 100 m (Figure 4). This is a substantial increase when compared to a study performed in the same region in the summer of 1991 and 1997, when the ice was much thicker (classified as multiyear ice), where very low POC export fluxes were found in July (17–26 mg C m−2 day−1 at 100 m, ~20–50 mg C m−2 day−1 at 20–25 m) (Andreassen et al., 1996). As Andreassen et al. (1996) describe pre-bloom conditions in July, with surface nitrate concentrations of 4–6 mM, we strongly suggest a trend that phytoplankton blooms are occurring earlier in the season under the new sea ice regime. The earlier shift in carbon export fluxes has been found in the Central Arctic (Lalande et al., 2019), although the flux is mainly governed by ice algae, which play a negligible role in this study (Olsen et al., 2017).
Very little is known about winter and early spring vertical export flux, when access to the northern SIZ is logistically challenging. Our study reveals that during winter and the pre-bloom phase, under very dense sea ice cover, generally low POC export fluxes prevailed (19–57 mg C m−2 day−1) (Figure 4). These fluxes are comparable to observations in the Barents Sea in March 1998 (20–70 mg C m−2 day−1, with lower values in Arctic water masses and higher values in Atlantic water masses) (Olli et al., 2002). The ice cover during the current study was mostly composed of first-year ice (FYI) and second-year ice (SYI) (Granskog et al., 2017; Katlein et al., 2019), and high vertical export fluxes between 72 and 513 mg C m−2 day−1 and Chl a standing stocks of 69–352 mg m−2 were found below sea ice cover of 91–100%, similar high values used to be typical only in the SIZ of the highly productive Barents Sea (Wassmann and Slagstad, 1993; Wassmann et al., 2006a; Reigstad et al., 2008). Our study shows one of the largest and earliest phytoplankton blooms recorded for the European Arctic north of 80°N and allows for the first time the evaluation of the strong seasonality in daily vertical carbon export of this previously inaccessible region of the European Arctic.
“The Under-Ice Productivity Belt”—Blooms and Accompanying Export Found up to 250 km Into the SIZ
As the SIZ of the European Arctic has shifted northwards from the Barents Sea to the area north of Svalbard, it has moved into a heterogeneous area. North of Svalbard, the continental slope encompasses sharp changes in bathymetry, which influences the behavior and location of the topographically steered AW inflow and the degree of mixing with surrounding water masses (Crews et al., 2018; Renner et al., 2018). The effects of AW advection are discussed in the Export in a Dynamic Advective Environment section below. Additionally, the thinner sea ice is moving and fragmenting more rapidly with the Transpolar Drift (Spreen et al., 2011; Krumpen et al., 2019). Situated in a dense but variable ice-covered area, our results show that the location in relation to the ice edge and open water was generally more important in determining the phytoplankton bloom magnitude (in terms of Chl a standing stocks) than the percentage ice cover itself (Figure 5). Closer to the ice edge, the sea ice is more likely to be fragmented and characterized by leads (Willmes and Heinemann, 2016), allowing for more light to penetrate into the water column (Assmy et al., 2017), which may be especially important before melt pond formation. We suggest that the distance to open water be considered as an important predictor of blooms in sea ice-covered ecosystems. The most intense bloom (532 mg Chl a m−2, standing stock at station C3) was found in waters covered by 44% sea ice, roughly 35 km from open water (where sea ice cover was <15%). This bloom was classified as an ice edge bloom, which is often extensive as long as growth conditions are favorable (Wassmann et al., 1999; Tremblay et al., 2006), and contributes a substantial export of organic carbon to deeper waters (170 mg C m−2 day−1, 100 m at station C3).
In contrast, considerable standing stocks between 300 and 370 mg Chl a m−2 in the upper 100 m were found at stations with >95% ice cover, and 50–130 km into the ice pack, illustrating that blooms can develop under densely ice-covered conditions. Early stages of a bloom (moderate Chl a standing stocks and high surface nitrates and silicic acid) were even found at 250 km from open water. These under-ice blooms are comparable to large ice edge blooms in the productive Barents and Beaufort Seas (Reigstad et al., 2008; Mundy et al., 2009) and show a similar or even higher daily vertical fluxes between 74 and 513 mg C m−2 day−1 at 100 m depth. The blooms of the current study are likely locally produced blooms under the ice for the stations over the Yermak Plateau [see Assmy et al. (2017)] and possibly advected under the ice for those on the shelf break north of Svalbard where the AW boundary current is prominent [such as in Johnsen et al. (2018)]. Observations of under-ice blooms date back to the 1950s (Apollonio, 1961), but an increasing number of under-ice blooms have been reported during the last two decades, either produced locally under the ice (Fortier et al., 2002; Arrigo et al., 2012; Lowry et al., 2014; Mundy et al., 2014; Assmy et al., 2017; Ardyna et al., 2020) or advected below the ice cover (Metfies et al., 2016; Johnsen et al., 2018). More frequent observations of under-ice blooms can be partly attributed to the increased research efforts in the Arctic but largely to the changing sea ice conditions (Ardyna and Arrigo 2020). The current study area may be especially prone to large under-ice blooms in the future, with declining sea ice thickness causing changes in light climate (Nicolaus et al., 2012; Oziel et al., 2017; Katlein et al., 2019) and being positioned at the principal gateway for Atlantic water masses entering the Arctic Ocean (Aagaard et al., 1987; Crews et al., 2018; Renner et al., 2018). Although the environmental drivers of under-ice blooms have been examined [Ardyna et al. (2020) and studies therein], no study could yet provide any estimate of the carbon export potential of these under-ice blooms (Ardyna and Arrigo, 2020). Our study can reveal that if these blooms provide between 150 and 500 mg m−2 day−1 of organic carbon to the deeper waters, they could certainly increase the productivity of mesopelagic and benthic habitats and must be included in productivity and carbon flow models of the Arctic Ocean.
Our results further highlight the importance of surface stratification for primary production and subsequent vertical export fluxes to increase in the SIZ. A clear seasonal trend with a sharp reduction in surface nitrate concentrations and a shallowing of the mixed layer depth was observed from winter to spring and summer (Figure 3). Notably, mixed layer depths of ≤30 m were always observed during blooms, suggesting that a shallow mixed layer (associated with melting sea ice) may aid locally produced blooms to occur under the ice [supported by Strass and Nöthig (1996), M. Fortier et al. (2002), Tremblay et al. (2006), Leu et al. (2015), and Oziel et al. (2019)]. This is further supported by the strong negative correlation between mixed layer depth and Chl a standing stocks (P = 0.000001, Supplementary Material).
Winter surface nitrate concentrations were lower in late January (4.6 mmol m−3) and increasing to a maximum of 9.4 mmol m−3 during pre-bloom conditions in May. The winter stations sampled during the N-ICE expedition were positioned further north in the Nansen Basin and northern Yermak Plateau where surface nutrients are generally lower (Bluhm et al., 2015), which likely explains this apparent increase. Continuous mixing throughout winter will further contribute to increasing surface nutrient concentrations toward early spring (Randelhoff and Guthrie, 2016). Blooms that occur earlier in the SIZ (i.e., in April) and further north in the AO where nitrate concentrations are lower and mixing is limited (Tremblay et al., 2015) would be subject to lower surface nutrient concentrations at the initiation of the bloom, potentially decreasing the bloom magnitude and the strength of pelagic–benthic coupling. On the other hand, surface nutrient concentrations have been shown to be well-mixed in the immediate Atlantic inflow using observations based on moorings equipped with nitrate sensors, deployed from 2012 to 2013 on the shelf break north of Svalbard (Randelhoff et al., 2015).
Seasonal Changes in Phytoplankton Community and Export Composition Are Reflected in the Magnitude of Export
Very few seasonal studies of daily export flux of organic material exist in the SIZ, especially during winter and for short-term sediment trap deployments [for other Arctic regions, see Juul-Pedersen et al. (2008), Olli et al. (2002), and Szymanski and Gradinger (2016)]. Samples collected using short-term sediment traps represent snapshots in time, but as they can be combined with in situ suspended water and community samples, they can examine central processes occurring in the upper water column, including the synchrony between phytoplankton blooms and zooplankton grazers, illustrating the partitioning of organic carbon in the ecosystems of the pelagic and benthic realms. Our results demonstrate how the seasonal and regional variability in the pelagic community and the composition of the exported material affect the magnitude and depth of exported POC in the SIZ north of Svalbard.
The flat winter profiles with low POC export fluxes and moderate loss rates indicate that the low amounts of organic matter were evenly spread through the water column (Figure 7). Pre-bloom POC standing stocks were similar to winter conditions, but Chl a standing stocks were 10-fold higher, which is noteworthy as it suggests a decoupling of phytoplankton from the heterotrophic community in the winter to pre-bloom transition at high latitudes (Behrenfeld and Boss, 2014). Furthermore, during the period preceding the bloom, one station in early May over the northern Yermak Plateau (station N4) had, despite low Chl a and POC standing stocks, elevated POC loss to 100 m (>3% day−1 of POC standing stock, Figure 8). The vertical export at this station was strongly dominated by the ciliate M. rubrum and coincided with the collapse of a dense M. rubrum bloom at the ice–water interface. The bloom collapse likely resulted in the downward migration of this species and interception by the deeper sediment traps (Olsen et al., 2019), which represents active export of organic matter as opposed to passive settling of particles.
During phytoplankton blooms, high biomass will accumulate as long as vertical export is low. This was the case at station C3, which had relatively low vertical export accounting for loss rates of only 0.7% POC day−1 and 0.6% Chl a day−1 at 100 m, allowing for the buildup of the highest Chl a (532 mg m−2) and POC (23 g C m−2) standing stocks observed in the study. On the other hand, the highest vertical export fluxes are generally associated with intense blooms at the end of their growth phase when nutrients are exhausted (Agustí et al., 2020), grazing pressure is low, and the community composition allows for aggregation or mass flux of ungrazed cells (Wassmann et al., 2006a; Henson et al., 2019). The vertical export and loss rates varied greatly between the stations sampled during blooms, which highlights the need to examine the composition and vertical profiles of the exported material in order to outline the processes involved in the sedimentation of the blooms.
Diatoms are ballasted by silica frustules and often form long chains, while the prymnesiophyte P. pouchetii is a small flagellate (~5 μm in diameter) that often forms large polysaccharide-embedded colonies during blooms (Wassmann et al., 1999). Once diatoms terminate their growth phase, they tend to aggregate and ungrazed cells or resting spores can sink out of the surface layers at high rates, often leading to mass export events (Smetacek, 1985; Henson et al., 2006; Assmy et al., 2019). Phaeocystis, on the other hand, may form large blooms, but their contribution to carbon export is generally considered to be low (Reigstad and Wassmann, 2007; Wolf et al., 2016), unless ballasted by cryogenic gypsum (Wollenburg et al., 2018) or deep-mixed by eddies (e.g., Lalande et al., 2011). Recent findings also conclude that ballasted and sticky diatoms are generally poorly attenuated in the upper water column compared to non-ballasted Phaeocystis, and therefore, the relative contribution of diatoms is a good predictor for carbon flux attenuation, especially in the cold waters of the Arctic (Wiedmann et al., 2020). The current study found that the largest blooms were formed by Phaeocystis, but with loss rates <2% day−1 of POC standing stock and with average POC flux of 190 mg C m−2 day−1 at 100 m. The diatom bloom on the shelf break revealed very high POC export fluxes out of the epipelagic (Figure 8), with loss rates >2.5% day−1 and flux >450 mg C m−2 day−1, despite having some nitrates and silicic acid available in the upper water column and a strongly stratified layer below the Chl a maximum. These POC export fluxes are comparable and higher than many previous investigations in the highly productive Barents Sea (Wassmann and Slagstad, 1993; Olli et al., 2002; Reigstad et al., 2008) and higher than export estimates for the future SIZ (Wassmann and Reigstad, 2011). Furthermore, even when organic carbon was strongly attenuated in the surface waters in diatom-dominated systems (Figure 7), their contribution to carbon export at 100 m was higher than during Phaeocystis blooms. This demonstrates that diatom contribution to pelagic–benthic coupling is substantial and will very likely play a role in the fate of these blooms including the eventual carbon sequestration on the sea floor.
Furthermore, the locally produced under-ice Phaeocystis blooms over the Yermak Plateau had the lowest contribution of PPC to total POC export at 100 m of the bloom stations (Figure 8). Station N7, considered to be at peak bloom, showed great attenuation of organic carbon in surface layers, where POC export at 100 m was only 17% of that at 25 m. This demonstrates that at its peak (usually as growth conditions become unfavorable), where pelagic–benthic coupling is generally highest, the under-ice Phaeocystis bloom was attenuated and remineralized or grazed in the surface layers. On the other hand, two of the Phaeocystis-dominated sampling stations had notably higher export fluxes and loss rates of POC (Figure 8). At these stations, the contribution of fecal pellets to the carbon exported was quite high (25–30%), produced by large calanoid copepods and krill. Our results cannot confirm that these grazers fed directly on P. pouchetii, but nevertheless, it is likely that they facilitated much of the export in a Phaeocystis-dominated system [as found by Hamm et al. (2001)]. It is significant to note that out of the seven stations where Phaeocystis blooms were found in the current study, only two had depleted silicic acid stocks in the surface (Supplementary Material). Previous studies have suggested that diatoms will generally dominate blooms as long as silicic acid is not limiting (Ardyna et al., 2020). This was not the case in our study, which suggests that the light climate was possibly the decisive factor in the succession of these blooms (Assmy et al., 2017).
The post-bloom settings in August were associated with warmer and more saline waters, with shallow mixed layer depths, small flagellates and coccolithophores, and intermediate carbon export fluxes at 100 m, though with a lowered contribution of PPC (Figure 8). Likewise, the standing stocks of POC remained considerable (12–14 g C m−2), while those of Chl a were low (Figure 4). The FPC contribution to carbon export was also relatively low during the post-bloom stages (6–15% of total POC), possibly indicating a more detritus-derived carbon source, where grazing by large zooplankton was low (Rivkin et al., 1996). Small heterotrophs were more prominent during the post-bloom period (Lavrentyev et al., 2019), which would likely increase recycling and remineralization in the upper water column, preventing organic matter from sinking out of the epipelagic zone (Olli et al., 2002) and allowing high POC standing stocks to remain suspended. These findings agree with previous observations and predictions for the future SIZ, where a longer ice-free period late in the summer would be characterized by regenerated production, where the quality of the exported material would be increasingly degraded and recycled (Wassmann and Reigstad, 2011; Flores et al., 2019).
Export in a Dynamic Advective Environment
Since the early 2000s, the area investigated in this study has been subject to “Atlantification,” and as a result, it is characterized by declining sea ice cover and weakening stratification between the Atlantic water and polar surface waters above it (Polyakov et al., 2017; Lind et al., 2018). Due to their positions at the inflow of Atlantic water into the Arctic Ocean, the stations over the Yermak Plateau are likely experiencing a different water mass stability than those north and northwest of Svalbard (Figure 1; Fer et al., 2017; Crews et al., 2018; Menze et al., 2019). Therefore, it is likely that spatial variability in blooms and subsequent export observed in the current study is to a large extent driven by the variability in Atlantic water advection.
The sampling stations in May and June were characterized by large spatial variability, ranging from pre-bloom to bloom conditions in a relatively small area. Pre-bloom conditions were found in June over the northern Yermak Plateau, possibly as a result of inadequate light [see Massicotte et al. (2019)], great distance to open water (≥200 km), a deep-mixed layer depth, and possibly weaker Atlantic water advection (pers. comm. Sebastian Menze). Over the southern Yermak Plateau, slightly closer to open water (50–130 km), the large P. pouchetii blooms were likely locally produced under the sea ice, as Atlantic water advection was not found to be prominent but the algal cells were adapted to the low but variable light conditions penetrating through refrozen leads (Assmy et al., 2017; Pavlov et al., 2017; Kauko et al., 2019). On the other hand, the P. pouchetii blooms at the southernmost stations closer to Fram Strait in May 2014 were likely ice edge blooms due to the reduced ice cover (44–52% cover) and seeded by the West Spitsbergen Current (Johnsen et al., 2018; Paulsen et al., 2018; Sanz-Martín et al., 2019; Vernet et al., 2019). The vertical export fluxes and relative contribution of PPC differed between these two types of Phaeocystis blooms. The locally produced bloom generally had lower POC export fluxes with a smaller contribution of PPC to total POC exported, while the advected ice edge Phaeocystis bloom had a larger contribution of both PPC and FPC to the POC export at 100 m (Figure 8). This might suggest that the latter advected bloom consisted of phytoplankton cells that were brought into less favorable conditions (nutrient or light limited) and that large grazers advected into the area and facilitated higher POC export fluxes out of the surface waters (Svensen et al., 2019; Vernet et al., 2019; Wassmann et al., 2019), as opposed to the under-ice bloom which was still growing under favorable conditions with limited grazing (Kauko et al., 2019).
The current study cannot ascertain whether the diatom blooms on the shelf break were locally grown or advected underneath the sea ice cover, but we suspect the latter. Model simulations suggest that the area along the shelf break receives up to 50 times more advected gross primary production than what is locally produced (Vernet et al., 2019). On the other hand, no ice edge blooms were observed in the area, using satellite imagery, in the days prior to these blooms. The blooms may nevertheless have been seeded by advection of deeper Atlantic water masses (found below 40–170 m at these stations). Very high vertical POC export fluxes were found in this area (>500 mg C m−2 day−1), mostly consisting of PPC (~70%). Diatoms have been suggested to require stable light conditions to sustain growth rates (Hoppe et al., 2015; Assmy et al., 2017) and tend to sink faster under limited silicic acid conditions (Gross, 1948; Krause et al., 2018; Agustí et al., 2020). The increase in export fluxes from stations T1 to T4 (Figure 8), which were separated in time but similar in location, may suggest that once silicic acid became limiting (Figure 2), the growth conditions for these diatoms were reduced and subsequently increased their sinking velocity (Agustí et al., 2020). This is further supported by the deepening of the Chl a maxima from 10 to 25 m during the 8 days between sampling at stations T1 and T4, a reduction in surface silicic acid, and a very low mean light transmittance of 0.4 and 0.2% at these stations, respectively (Katlein et al., 2019). If the diatom bloom was advected under the pack ice, the change in light conditions may have contributed to the increased export flux, but unfortunately, our study cannot provide further evidence for the origin of this bloom.
The variability in FPC contribution to total POC export during the blooms (Figure 8) may also have been a result of the variable presence of Atlantic water and time of year. Large copepods (such as Calanus spp.) and krill were generally the main contributor to FPC export (data not shown). The southernmost region closer to Fram Strait and the WSC, where FPC export was the highest, is likely to receive larger advective biomass of Calanus earlier in the spring than areas further northeast along the AW boundary current, where they arrive or develop later in July and August (Basedow et al., 2018; Wassmann et al., 2019). This suggests that the reduced FPC contribution to POC export on the shelf break north of Svalbard may be a consequence of mismatch in timing between the phytoplankton bloom and the presence of large grazers (Wexels Riser et al., 2008).
Finally, advective variability highlights three concerns in the sampling methodology: (1) sampling of suspended biomass and calculations of depth-integrated standing stocks represent a snapshot in time, and therefore, subsequent comparisons to exported material (integrating over ≥24 h) and loss rates can be over- or underestimated; (2) sediment traps that drift with the ice instead of the water column may not follow even a semi-Lagrangian drift, an assumption upon which the calculations of loss rates and export fluxes are based (Olli et al., 2007); and (3) confounding of spatial and temporal trends by geographic spread of the stations. These considerations are especially important in advective areas, where production and sedimentation can occur many kilometers apart. Although these concerns add uncertainty to the results, the ice-tethered sediment traps are currently the only feasible method for collecting direct measurements of daily vertical export flux in ice-covered waters in combination with suspended particle stocks, and their long history of use makes them instrumental for comparisons.
Conclusion
Through extrapolation of the short-term measurements of vertical POC export from the current study, rough estimations of annual POC flux at 100 m for the area were found to be in the range of 24–34.5 g C m−2 year−1, depending on the conservativism of the estimate (for details, see Supplementary Materials). This calculation, although rough, is the first estimate of annual carbon fluxes in the new SIZ north of Svalbard, including under-ice blooms. Notably, it is comparable to sediment trap estimates from the southern Barents Sea (32–97 g C m−2 year−1) (Slagstad and Wassmann, 1996; Reigstad et al., 2008), but much higher than long-term sediment trap deployment estimates for other parts of the Arctic (0.1–10 g C m−2 year−1), with the lowest values from the central Arctic Ocean, summarized in Stein and Macdonald (2004).
Moreover, the present export fluxes were higher and occurred earlier in the year than previously observed in the same region (Andreassen et al., 1996; Lalande et al., 2014). Our results indicate that the thinner and more deteriorated sea ice in the area (Itkin et al., 2017) has extended the SIZ further north. Previously, the marginal ice zone was considered the most productive region in the area. Our study found intense phytoplankton biomasses and high carbon export fluxes, of up to 513 mg C m−2 day−1, to be found up to 250 km from open water, demonstrating stronger pelagic–benthic coupling in ice-covered waters than formerly reported.
The vertical export fluxes of POC followed the seasonal bloom progression, but the mass export of organic matter was influenced by the bloom composition and synchrony with grazers. Whether diatoms or P. pouchetii dominated the bloom had an impact on the carbon export, as the highest export fluxes were found in stations dominated by diatoms (Figure 9). If Phaeocystis blooms become more common in the Arctic (Orkney et al., 2020), it is likely to reduce absolute mass flux and thus limit pelagic–benthic coupling in the future Arctic SIZ, especially if no special circumstances are present to facilitate their export (e.g., Wollenburg et al., 2018). The presence of advected Atlantic water masses likely affected the magnitude of export fluxes by changing the growth conditions of phytoplankton blooms and their synchrony with the large zooplankton grazers. We emphasize the need to monitor seasonal successions of flux compositions, the timing and growth conditions of blooming phytoplankton under the ice, and their interactions with heterotrophic communities in order to make accurate predictions about the fate of productivity and the partitioning of organic carbon in the ecosystems of the pelagic and benthic realms in the future Arctic seasonal sea ice zone.
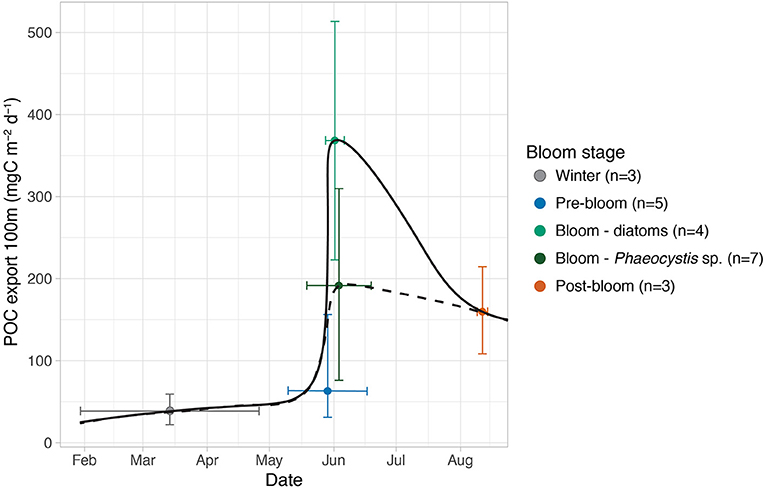
Figure 9. General seasonal progression of vertical POC export fluxes at 100 m in the region north of Svalbard (mean mg POC m−2 day−1, +/– full range). The export fluxes are separated into bloom conditions and dominant phytoplankton groups during the blooms (n, number of measurements). Black lines: rough visual interpolation of seasonal trend using diatoms (solid) and Phaeocystis (dashed) blooms.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated for this study are available on request to the corresponding author. All data are made available to the public; see PANGEA (https://www.pangae.de) and the Norwegian Polar Data Center (https://data.npolar.no).
Author Contributions
PA, MR, IP, and AN planned parts of the various field campaigns. CD, PA, LO, AR, MR, and TK collected the samples and conducted field measurements. AR and AN conducted oceanographic measurements. TK contributed to the sea ice data and performed sea ice analyses from satellite data. CD, AT, and JW did the microscopy analyses. IP performed the HPLC analysis. CD did the data analysis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all co-authors contributed to the final version. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
The N-ICE2015 project, PA and LO were supported by the former Center for Ice, Climate and Ecosystems (ICE) at the Norwegian Polar Institute; the Ministry of Climate and Environment, Norway; the Research Council of Norway (project No. 244646); and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Norway (project ID Arctic). MR and AR were supported by the CarbonBridge project, funded by the Research Council of Norway (project No. 226415). TRANSSIZ was funded by the PACES (Polar Regions and Coasts in a Changing Earth System) program of the Helmholtz Association (Grant No. AWI_PS92_00). CD and MR are funded by UiT–The Arctic University of Norway and the Tromsø Research Foundation through project Arctic SIZE (Arctic Seasonal Ice Zone Ecology, project No. 01vm/h15). The publication charges for this article have been funded by a grant from the publication fund of UiT–The Arctic University of Norway.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the captains and crews of R/V Lance, R/V Helmer Hanssen, and R/V Polarstern for their excellent support during the field work. We recognize the efforts of the CarbonBridge, N-ICE2015, and TRANSSIZ teams, and especially M. McGovern (UiT), for sample collection; A. Meyer (NPI), S. Menze (UiB), and R. Ingvaldsen (UiB) for their support with hydrographical analyses; and Magdalena Rózańska-Pluta (IO PAN) for microscopy analysis. We thank the two reviewers for their constructive comments.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2020.525800/full#supplementary-material
References
Aagaard, K., Foldvik, A., and Hillman, S. R. (1987). The west spitsbergen current: disposition and water mass transformation. J. Geophys. Res. 92:3778. doi: 10.1029/JC092iC04p03778
Agustí, S., Krause, J. W., Marquez, I. A., Wassmann, P., Kristiansen, S., and Duarte, C. M. (2020). Arctic (Svalbard islands) active and exported diatom stocks and cell health status. Biogeosciences 17, 35–45. doi: 10.5194/bg-17-35-2020
Andreassen, I., Nöthig, E. M., and Wassmann, P. (1996). Vertical particle flux on the shelf off northern Spitsbergen, Norway. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 137, 215–228. doi: 10.3354/meps137215
Apollonio, S. (1961). The chlorophyll content of Arctic sea-ice. JSTOR. 14, 197–200. doi: 10.14430/arctic3674
Ardyna, M., and Arrigo, K. R. (2020). Phytoplankton dynamics in a changing Arctic Ocean. Nat. Clim. Change 10, 892–903. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0905-y
Ardyna, M., Mundy, C. J., Mills, M. M., Oziel, L., Grondin, P.-L., Lacour, L., et al. (2020). Environmental drivers of under-ice phytoplankton bloom dynamics in the Arctic Ocean. Elem. Sic. Anth. 8:30. doi: 10.1525/elementa.430
Arrigo, K. R., Perovich, D. K., Pickart, R. S., Brown, Z. W., van Dijken, G. L., Lowry, K. E., et al. (2012). Massive phytoplankton blooms under Arctic sea ice. Science 336, 1408–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.1215065
Assmy, P., Fernández-Méndez, M., Duarte, P., Meyer, A., Randelhoff, A., Mundy, C. J., et al. (2017). Leads in Arctic pack ice enable early phytoplankton blooms below snow-covered sea ice. Sci. Rep. 7:40850. doi: 10.1038/srep40850
Assmy, P., Smetacek, V., Montresor, M., and Ferrante, M. I. (2019). “Algal Blooms,” in Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 4 Edn, ed T. M. Schmidt (Elsevier, Academic Press), 61–76.
Banse, K. (1977). Determining the carbon-to-chlorophyll ratio of natural phytoplankton. Mar. Biol. 41, 199–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00394907
Basedow, S. L., Sundfjord, A., Appen, von, W.-J., Halvorsen, E., Kwasniewski, S., and Reigstad, M. (2018). Seasonal variation in transport of zooplankton into the Arctic basin through the Atlantic gateway, fram strait. Front. Mar. Sci. 5:7. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00194
Bauerfeind, E., Nöthig, E.-M., Beszczynska, A., Fahl, K., Kaleschke, L., Kreker, K., et al. (2009). Variations in vertical particle flux in the Eastern fram strait (79°N/4°E) during 2000-2005. Results from the deep-sea long-term observatory HAUSGARTEN. Deep Sea Res. 56, 1471–1487. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2009.04.011
Behrenfeld, M. J., and Boss, E. S. (2014). Resurrecting the ecological underpinnings of ocean plankton blooms. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 6, 167–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-052913-021325
Bluhm, B. A., Kosobokova, K. N., and Carmack, E. C. (2015). A tale of two basins: An integrated physical and biological perspective of the deep Arctic Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 139, 89–121. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2015.07.011
Boyd, P. W., Claustre, H., Levy, M., Siegel, D. A., and Weber, T. (2019). Multi-faceted particle pumps drive carbon sequestration in the ocean. Nature 568, 327–335. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1098-2
Boyd, P. W., and Trull, T. W. (2007). Understanding the export of biogenic particles in oceanic waters: is there consensus? Prog. Oceanogr. 72, 276–312. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2006.10.007
Crews, L., Sundfjord, A., and Hattermann, T. (2018). How the yermak pass branch regulates Atlantic water inflow to the Arctic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 124, 267–280. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014476
Ducklow, H., Steinberg, D., and Buesseler, K. (2001). Upper ocean carbon export and the biological pump. Oceanog 14, 50–58. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2001.06
Ezraty, R., Girard-Ardhuin, F., Piollé, J.-F., Kaleschke, L., and Heygster, G. (2007). Arctic and Antarctic Sea Ice Concentration and Arctic Sea Ice Drift Estimated From Special Sensor Microwave Data – User's Manual, 2.1 Edition. Brest: Department d'Oceanographie Physique et Spatial; IFREMER; University of Bremen.
Fer, I., Sundfjord, A., and Randelhoff, A. (2017). Turbulent upper-ocean mixing affected by meltwater layers during arctic summer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 47, 835–853. doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-16-0200.1
Flores, H., David, C., Ehrlich, J., Hardge, K., Kohlbach, D., Lange, B. A., et al. (2019). Sea-ice properties and nutrient concentration as drivers of the taxonomic and trophic structure of high-Arctic protist and metazoan communities. Polar Biol. 42, 1377–1395. doi: 10.1007/s00300-019-02526-z
Fortier, M., Fortier, L., Michel, C., and Legendre, L. (2002). Climatic and biological forcing of the vertical flux of biogenic particles under seasonal Arctic sea ice. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 225, 1–16. doi: 10.3354/meps225001
Fragoso, G. M., Poulton, A. J., Yashayaev, I. M., Head, E. J. H., and Purdie, D. A. (2017). Spring phytoplankton communities of the Labrador Sea (2005-2014): pigment signatures, photophysiology and elemental ratios. Biogeosciences 14, 1235–1259. doi: 10.5194/bg-14-1235-2017
González, H. E. (2000). The role of faecal material in the particulate organic carbon flux in the northern humboldt current, chile (23degreesS), before and during the 1997-1998 El Nino. J. Plankton Res. 22, 499–529. doi: 10.1093/plankt/22.3.499
Granskog, M. A., Rösel, A., Dodd, P. A., Divine, D., Gerland, S., Martma, T., et al. (2017). Snow contribution to first-year and second-year Arctic sea ice mass balance North of Svalbard. J. Geophys. Res. 122, 2539–2549. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012398
Gross, F. (1948). The buoyancy of plankton diatoms: a problem of cell physiology. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 135, 382–389. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1948.0017
Hamm, C., Reigstad, M., Riser, C. W., Mühlebach, A., and Wassmann, P. (2001). On the trophic fate of Phaeocystis pouchetii. VII. Sterols and fatty acids reveal sedimentation of P. pouchetii-derived organic matter via krill fecal strings. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 209, 55–69. doi: 10.3354/meps209055
Hátún, H., Azetsu-Scott, K., Somavilla, R., Rey, F., Johnson, C., Mathis, M., et al. (2017). The subpolar gyre regulates silicate concentrations in the North Atlantic. Sci. Rep. 7, 14576–14579. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14837-4
Henson, S., Le Moigne, F., and Giering, S. (2019). Drivers of carbon export efficiency in the global ocean. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 33, 891–903. doi: 10.1029/2018GB006158
Henson, S. A., Sanders, R., Holeton, C., and Allen, J. T. (2006). Timing of nutrient depletion, diatom dominance and a lower-boundary estimate of export production for Irminger Basin, North Atlantic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 313, 73–84. doi: 10.3354/meps313073
Higgins, H., Wright, S., and Schlüter, L. (2011). “Quantitative interpretation of chemotaxonomic pigment Data,” in Phytoplankton Pigments: Characterization, Chemotaxonomy and Applications in Oceanography, Cambridge Environmental Chemistry Series, eds S. Roy, C. Llewellyn, E. Egeland, and G. Johnsen (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), 257–313. doi: 10.1017/CBO9780511732263.010
Hodal, H., and Kristiansen, S. (2008). The importance of small-celled phytoplankton in spring blooms at the marginal ice zone in the northern Barents Sea. Deep Sea Res. Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 55, 2176–2185. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.05.012
Holm-Hansen, O., and Riemann, B. (1978). Chlorophyll a determination: improvements in methodology. Oikos 30:438. doi: 10.2307/3543338
Hoppe, C. J. M., Holtz, L. M., Trimborn, S., and Rost, B. (2015). Ocean acidification decreases the light-use efficiency in an Antarctic diatom under dynamic but not constant light. New Phytol. 207, 159–171. doi: 10.1111/nph.13334
IPCC Report (2019): IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate eds H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer. IPCC Report. Available online at: https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/
Itkin, P., Spreen, G., Cheng, B., Doble, M., Girard-Ardhuin, F., Haapala, J., et al. (2017). Thin ice and storms: Sea ice deformation from buoy arrays deployed during N-ICE2015. J. Geophys. Res. 122, 4661–4674. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012403
Johnsen, G., Norli, M., Moline, M., Robbins, I., and Quillfeldt von, C., Sørensen, K., et al. (2018). The advective origin of an under-ice spring bloom in the Arctic Ocean using multiple observational platforms. Polar Biol. 41, 1197–1216. doi: 10.1007/s00300-018-2278-5
Juul-Pedersen, T., Michel, C., and Gosselin, M. (2010). Sinking export of particulate organic material from the euphotic zone in the eastern Beaufort Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 410, 55–70. doi: 10.3354/meps08608
Juul-Pedersen, T., Michel, C., Gosselin, M., and Seuthe, L. (2008). Seasonal changes in the sinking export of particulate material under first-year sea ice on the mackenzie shelf (Western Canadian Arctic). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 353, 13–25. doi: 10.3354/meps07165
Kahru, M., Brotas, V., Sarabia, M. M., and Mitchell, B. G. (2011). Are phytoplankton blooms occurring earlier in the Arctic? Glob. Chang. Biol. 17, 1733–1739. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02312.x
Katlein, C., Arndt, S., Belter, H. J., Castellani, G., and Nicolaus, M. (2019). Seasonal evolution of light transmission distributions through Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 4:1705. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014833
Kauko, H. M., Pavlov, A. K., Johnsen, G., Granskog, M. A., Peeken, I., and Assmy, P. (2019). Photoacclimation state of an Arctic underice phytoplankton bloom. J. Geophys. Res. 124, 1750–1762. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014777
Kilias, E., Wolf, C., Nöthig, E.-M., Peeken, I., and Metfies, K. (2013). Protist distribution in the Western fram strait in summer 2010 based on 454-pyrosequencing of 18S rDNA. J. Phycol. 49, 996–1010. doi: 10.1111/jpy.12109
Kiørboe, T., Hansen, J. L. S., Alldredge, A. L., Jackson, G. A., Passow, U., Dam, H. G., et al. (1996). Sedimentation of phytoplankton during a diatom bloom: rates and mechanisms. J. Mar. Res. 54, 1123–1148. doi: 10.1357/0022240963213754
Kowalczuk, P., Meler, J., Kauko, H. M., Pavlov, A. K., Zabłocka, M., Peeken, I., et al. (2017). Bio-optical properties of Arctic drift ice and surface waters north of Svalbard from winter to spring. J. Geophys. Res. 8, 2219–2227. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012589
Krause, J. W., Duarte, C. M., Marquez, I. A., Assmy, P., Fernández-Méndez, M., Wiedmann, I., et al. (2018). Biogenic silica production and diatom dynamics in the Svalbard region during spring. Biogeosciences 15, 6503–6517. doi: 10.5194/bg-15-6503-2018
Krumpen, T., Belter, H. J., Boetius, A., Damm, E., Haas, C., Hendricks, S., et al. (2019). Arctic warming interrupts the transpolar drift and affects long-range transport of sea ice and ice-rafted matter. Sci. Rep. 9:5459. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41456-y
Kubiszyn, A. M., Wiktor, J. M., Wiktor, J. M. Jr., Griffiths, C., Kristiansen, S., and Gabrielsen, T. M. (2017). The annual planktonic protist community structure in an ice-free high Arctic fjord (Adventfjorden, West Spitsbergen). J. Marine Syst. 169, 61–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2017.01.013
Lalande, C., Bauerfeind, E., and Nöthig, E. M. (2011). Downward particulate organic carbon export at high temporal resolution in the eastern Fram Strait: influence of Atlantic water on flux composition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 440, 127–136. doi: 10.3354/meps09385
Lalande, C., Nöthig, E.-M., and Fortier, L. (2019). Algal export in the Arctic ocean in times of global warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 46, 5959–5967. doi: 10.1029/2019GL083167
Lalande, C., Nöthig, E.-M., Somavilla, R., Bauerfeind, E., Shevchenko, V., and Okolodkov, Y. (2014). Variability in under-ice export fluxes of biogenic matter in the Arctic Ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 28, 571–583. doi: 10.1002/2013GB004735
Lavrentyev, P. J., Franzè, G., and Moore, F. B. (2019). Microzooplankton distribution and dynamics in the Eastern fram strait and the Arctic Ocean in may and august 2014. Front. Mar. Sci. 6:264. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00264
Leu, E., Mundy, C. J., Assmy, P., Campbell, K., Gabrielsen, T. M., Gosselin, M., et al. (2015). Arctic spring awakening – steering principles behind the phenology of vernal ice algal blooms. Prog. Oceanogr. 139, 151–170. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2015.07.012
Li, W. K. W., McLaughlin, F. A., Lovejoy, C., and Carmack, E. C. (2009). Smallest algae thrive as the Arctic ocean freshens. Science 326, 539–539. doi: 10.1126/science.1179798
Lind, S., Ingvaldsen, R. B., and Furevik, T. (2018). Arctic warming hotspot in the northern barents sea linked to declining sea-ice import. Nat. Clim. Change 8, 634–639. doi: 10.1038/s41558-018-0205-y
Lowry, K. E., van Dijken, G. L., and Arrigo, K. R. (2014). Evidence of under-ice phytoplankton blooms in the Chukchi sea from 1998 to 2012. Deep Sea Res. 105, 105–117. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2014.03.013
Mackey, M. D., Mackey, D. J., Higgins, H. W., and Wright, S. W. (1996). CHEMTAX - a program for estimating class abundances from chemical markers:application to HPLC measurements of phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 144, 265–283. doi: 10.3354/meps144265
Massicotte, P., Peeken, I., Katlein, C., Flores, H., Huot, Y., Castellani, G., et al. (2019). Sensitivity of phytoplankton primary production estimates to available irradiance under heterogeneous sea ice conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 124, 5436–5450. doi: 10.1029/2019JC015007
Massonnet, F., Fichefet, T., Goosse, H., Bitz, C. M., Philippon-Berthier, G., Holland, M. M., et al. (2012). Constraining projections of summer Arctic sea ice. Cryosphere 6, 1383–1394. doi: 10.5194/tc-6-1383-2012
Menden-Deuer, S., and Lessard, E. J. (2000). Carbon to volume relationships for dinoflagellates, diatoms, and other protist plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 45, 569–579. doi: 10.4319/lo.2000.45.3.0569
Menze, S., Ingvaldsen, R. B., Haugan, P., Fer, I., Sundfjord, A., Moeller, A. B., et al. (2019). Atlantic water pathways along the north-western svalbard shelf mapped using vessel-mounted current profilers. J. Geophys. Res. 124, 1699–1716. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014299
Metfies, K., Appen, W.-J., Kilias, E., Nicolaus, A., and Nöthig, E.-M. (2016). Biogeography and photosynthetic biomass of arctic marine pico-eukaroytes during summer of the record sea ice minimum 2012. PLoS ONE 11:e0148512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148512
Meyer, A., Fer, I., Sundfjord, A., and Peterson, A. K. (2017). Mixing rates and vertical heat fluxes north of Svalbard from Arctic winter to spring. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 3778–3718. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012441
Moigne, F. A. C., Poulton, A. J., Henson, S. A., Daniels, C. J., Fragoso, G. M., Mitchell, E., et al. (2015). Carbon export efficiency and phytoplankton community composition in the Atlantic sector of the Arctic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 120, 3896–3912. doi: 10.1002/2015JC010700
Mundy, C. J., Gosselin, M., Ehn, J., Gratton, Y., Rossnagel, A., Barber, D. G., et al. (2009). Contribution of under-ice primary production to an ice-edge upwelling phytoplankton bloom in the Canadian Beaufort Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36:1111. doi: 10.1029/2009GL038837
Mundy, C. J., Gosselin, M., Gratton, Y., Brown, K., Galindo, V., Campbell, K., et al. (2014). Role of environmental factors on phytoplankton bloom initiation under landfast sea ice in resolute Passage, Canada. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 497, 39–49. doi: 10.3354/meps10587
Nicolaus, M., Katlein, C., Maslanik, J., and Hendricks, S. (2012), Changes in Arctic sea ice result in increasing light transmittance and absorption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 39:L24501. doi: 10.1029/2012GL053738
Nikolopoulos, A., Janout, M., Hölemann, J. A., Juhls, B., Korhonen, M., and Randelhoff, A. (2016). Physical Oceanography During POLARSTERN Cruise PS92 (ARK-XXIX/1). Bremerhaven: Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research, PANGAEA.
Olli, K., Wassmann, P., Reigstad, M., Ratkova, T. N., Arashkevich, E., Pasternak, A., et al. (2007). The fate of production in the central Arctic Ocean – top–down regulation by zooplankton expatriates? Prog. Oceanogr. 72, 84–113. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2006.08.002
Olli, K., Wexels Riser, C., Wassmann, P., Ratkova, T., Arashkevich, E., and Pasternak, A. (2002). Seasonal variation in vertical flux of biogenic matter in the marginal ice zone and the central Barents Sea. J. Marine Syst. 38, 189–204. doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(02)00177-X
Olsen, L. M., Duarte, P., Peralta-Ferriz, C., Kauko, H. M., Johansson, M., Peeken, I., et al. (2019). A red tide in the pack ice of the Arctic Ocean. Sci. Rep. 9, 9536–9513. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45935-0
Olsen, L. M., Laney, S. R., Duarte, P., Kauko, H. M., Fernández-Méndez, M., Mundy, C. J., et al. (2017). The seeding of ice algal blooms in Arctic pack ice: the multiyear ice seed repository hypothesis. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 11, 643–620. doi: 10.1002/2016JG003668
Orkney, A., Platt, T., Narayanaswamy, B. E., Kostakis, I., and Bouman, H. A. (2020). Bio-optical evidence for increasing Phaeocystis dominance in the Barents Sea. Philo. Trans. R. Soc. 378:20190357. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2019.0357
Oziel, L., Massicotte, P., Randelhoff, A., Ferland, J., Vladoiu, A., Lacour, L., et al. (2019). Environmental factors influencing the seasonal dynamics of spring algal blooms in and beneath sea ice in western Baffin Bay. Elementa 7:34. doi: 10.1525/elementa.372
Oziel, L., Neukermans, G., Ardyna, M., Lancelot, C., Tison, J.-L., Wassmann, P., et al. (2017). Role for Atlantic inflows and sea ice loss on shifting phytoplankton blooms in the Barents Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 122, 5121–5139. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012582
Paulsen, M. L., Seuthe, L., Reigstad, M., Larsen, A., Cape, M. R., and Vernet, M. (2018). Asynchronous accumulation of organic carbon and nitrogen in the Atlantic Gateway to the Arctic Ocean. Front. Marine Sci. 5:416. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00416
Pavlov, A. K., Taskjelle, T., Kauko, H. M., Hamre, B., Hudson, S. R., Assmy, P., et al. (2017). Altered inherent optical properties and estimates of the underwater light field during an Arctic under-ice bloom of Phaeocystis pouchetii. J. Geophys. Res. 10, 4493–4423. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012471
Peeken, I. (2016). The Expedition PS92 of the Research Vessel POLARSTERN to the Arctic Ocean in 2015. Berichte zur Polar- und Meeresforschung Reports on Polar and Marine Research. Bremerhaven: Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research.
Peter, K. H., and Sommer, U. (2012). Phytoplankton cell size: intra- and interspecific effects of warming and grazing. PLoS ONE 7:e49632. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049632
Polyakov, I. V., Pnyushkov, A. V., Alkire, M. B., Ashik, I. M., Baumann, T. M., Carmack, E. C., et al. (2017). Greater role for Atlantic inflows on sea-ice loss in the Eurasian basin of the Arctic Ocean. Science 356, 285–291. doi: 10.1126/science.aai8204
Randelhoff, A., and Guthrie, J. D. (2016). Regional patterns in current and future export production in the central Arctic Ocean quantified from nitrate fluxes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 8600–8608. doi: 10.1002/2016GL070252
Randelhoff, A., Reigstad, M., Chierici, M., Sundfjord, A., Ivanov, V., Cape, M., et al. (2018). Seasonality of the physical and biogeochemical hydrography in the inflow to the Arctic ocean through fram strait. Front. Mar. Sci. 5:3778. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00224
Randelhoff, A., Sundfjord, A., and Reigstad, M. (2015). Seasonal variability and fluxes of nitrate in the surface waters over the Arctic shelf slope. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 3442–3449. doi: 10.1002/2015GL063655
Reigstad, M., and Wassmann, P. (2007). Does Phaeocystis spp. contribute significantly to vertical export of organic carbon? Biogeochemistry 83, 217–234. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-6214-8_16
Reigstad, M., Wassmann, P., Wexels Riser, C., Øygarden, S., and Rey, F. (2002). Variations in hydrography, nutrients and chlorophyll a in the marginal ice-zone and the central Barents Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 38, 9–29. doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(02)00167-7
Reigstad, M., Wexels Riser, C., Wassmann, P., and Ratkova, T. (2008). Vertical export of particulate organic carbon: attenuation, composition and loss rates in the northern Barents Sea. Deep Sea Res. Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 55, 2308–2319. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.05.007
Renaud, P. E., Morata, N., Carroll, M. L., Denisenko, S. G., and Reigstad, M. (2008). Pelagic–benthic coupling in the western Barents Sea: processes and time scales. Deep Sea Res. Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 55, 2372–2380. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.05.017
Renner, A. H. H., Sundfjord, A., Janout, M. A., Ingvaldsen, R. B., Möller, A. B., Pickart, R. S., et al. (2018). Variability and redistribution of heat in the atlantic water boundary current North of Svalbard. J. Geophys. Res. 123, 6373–6391. doi: 10.1029/2018JC013814
Riebesell, U., Reigstad, M., Wassmann, P., and Noji, T. (1995). On the trophic fate of phaeocystis pouchetii (Hariot): VI. Significance of Phaeocystis-derived mucus for vertical flux. Nether. J. Sea Res. 33, 193–203. doi: 10.1016/0077-7579(95)90006-3
Rivkin, R., Legendre, L., Deibel, D., Tremblay, J., Klein, B., Crocker, K., et al. (1996). Vertical flux of biogenic carbon in the ocean: is there food web control? Science 272, 1163–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5265.1163
Roca-Martí, M., Puigcorbé, V., Iversen, M. H., van der Loeff, M. R., Klaas, C., Cheah, W., et al. (2017). High particulate organic carbon export during the decline of a vast diatom bloom in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res. 138, 102–115. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.12.007
Rudels, B., Meyer, R., Fahrbach, E., Ivanov, V. V., and Østerhus, S., Quadfasel, D., et al. (2000). Water mass distribution in fram strait and over the yermak plateau in summer 1997. Ann. Geophys. 18, 687–705. doi: 10.1007/s00585-000-0687-5
Sanz-Martín, M., Vernet, M., Cape, M. R., Mesa, E., Delgado-Huertas, A., Reigstad, M., et al. (2019). Relationship between carbon- and oxygen-based primary productivity in the Arctic ocean, Svalbard Archipelago. Front. Mar. Sci. 6:191. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00468
Sathyendranath, S., Stuart, V., Nair, A., Oka, K., Nakane, T., Bouman, H., et al. (2009). Carbon-to-chlorophyll ratio and growth rate of phytoplankton in the sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 383, 73–84. doi: 10.3354/meps07998
Slagstad, D., and Wassmann, P. (1996). Climate change and carbon flux in the Barents Sea: 3-D simulations of ice-distribution, primary production and vertical export of particulate organic carbon. Mem. Natl. Inst. Polar Res. 51, 119–141.
Smetacek, V. S. (1985). Role of sinking in diatom life-history cycles: ecological, evolutionary and geological significance. Mar. Biol. 84, 239–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00392493
Spreen, G., Kwok, R., and Menemenlis, D. (2011), Trends in Arctic sea ice drift role of wind forcing: 1992–2009. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38:L19501. doi: 10.1029/2011GL048970
Stein, R., and Macdonald, R. W. (2004). The Organic Carbon Cycle in the Arctic Ocean. Berlin: Springer.
Strass, V. H., and Nöthig, E. M. (1996). Seasonal shifts in ice edge phytoplankton blooms in the Barents Sea related to the water column stability. Polar Biol. 16, 409–422. doi: 10.1007/BF02390423
Stroeve, J., and Notz, D. (2018). Changing state of Arctic sea ice across all seasons. Environ. Res. Lett. 13:103001. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aade56
Sundfjord, A., Ellingsen, I., Slagstad, D., and Svendsen, H. (2008). Vertical mixing in the marginal ice zone of the northern Barents Sea—Results from numerical model experiments. Deep Sea Res. Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 55, 2154–2168. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.05.027
Svensen, C., Halvorsen, E., Vernet, M., Franzè, G., Dmoch, K., Lavrentyev, P. J., et al. (2019). Zooplankton communities associated with new and regenerated primary production in the atlantic inflow North of Svalbard. Front. Mar. Sci. 6:528. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00293
Szymanski, A., and Gradinger, R. (2016). The diversity, abundance and fate of ice algae and phytoplankton in the Bering Sea. Polar Biol. 39, 309–325. doi: 10.1007/s00300-015-1783-z
Tremblay, J.-E., Anderson, L. G., Matrai, P., Coupel, P., Bélanger, S., Michel, C., et al. (2015). Global and regional drivers of nutrient supply, primary production and CO2 drawdown in the changing Arctic Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 139, 171–196. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2015.08.009
Tremblay, J.-E., Michel, C., Hobson, K. A., Gosselin, M., and Price, N. M. (2006). Bloom dynamics in early opening waters of the Arctic Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 51, 900–912. doi: 10.4319/lo.2006.51.2.0900
Vernet, M., Ellingsen, I., Seuthe, L., Slagstad, D., Cape, M. R., and Matrai, P. A. (2019). Influence of phytoplankton advection on the productivity along the Atlantic Water Inflow to the Arctic Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 6:583. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00583
Vernet, M., Richardson, T. L., Metfies, K., Nöthig, E.-M., and Peeken, I. (2017). Models of plankton community changes during a warm water anomaly in Arctic waters show altered trophic pathways with minimal changes in carbon export. Front. Mar. Sci. 4:2441. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2017.00160
Wadhams, P. (1986). “The seasonal ice zone,” in The Geophysics of Sea Ice, NATO ASI Series (Series B: Physics), ed N. Untersteiner (Boston, MA: Springer). doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-5352-0_15
Wang, M., and Overland, J. E. (2012). A sea ice free summer Arctic within 30 years: an update from CMIP5 models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 39:341. doi: 10.1029/2012GL052868
Wassmann, P., Ratkova, T., Andreassen, I., Vernet, M., Pedersen, G., and Rey, F. (1999). Spring bloom development in the marginal ice zone and the central Barents Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 20, 321–346. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0485.1999.2034081.x
Wassmann, P., and Reigstad, M. (2011). Future Arctic Ocean seasonal ice zones and implications for pelagic-benthic coupling. Oceanography 24, 220–231. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2011.74
Wassmann, P., Reigstad, M., Haug, T., Rudels, B., Carroll, M. L., Hop, H., et al. (2006a). Food webs and carbon flux in the Barents Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 71, 232–287. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2006.10.003
Wassmann, P., and Slagstad, D. (1993). Seasonal and annual dynamics of particulate carbon flux in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 13, 363–372. doi: 10.1007/BF01681977
Wassmann, P., Slagstad, D., and Ellingsen, I. H. (2019). Advection of mesozooplankton into the Northern Svalbard shelf region. Front. Mar. Sci. 6:304. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00458
Wassmann, P., Slagstad, D., Riser, C. W., and Reigstad, M. (2006b). Modelling the ecosystem dynamics of the Barents Sea including the marginal ice zone. J. Mar. Syst. 59, 1–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2005.05.006
Wexels Riser, C., Reigstad, M., Wassmann, P., Arashkevich, E., and Falk-Petersen, S. (2006). Export or retention? copepod abundance, faecal pellet production and vertical flux in the marginal ice zone through snap shots from the northern Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 30, 719–730. doi: 10.1007/s00300-006-0229-z
Wexels Riser, C., Wassmann, P., Reigstad, M., and Seuthe, L. (2008). Vertical flux regulation by zooplankton in the northern Barents Sea during Arctic spring. Deep Sea Res. Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 55, 2320–2329. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.05.006
Wiedmann, I., Romero, E. C., Alfageme, M. V., Renner, A. H. H., Dybwad, C., van der Jagt, H., et al. (2020). Arctic observations identify phytoplankton community composition as driver of carbon flux attenuation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 47:13. doi: 10.1029/2020GL087465
Willmes, S., and Heinemann, G. (2016). Sea-Ice wintertime lead frequencies and regional characteristics in the Arctic, 2003–2015. Remote Sens. 8:4. doi: 10.3390/rs8010004
Wolf, C., Iversen, M., Klaas, C., and Metfies, K. (2016). Limited sinking of phaeocystisduring a 12 days sediment trap study. Mol. Ecol. 25, 3428–3435. doi: 10.1111/mec.13697
Keywords: vertical carbon export, sea ice, phytoplankton, seasonality, Arctic ocean, under-ice bloom
Citation: Dybwad C, Assmy P, Olsen LM, Peeken I, Nikolopoulos A, Krumpen T, Randelhoff A, Tatarek A, Wiktor JM and Reigstad M (2021) Carbon Export in the Seasonal Sea Ice Zone North of Svalbard From Winter to Late Summer. Front. Mar. Sci. 7:525800. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.525800
Received: 10 January 2020; Accepted: 01 December 2020;
Published: 21 January 2021.
Edited by:
Gordon T. Taylor, Stony Brook University, United StatesReviewed by:
Jun Sun, Tianjin University of Science and Technology, ChinaLennart Thomas Bach, University of Tasmania, Australia
Copyright © 2021 Dybwad, Assmy, Olsen, Peeken, Nikolopoulos, Krumpen, Randelhoff, Tatarek, Wiktor and Reigstad. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Christine Dybwad, christine.dybwad@uit.no
 Christine Dybwad
Christine Dybwad Philipp Assmy
Philipp Assmy Lasse M. Olsen
Lasse M. Olsen Ilka Peeken
Ilka Peeken Anna Nikolopoulos
Anna Nikolopoulos Thomas Krumpen
Thomas Krumpen Achim Randelhoff2,5
Achim Randelhoff2,5  Agnieszka Tatarek
Agnieszka Tatarek Józef M. Wiktor
Józef M. Wiktor Marit Reigstad
Marit Reigstad