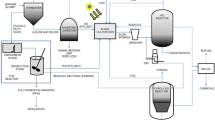
Abstract
A new methodology of biological treatment and conversion of farm waste (manure and wash water) with the use of intensively cultivated phototrophic microorganisms (microalgae) is reviewed. Criteria for selection of microalgae and peculiarities of their intensive cultivation for efficient removal of biogenic elements from and destruction of the organic components of the wastes as well as the possibilities of cost-effective utilization of the resulting microalgal biomass are considered. Advantages and drawbacks of the new methodology are compared with those of conventional anaerobic techniques. Special attention is paid to the integrated technologies combining the aerobic conversion methods with microalgal post-treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mulbry, W., Kondrad, S., Pizarro, C., and KebedeWesthead, E., Treatment of dairy manure effluent using freshwater algae: algal productivity and recovery of manure nutrients using pilot-scale algal turf scrubbers, Bioresour. Technol., 2008, vol. 99, pp. 8137–8142.
Kim, M.K., Park, J.W., Park, C.S., Kim, S.J., Jeune, K.H., Chang, M.U., and Acreman, J., Enhanced production of Scenedesmus spp. (green microalgae) using a new medium containing fermented swine wastewater, Bioresour. Technol., 2007, vol. 98, pp. 2220–2228.
Ntp 17-99. Normy tekhnologicheskogo proektirovaniya sistem udaleniya i podgotovki k ispol’zovaniyu navoza i pometa (Ntp 17-99. Engineering Standards for the Systems for Removal and Preparation of Manure and Dung for Use), Moscow: Minist. S-kh. Ross. Fed., 2001.
Afanas’ev, A., Analysis of technologies for processing manure and dung, Vestn. Vseross. Nauchno-Issled. Proektno-Tekhnol. Inst. Mekhaniz. Zhivotnovod., 2012, vol. 4, pp. 28–35.
Oswald, W.J. and Gotaas, H.B., Photosynthesis in sewage treatment, Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng., 1957, vol. 122, pp. 73–105.
Sivakumar, G., Xu, J., Thompson, R.W., Yang, Y., Randol-Smith, P., and Weathers, P.J., Integrated green algal technology for bioremediation and biofuel, Bioresour. Technol., 2011.
Munoz, R. and Guieysse, B., Algal-bacterial processes for the treatment of hazardous contaminants: a review, Water Res., 2006, vol. 40, pp. 2799–2815.
Mallick, N., Biotechnological potential of immobilized algae for wastewater N, P and metal removal: a review, BioMetals, 2002, vol. 15, pp. 377–390.
Crawford, M., Golfetto, I., Ghebremeskel, K., Min, Y., Moodley, T., Poston, L., Phylactos, A., Cunnane, S., and Schmidt, W., The potential role for arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acids in protection against some central nervous system injuries in preterm infants, Lipids, 2003, vol. 38, pp. 303–315.
Wang, X., Lin, H., and Gu, Y., Multiple roles of dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid against proliferation diseases, Lipids Health Dis., 2012, vol. 11, p. 25.
Cohen, Z. and Khozin-Goldberg, I., Searching for PUFA-rich microalgae, Single Cell Oils, Cohen, Z. and Ratledge, C., Eds., Champaign, IL: American Oil Chemists’ Society, 2010, pp. 201–224.
Guschina, I.A. and Harwood, J.L., Algal lipids and their metabolism, Algae for Biofuels and Energy, Borowitzka, M.A. and Moheimani, N.R., Eds., Dordrecht: Springer, 2013, pp. 17–36.
Dhankhar, J., Kadian, S.S., and Sharma, A., Astaxanthin: a potential carotenoid, Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res., 2012, vol. 3, pp. 1246–1259.
Takaichi, S., Carotenoids in algae: distributions, biosyntheses and functions, Mar. Drugs, 2011, vol. 9, pp. 1101–1118.
Park, J.B.K., Craggs, R.J., and Shilton, A.N., Wastewater treatment high rate algal ponds for biofuel production, Bioresour. Technol., 2011, vol. 102, pp. 35–42.
Georgianna, D.R. and Mayfield, S.P., Exploiting diversity and synthetic biology for the production of algal biofuels, Nature, 2012, vol. 488, pp. 329–335.
Pittman, J.K., Dean, A.P., and Usundeko, O., The potential of sustainable algal biofuel production using wastewater resources, Bioresour. Technol., 2011, vol. 102, pp. 17–25.
Fu, W., Guemundsson, O., Paglia, G., Herjolfsson, G., Andresson, O., Palsson, B., and Brynjolfsson, S., Enhancement of carotenoid biosynthesis in the green microalgal Dunaliella salina with light-emitting diodes and adaptive laboratory evolution, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 97, pp. 2395–2403.
Vance, C.P., Uhde-Stone, C., and Allan, D., L. phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource, New Phytol., 2003, vol. 157, pp. 423–447.
Lebedev, E., Possible environmental consequences of excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers, in Mineral’nyi i biologicheskii azot v SSSR (Mineral and Organic Nitrogen in the USSR), Moscow: Nauka, 1985, pp. 41–60.
Carpenter, S.R., Caraco, N.F., Correll, D.L., Howarth, R.W., Sharpley, A.N., and Smith, V.H., Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen, Ecol. Appl., 1998, vol. 8, pp. 559–568.
Mulbry, W., Kondrad, S., and Buyer, J., Treatment of dairy and swine manure effluents using freshwater algae: fatty acid content and composition of algal biomass at different manure loading rates, J. Appl. Phycol., 2008, vol. 20, pp. 1079–1085.
Mulbry, W., Westhead, E.K., Pizarro, C., and Sikora, L., Recycling of manure nutrients: use of algal biomass from dairy manure treatment as a slow release fertilizer, Bioresour. Technol., 2005, vol. 96, pp. 451–458.
Olguin, E.J., Phycoremediation: key issues for costeffective nutrient removal processes, Biotechnol. Adv., 2003, vol. 22, pp. 81–91.
Aslan, S. and Kapdan, I.K., Batch kinetics of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from synthetic wastewater by algae, Ecol. Eng., 2006, vol. 28, pp. 64–70.
Ruiz-Marin, A., Mendoza-Espinosa, L.G., and Stephenson, T., Growth and nutrient removal in free and immobilized green algae n batch and semi-continuous cultures treating real wastewater, Bioresour. Technol., 2010, vol. 101, pp. 58–64.
Kebede-Westhead, E., Pizarro, C., and Mulbry, W.W., Treatment of swine manure effluent using freshwater algae: production, nutrient recovery, and elemental composition of algal biomass at four effluent loading rates, J. Appl. Phycol., 2006, vol. 18, pp. 41–46.
Lincoln, E., Wilkie, A., and French, B., Cyanobacterial process for renovating dairy wastewater, Biomass Bioenergy, 1996, vol. 10, pp. 63–68.
Pizarro, C., Mulbry, W., Blersch, D., and Kangas, P., An economic assessment of algal turf scrubber technology for treatment of dairy manure effluent, Ecol. Eng., 2006, vol. 26, pp. 321–327.
Travieso, L., Benitez, F., and Dupeiron, R., Sewage treatment using immobilized microalgae, Bioresour. Technol., 1992, vol. 40, pp. 183–187.
Hoffman, J.P., Wastewater treatment with suspended and nonsuspended algae, J. Phycol., 2002, vol. 34, pp. 757–763.
Jimenez-Perez, M., Sanchez-Castillo, P., Romera, O., Fernandez-Moreno, D., and Perez-Martinez, C., Growth and nutrient removal in free and immobilized planktonic green algae isolated from pig manure, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2004, vol. 34, pp. 392–398.
Richmond, A., Principles for attaining maximal microalgal productivity in photobioreactors: an overview, Hydrobiologia, 2004, vol. 512, pp. 33–37.
Zarmi, Y., Bel, G., and Aflalo, G., Theoretical analysis of culture growth in glat-plate bioreactors: the essential role of timescales, Handbook of Microalgal Culture, Richmond, A. and Hu, Q., Eds., Wiley-Blackwell, 2013, pp. 205–224.
Lee, C.G. and Palsson, B., High-density algal photobioreactors using light-emitting diodes, Biothechnol. Bioeng., 1994, vol. 44, pp. 1161–1167.
Richmond, A., Cheng-Wu, Z., and Zarmi, Y., Efficient use of strong light for high photosynthetic productivity: interrelationships between the optical path, the optima population density and cell-growth inhibition, Biomol. Eng., 2003, vol. 20, pp. 229–236.
Vejrazka, C., Janssen, M., Streefland, M., and Wijffels, R.H., Photosynthetic efficiency of Chlamydomonas reingardtii in attenuated, flashing light, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2012.
Konig, A., Pearson, H., and Silva, S.A., Ammonia toxicity to algal growth in waste stabilization ponds, Water Sci. Technol., 1987, vol. 19, pp. 115–122.
Masseret, E., Amblard, C., Bourdier, G., and Sargos, D., Effects of a waste stabilization lagoon discharge on bacterial and phytoplanktonic communities of a stream, Water Environ. Res., 2000, vol. 72, pp. 285–294.
Javanmardian, M. and Palsson, B.O., High-density photoautotrophic algal cultures: design, construction, and operation of a novel photobioreactor system, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2004, vol. 38, pp. 1182–1189.
Chen, C.-Y., Yeh, K.-L., Aisyah, R., Lee, D.-J., and Chang, J.-S., Cultivation, photobioreactor design and harvesting of microalgae for biodiesel production: a critical review, Bioresour. Technol., 2011, vol. 102, pp. 71–81.
Ugwu, C.U., Aoyagi, H., and Uchiyama, H., Photobioreactors for mass cultivation of algae, Bioresour. Technol., 2008, vol. 99, pp. 4021–4028.
Camacho, RubioF., Sanchez, MironA., Ceron, GarciaM., Garcia, CamachoF., Molina, GrimaE., and Chisti, Y., Mixing in bubble columns: a new approach for characterizing dispersion coefficients, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2004, vol. 59, pp. 4369–4376.
Holland, A.D. and Wheler, D.R., Intrinsis autotrophic biomass yield and productivity in algae: modeling spectral and mixing-rate dependence, Biotechnol. J., 2011, vol. 6, pp. 584–599.
Guschina, I.A. and Harwood, J.L., Algla lipids and effect of the environment on their biochemistry, in Lipids in Aquatic Ecosystems, Kainz, M., Brett, M., and Arts, M., Eds., Dordrecht: Springer, 2009, pp. 1–24.
Lau, P., Tam, N., and Wong, Y., Effect of algal density on nutrient removal from primary settled wastewater, Environ. Pollut., 1995, vol. 89, pp. 59–66.
Lavoie, A. and de la Noue, J., Hyperconcentrated cultures of Scenedesmus obliquus: a new approach for wastewater biological tertiary treatment? Water. Res., 1985, vol. 19, pp. 1437–1442.
Johnson, M.B. and Wen, Z., Development of an attached microalgal growth system for biofuel production, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, vol. 85, pp. 525–534.
Abeliovich, A. and Azov, Y., Toxicity of ammonia to algae in sewage oxidation ponds, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1976, vol. 31, p. 801.
Azov, Y. and Goldman, J.C., Free ammonia inhibition of algal photosynthesis in intensive cultures, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1982, vol. 43, p. 735.
Brennan, L. and Owende, P., Biofuels form microalgae: a review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2010, vol. 14, pp. 557–577.
Solovchenko, A., Lobakova, E., Barskii, E., Savanina, Ya., Dol’nikova, G., Luk’yanov, A., and Kirpichnikov, M., Environmental photobiotechnologies for sewage treatment, Biotekhnologiya, 2011, no. 6.
Abeliovich, A., Water purification: algae in wastewater oxidation ponds, Handbook of Microalgal Culture: Biotechnology and Applied Phycology, Richmond, A., Ed., Blackwell, 2004, pp. 430–438.
Grobbelaar, J., Microalgal biomass productions: challenges and realities, Photosynth. Res., 2010, vol. 106, pp. 135–144.
Morweiser, M., Kruse, O., Hankamer, B., and Posten, C., Developments and perspectives of photobioreactors for biofuel production, Appl. Microbiol. Biotehcnol., 2010, vol. 887, pp. 1–11.
Molina, GrimaE., Fernandez, F., Garcia, CamachoF., and Chisti, Y., Photobioreactors: light regime, mass transfer, and scaleup, J. Biotehcnol., 1999, vol. 70, pp. 231–247.
Pulz, O. and Scheibenbogen, K., Photobioreactors: design and performance with respect to light energy input, Bioprocess and Algae Reactor Technology, Scheper, T., Ed., Berlin: Springer, 1998, pp. 123–152.
Bashan, L.E. and Bashan, Y., Immobilized microalgae for removing pollutants: review of practical aspects, Bioresour. Technol., 2010, vol. 101, pp. 1611–1627.
Abe, K., Takahashi, E., and Hirano, M., Development of laboratory-scale photobioreactor for water purification by use of a biofilter composed of the aerialmicroalga Trentepohlia aurea (Chlorophyta), J. Appl. Phycol., 2008, vol. 20, pp. 283–288.
Zhang, E., Wang, B., Wang, Q., Zhang, S., and Zhao, B., Ammonia-nitrogen and orthophosphate removal by immobilized Scenedesmus sp. isolated from municipal wastewater for potential use in tertiary treatment, Bioresour. Technol., 2008, vol. 99, pp. 3787–3793.
Molina Grima, E., Belarbi, E.H., Acien Fernandez, F., Robles Medina, A., and Chisti, Y., Recovery of microalgae biomass and metabolites: process options and economics, Biotechnol. Adv., 2003, vol. 20, pp. 491–515.
Divakaran, R. and Sivasankara Pillai, V., Flocculation of algae using chitosan, J. Appl. Phycol., 2002, vol. 14, pp. 419–422.
Olaizola, M., Microalgal removal of Co2 from flue gases: changes in medium ph and flue gas composition do not appear to affect the photochemical yield of microalgal cultures, Biotechnol. Bioproc. Engin., 2003, vol. 8, pp. 360–367.
Solovchenko, A., Physiological role of neutral lipid accumulation in eukaryotic microalgae under stresses, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2012, vol. 59, pp. 167–176.
Vooren, G.V., Le Grand, F., Legrand, J., Cuine, S., Peltier, G., and Pruvost, J., Investigation of fatty acids accumulation in 〈I〉 Nannochloropsis oculata 〈/I〉 for biodiesel application, Bioresour. Technol., 2012.
Solovchenko, A., Khozin-Goldberg, I., Recht, L., and Boussiba, S., Stress-induced changes in optical properties, pigment and fatty acid content of Nannochloropsis sp.; implications for non-destructive assay of total fatty acids, Mar. Biotehcnol., 2011, vol. 13, pp. 527–535.
Wilkie, A.C. and Mulbry, W.W., Recovery of dairy manure nutrients by benthic freshwater algae, Bioresour. Technol., 2002, vol. 84, pp. 81–91.
Woertz, I., Feffer, A., Lundquist, T., and Nelson, Y., Algae grown on dairy and municipal wastewater for simultaneous nutrient removal and lipid production for biofuel feedstock, J. Environ. Eng., 2009, vol. 135, pp. 1115–1122.
An, J.-Y., Sim, S.-J., Lee, J., and Kim, B., Hydrocarbon production form secondarily treated piggery waste-water by the green alga Botryococcus braunii, J. Appl. Phycol., 2003, vol. 15, pp. 185–191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.E. Solovchenko, A.A. Lukyanov, S.G. Vasilieva, Ya.V. Savanina, O.V. Solovchenko, E.S. Lobakova, 2013, published in Vestnik Moskovskogo Universiteta. Biologiya, 2013, No. 4, pp. 38–49.
The article was translated by the authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Solovchenko, A.E., Lukyanov, A.A., Vasilieva, S.G. et al. Possibilities of bioconversion of agricultural waste with the use of microalgae. Moscow Univ. Biol.Sci. Bull. 68, 206–215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392514010118
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0096392514010118