Abstract
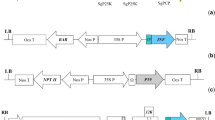
Development of RNAi-based therapeutics is a fast growing field of the pharmaceutical industry. Using plants for production of pharmaceutically valuable siRNAs may have significant advantages of costeffectiveness, scalability, and low risk of contamination with human pathogens. If edible plant species are genetically engineered to synthesize siRNAs, the costly stage of target product purification may be omitted. We describe the establishment of transgenic lettuce plants producing shRNA targeting delta isoform of protein kinase C (PKC-delta), an effective target for RNAi-based treatment of arterial hypertension. Transgenic lettuce plants were obtained by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation with genetic constructs harboring antiPKC and scrambled (control) shRNA genes. The presence of transgenes was proven by PCR analysis, and the accumulation of antiPKC shRNA was estimated using the RT-qPCR technique. Six transgenic lettuce lines showed varying levels of antiPKC shRNA expression with the highest value reaching 14 ± 9% of highly abundant endogenous lettuce micro RNA (miR156a), or 12.7 fmol/g dry weight. Plants carrying either antiPKC or scrambled shRNA genes flowered normally but did not produce seeds. The described transgenic lettuce plants accumulating antiPKC siRNA are the subject for animal testing and can be considered as raw material for the development of novel antihypertensive drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sibley, C.R., Seow, Y., and Wood, M.J., Novel RNAbased strategies for therapeutic gene silencing, Mol. Ther., 2010, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 466–476.
Gavrilov, K. and Saltzman, W.M., Therapeutic siRNA: principles, challenges, and strategies, Yale J. Biol. Med., 2012, vol. 85, no. 2, pp. 187–200.
Behlke, M.A., Chemical modification of siRNAs for in vivo use, Oligonucleotides, 2008, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 305–319.
Yu, B., Yang, Z., Li, J., Minakhina, S., Yang, M., Padgett, R.W., Steward, R., and Chen, X., Methylation as a crucial step in plant microRNA biogenesis, Science, 2005, vol. 307, no. 5711, pp. 932–935.
Lilley, C.J., Bakhetia, M., Charlton, W.L., and Urwin, P.E., Recent progress in the development of rna interference for plant parasitic nematodes, Mol. Plant Pathol., 2007, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 701–711.
Baum, J.A., Bogaert, T., Clinton, W., Heck, G.R., Feldmann, P., Ilagan, O., Johnson, S., Plaetinck, G., Munyikwa, T., Pleau, M., Vaughn, T., and Roberts, J., Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference, Nat. Biotechnol., 2007, vol. 25, no. 11, pp. 1322–1326.
Mao, Y.B., Cai, W.J., Wang, J.W., Hong, G.J., Tao, X.Y., Wang, L.J., Huang, Y.P., and Chen, X.Y., Silencing a cotton bollworm P450 monooxygenase gene by plantmediated RNAi impairs larval tolerance of gossypol, Nat. Biotechnol, 2007, vol. 25, no. 11, pp. 1307–1313.
Jin, S., Singh, N.D., Li, L., Zhang, X., and Daniell, H., Engineered chloroplast dsrna silences cytochrome p450 monooxygenase, V-ATPase and chitin synthase genes in the insect gut and disrupts Helicoverpa armigera larval development and chitin synthase genes in the insect gut and disrupts Helicoverpa armigera larval development and pupation, Plant Biotechnol. J., 2015, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 435–446.
Zhang, L., Hou, D., Chen, X., Li, D., Zhu, L., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Bian, Z., Liang, X., Cai, X., Yin, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, T., Zhu, D., Zhang, D., Xu, J., Chen, Q., Ba, Y., Liu, J., Wang, Q., Chen, J., Wang, J., Wang, M., Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., Zen, K., and Zhang, C.Y., Exogenous plant mir168a specifically targets mammalian ldlrap1: evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA, Cell Res., 2012, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 107–126.
Liang, H., Zhang, S., Fu, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, N., Liu, Y., Zhao, C., Wu, J., Hu, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, X., Zen, K., and Zhang, C.Y., Effective detection and quantification of dietetically absorbed plant microRNAs in human plasma, J. Nutr. Biochem., 2015, vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 505–512.
Lukasik, A. and Zielenkiewicz, P., In silico identification of plant mirnas in mammalian breast milk exosomes— a small step forward?, PLoS One, 2014, vol. 9, no. 6, p. e99963.
Li, J., Zhang, Y., Li, D., Liu, Y., Chu, D., Jiang, X., Hou, D., Zen, K., and Zhang, C.Y., Small non-coding RNAs transfer through mammalian placenta and directly regulate fetal gene expression, Protein Cell, 2015, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 391–396.
Dickinson, B., Zhang, Y., Petrick, J.S., Heck, G., Ivashuta, S., and Marshall, W.S., Lack of detectable oral bioavailability of plant microRNAs after feeding in mice, Nat. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 31, no. 11, pp. 965–967.
Bagci, C. and Allmer, J., One step forward, two steps back; xeno-microRNAs reported in breast milk are artifacts, PLoS One, 2016, vol. 11, no. 1, p. e0145065.
Chen, X., Zen, K., and Zhang, C.Y., Reply to lack of detectable oral bioavailability of plant microRNAs after feeding in mice, Nat. Biotechnol, 2013, vol. 31, no. 11, pp. 967–969.
Zhou, Z., Li, X., Liu, J., Dong, L., Chen, Q., Kong, H., Zhang, Q., Qi, X., Hou, D., Zhang, L., Zhang, G., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Wang, J., Chen, X., Wang, H., Zhang, J., Chen, H., Zen, K., and Zhang, C.Y., Honeysuckle-encoded atypical microRNA 2911 directly targets influenza a viruses, Cell Res., 2015, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 39–49.
Mlotshwa, S., Pruss, G.J., Macarthur, J.L., Endres, M.W., Davis, C., Hofseth, L.J., Pena, M.M., and Vance, V., A novel chemopreventive strategy based on therapeutic microRNAs produced in plants, Cell Res., 2015, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 521–524.
Petrick, J.S., Moore, W.M., Heydens, W.F., Koch, M.S., Sherman, J.H., and Lemke, S.L., A 28-day oral toxicity evaluation of small interfering RNAs and a long double-stranded RNA targeting vacular ATPase in mice, Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2014, vol. 71, no. 1, pp. 8–23.
Liu, N. and Olson, E.N., microRNA regulatory networks in cardiovascular development, Dev. Cell, 2010, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 510–525.
Silvestri, P., Di Russo, C., Rigattieri, S., Fedele, S., Todaro, D., Ferraiuolo, G., Altamura, G., and Loschiavo, P., Micrornas and ischemic heart disease: towards a better comprehension of pathogenesis, new diagnostic tools and new therapeutic targets, Recent Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug. Discov., 2009, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 109–118.
Novokhatska, T., Tishkin, S., Dosenko, V., Boldyriev, A., Ivanova, I., Strielkov, I., and Soloviev, A., Correction of vascular hypercontractility in spontaneously hypertensive rats using shrnas-induced delta protein kinase c gene silencing, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2013, vol. 718, nos. 1–3, p. 401–407.
Marillonnet, S., Thoeringer, C., Kandzia, R., Lkimyuk, V., and Gleba, Y., Systemic agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transfection of viral replicon for efficient transient expression in plants, Nat. Biotechnol., 2005, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 718–723.
Matveeva, N.A., Vasylenko, M., Shakhovsky, A.M., and Kuchuk, N.V., Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) with genes coding bacterial antigens from mycobacterium tuberculosis, Cytol. Genet., 2009, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 94–98.
Querci, M., Jermini, M., and Van der Eede, G., The analysis of food samples for the presence of genetically modified organisms. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, 2006.
Berdichevets, I.N., Shimshilashvili, H.R., Gerasymenko, I.M., Sindarovska, Y.R., Sheludko, Y.V., and Goldenkova-Pavlova, I.V., Miltiplex pcr assay for detection of recombinant genes encoding fatty acid desaturases fused with lichenase reporter protein in GM plants, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2010, vol. 397, no. 6, pp. 2289–2293.
Kurihara, Y., Takashi, Y., and Watanabe, Y., The interaction between dcl1 and hyl1 is important for efficient and precise processing of pri-miRNA in plant microRNA biogenesis, RNA, 2006, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 206–212.
Arif, M.A., Frank, W., and Khraiwesh, B., Role of RNA interference (RNAi) in the moss Physcomitrella patens, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2013, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 1516–1540.
Kramer, M.F., Stem-loop RT-qRCR for miRNAs, Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol., 2011, vol. 15, unit 15–10.
Hong, Y. and Jackson, S., Floral induction and flower formation—the role and potential applications of mRNAs, Plant Biotechnol. J., 2015, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 282–292.
Wang, C.Y., Zhang, S., Yu, Y., Luo, Y.C., Liu, Q., Ju, C., Zhang, Y.C., Qu, L.H., Lucas, W.J., Wang, X., and Chen, Y.Q., Mir397b regulated both lignin content and seed number in Arabidopsis via modulating a laccase involved in lignin biosynthesis, Plant Biotechnol. J., 2014, vol. 12, no. 8, pp. 1132–1142.
Barik, S., RNAi in moderation, Nat. Biotechnol., 2006, vol. 24, no. 7, pp. 796–797.
Tiwari, M., Sharma, D., and Trivedi, P.K., Artificial microRNA mediated gene silencing in plants: progress and perspectives, Plant. Mol. Biol., 2014, vol. 86, nos. 1–2, p. 1–18.
McBride, J.L., Boudreau, R.L., Harper, S.Q., Staber, P.D., Monteys, A.M., Martins, I., Gilmore, B.L., Burstein, H., Peluso, R.W., Polisky, B., Carter, B.J., and Davidson, B.L., Artificial miRNAs mitigate shRNAmediated toxicity in the brain: implications for the therapeutic development of RNAi, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, vol. 105, no. 15, pp. 5868–5873.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.M. Gerasymenko, V.V. Kleschevnikov, V.R. Kedlian, L.O. Sakhno, I.A. Arbuzova, Y.V. Sheludko, V.E. Dosenko, N.V. Kuchuk, 2017, published in Tsitologiya i Genetika, 2017, Vol. 51, No. 1, pp. 3–11.
About this article
Cite this article
Gerasymenko, I.M., Kleschevnikov, V.V., Kedlian, V.R. et al. Establishment of transgenic lettuce plants producing potentially antihypertensive ShRNA. Cytol. Genet. 51, 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452717010054
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452717010054