Abstract
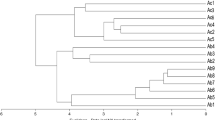
Southern root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita is the most widespread-species, causing serious yield losses in protected vegetables fields in the West Mediterranean region of Turkey. The knowledge of genetic variation within M. incognita is required for disease management and improvement of resistant varieties by breeding programs. In the present study, the isolates were classified into different groups based on sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) fingerprints. To our knowledge, this is the first study carried out on the characterization of M. incognita isolates using SRAP. The schematic diagram by tested primers to differentiate of M. incognita isolates was formed in discrimination of nematodes as an effective molecular tool since it is cost effective and easiness. Data presents a genetic variation on root-knot nematode species. These selected SRAP markers can be used to follow genetic structure and differentiation on M. incognita isolates in a certain region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baysal Ö., Siragusa M., İkten H., Polat İ., Gümrükçü E., Yiğit F., Caramini F., Teixeira da Silva J.A. 2009. Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici races and their genetic discrimination by molecular markers in West Mediterranean region of Turkey. Physiol. Molec. Plant Pathol. 74(1): 68–75. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2009.09.008
Budak H., Shearman R.C., Parmaksız I. & Dweikat I. 2004. Comparative analysis of seeded and vegetative buffalograsses based on phylogenetic relationships using ISSR, SSR, RAPD and SRAP. Theor. Appl. Genet. 109(2): 280–288. DOI: 10.1007/s00122-004-1630-z
Carneiro R.M.D.G., Casragnone-Sereno P. & Dickson D.E. 1998. Variability among four populations of Meloidogyne javanica from Brazil. Fund. Appl. Nematol. 21(4): 319–326.
Curran J.N., McClure M.A. & Webster J.M. 1986. Genotypic differentiation of Meloidogyne populations by detection of restriction fragment length difference in total DNA. J. Nematol. 18(1): 83–86.
Devran Z., Mutlu N., Özarslandan A. & Elekçioğlu İ.H. 2009. Identification and genetic diversity of Meloidogyne chitwoodi in potato production areas of Turkey. Nematropica 39(1): 75–83.
Devran Z. & Söğüt M.A. 2009. Distribution and identification of root-knot nematodes from Turkey. J. Nematol. 41(2): 128–133.
Devran Z., Söğüt M.A., Gözel U., Tör M. & Elekçioğlu İ.H. 2008. Analysis of genetic variation between populations of Meloidogyne spp. from Turkey. Rus. J. Nematol. 16(2): 143–149.
Esposita M.A., Martin E.A., Cravero V.P. & Cointry E. 2007. Characterization of pea accessions by SRAP’s markers. Sci. Horticult. 113(4): 329–335. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2007.04.006
Fargete M., Lollier V., Phillip M., Blok V. & Frutos R. 2005. AFLP analysis of the genetic diversity of Meloidogyne chitwoodi and M. fallax, major agricultural pests. Curr. Biol. 328(5): 455–462. DOI: 10.1016/j.crvi.2005.02.001
Ferriol M., Picó B. & Nuez F. 2003. Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP marker. Theor. Appl. Genet. 107(2): 271–282. DOI: 10.1007/s00122-003-1242-z
Gryta H., Carriconde F., Charcosset J.Y., Jargeat P. & Gardes M. 2005. Population dynamics of the ectomycorrhizal fungal species Tricholoma populinum and Tricholoma scalpturatum associated with black poplar under differing environmental conditions. Environ. Microbiol. 8(5): 773–786. DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00957.x
Guirao P., Moya A. Cenis J.L. 1995. Optimal use of random amplified polymorphic DNA in estimating the genetic relationship of four major Meloidogyne spp. Phytopathology 85(5): 547–551. DOI: 10.1094/Phyto-85-547
Gülşen O., Karagül S. & Abak K. 2007. Diversity and relationships among Turkish germplasm by SRAP and phenotypic marker polymorphism. Biologia 62(1): 41–45. DOI:10.2478/s11756-007-0010-y
Karssen G. & Moens M. 2006. Root-knot nematodes, pp. 59–90. In: Perry R.N. & Moens M. (eds), Plant Nematology, CABI, Wallingford, UK. ISBN:978-1-84593-056-1, 1-84593-056-
Krauss S.L. 2000. Accurate gene diversity estimates from ampli-fied fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers. Molec. Ecol. 9(9): 1241–1245. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.01001.x
Li G. & Quiros C.F. 2001. Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: Its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor. Appl. Genet. 103(2–3): 455–461. DOI: 10.1007/s001220100570
Lin Z.X., Zhang X.L. & Nie Y.C. 2004. Evaluation of application of a new molecular marker SRAP on analysis of segregation population and genetic diversity in cotton. Acta Genet. Sin. 31(6): 622–626. PMID: 15490882
Lynch M. & Milligan B.G. 1994. Analysis of population genetic structure with RAPD markers. Molec. Ecol. 3(2): 91–99. PMID: 8019690
Nei M. & Li W.H. 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 76(10): 5269–5273.
Rohlf F.J. 1994. NTSYS-pc: Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.02. State University of New York, Stony Brook, NY, USA.
Semblat J.P., Wajnberg E., Dalmasso A., Abad P. & Castagnone-Sereno P. 1998. High-resolution DNA fingerprinting of parthenogenetic root-knot nematodes using AFLP analysis. Molec. Ecol. 7(1): 119–125. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.1998.00326.x
Siddiqi M.R. 2000. Tylenchida: Parasites of Plants and Insects. 2nd Edition. CABI Publishingl, 833 pp. ISBN: 0851992021, 9780851992020
Sneath P.H. & Sokal R.R. 1973. Numerical taxonomy: the principles and practice of numerical classification. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco Steekelenburg NAM, 573 pp. ISBN: 0716706970.
Tzortzakakis E.A., Blok V.C., Phillips M.S. & Trudgill D.L. 1999. Variation in root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp) in Crete in relation to control with resistant tomato and pepper. Nematology 1: 499–506. DOI: 10.1163/156854199508496
Vos P., Hogers R., Bleeker M., Reijans M., van de Lee, T., Hornes M., Friters A., Pot J., Paleman J., Kuiper M. & Zabeau M. 1995. AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acid Res. 23(21): 4407–4414. DOI: 10.1093/nar/23.21.4407
Yeh F.C., Yang R.C., & Boyle T. 1999. Popgene, Version 1.31. Centre for International Forestry Research and University of Alberta. Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, 29 pp. http://www.ualberta.ca/~fyeh/popgene.pdf
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Both authors have equal contribution on the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devran, Z., Baysal, Ö. Genetic characterization of Meloidogyne incognita isolates from Turkey using sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP). Biologia 67, 535–539 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-012-0028-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-012-0028-7