Abstract
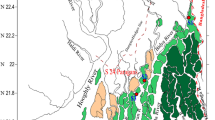
Stratigraphic records from sediment cores collected in a freshwater tidal marsh and in the estuary upstream and downstream from the marsh were used to determine the accumulation of nutrients and trace metals over long time periods. Analysis of pollen and seeds show that the high marsh has formed only within the past 100 yr, following increased sedimentation rates in the area. Variations in nutrient and trace metal accumulations over several decades show that pollutants from agricultural runoff and wastewater discharge are stored to a greater extent in high-marsh than in low-marsh sediments. Greater accumulation rates in the high marsh are probably related to its greater sedimentary organic carbon concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Alliance for the Chesapeake Bay. 1988. The Patuxent river fact sheet. Allance for the Chesapeake Bay, Baltimore, Maryland.
Ashbaugh, B. L. and G. N. Brancato. 1958. Maryland's Weather. United States Weather Bureau, Deparment of Research and Education, Solomons, Maryland.
Barth, J. 1978. Of Matchoomaco, Temple of the Patuxent, of sot-weed, and the White Flood: A history of the Patuxent River valley. Little Patuxent Review 2:2–3.
Birks, H. J. B. and H. H. Birks. 1980. Quaternary Palaeoecology. University Park Press, Baltimore, Maryland.
Birks, H. H., C. Whiteside, D. M. Stark, and R. C. Bright. 1976. Recent paleolimnology of three lakes in northwestern Minnesota. Quaternary Research 6:249–272.
Bortleson, G. C. and G. F. Lee 1972. Recent sedimentary history of Lake Mendota, Wis. Environmental Science and Technology 6:799–808.
Bowden, W. B. 1987. The biogeochemistry of nitrogen in fresh-water wetlands. Biogeochemistry 4:313–348.
Bruland, K. W., K. Bertine, M. Koide, and E. D. Goldberg. 1974. History of metal pollution in Southern California coastal zone. Environmental Science and Technology 8:425–432.
Brush, G. S. 1984. Patterns of recent sediment accumulation in Chesapeake Bay (Virginia-Maryland, U.S.A.) tributaries. Chemical Geology 44:227–242.
Brush, G. S. 1989. Rates and patterns of estuarine sediment accumulation. Limnology and Oceanography 34:1235–1246.
Brush, G. S. and F. W. Davis. 1984. Stratigraphic evidence of human disturbance in an estuary. Quaternary Research 22:91–108.
Brush, G. S. and R. S. DeFries. 1981. Spatial distributions of pollen in surface sediments of the Potomac estuary. Limnology and Oceanography 26:295–309.
Cantillo, A. Y., S. A. Sinex, and G. R. Helz. 1984. Elemental analysis of estuarine sediments by lithium metaborate fusion and direct plasma emission spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry 56:33–37.
Carmichael, D. P. 1980. A record of environmental change during recent millennia in the Hackensack tidal marsh, New Jersey. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 107:514–524.
Clark, J. S. and W. A. Patterson, III. 1985. The development of a tidal marsh: Upland and oceanic influences. Ecological Monographs 55:189–217.
Cooper, S. R. and G. S. Brush. 1991. Long-term history of Chesapeake Bay anoxia. Science 254:992–996.
Davis, F. W. 1985. Historical changes in submerged macrophyte communities of upper Chesapeake Bay. Ecology 66:981–993.
DeFries, R. S. 1980. Sedimentation patterns in the Potomac estuary since European settlement: A palynological approach. Ph.D. Dissertation, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
DeLaune, R. D., C. J. Smith, and M. N. Sarafyan. 1986. Nitrogen cycling in a freshwater marsh of Panicum hemitomon on the deltaic plain of the Mississippi River. Journal of Ecology 74:249–256.
Dolan, T. J., S. E. Bayley, J. Zoltek, and A. J. Hermann. 1981. Phosphorus dynamics of a Florida freshwater marsh receiving treated wastewater. Journal of Applied Ecology 18:205–219.
Donoghue, J. F. 1990. Trends in Chesapeake Bay sedimentation rates during the late Holocene. Quaternary Research 34:33–46.
Dubinski, B. J., R. L. Simpson, and R. E. Good. 1986. The retention of heavy metals in sewage sludge applied to a freshwater tidal wetland. Estuaries 9:102–111.
Faegri, K. and J. Iversen. 1989. Textbook of Pollen Analysis. John Wiley and Sons Ltd., Chichester, United Kingdom.
Findlay, S., K. Howe, and H. K. Austin. 1990. Comparison of detritus dynamics in two tidal freshwater wetlands. Ecology 71:288–295.
Froomer, N. 1978. Geomorphic changes in some Western Shore estuaries during historic times. Ph.D. Dissertation, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland.
Froomer, N. 1980. Morphologic changes in some Chesapeake Bay tidal marshes resulting from accelerated soil erosion. Zeitschrift fur Geomorphologie N.F. 34:242–254.
Goldberg, E. D., V. Hodge, M. Koide, J. Griffin, E. Gamble, O. P. Bricker, G. Matisoff, G. R. Holdreu, Jr., and R. Braun. 1978. A pollution history of Chesapeake Bay. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 42:1413–1425.
Grant, R. R., Jr. and R. Patrick. 1970. Tinicum Marsh as a water purifier, p. 105–123. In J. McCormick, R. R. Grant, Jr., and R. Patrick (eds.), Two Studies of Tinicum Marsh, Delaware and Philadelphia counties, Pa. The Conservation Foundation, Washington, D.C.
Helz, G. R., R. J. Huggett, and J. M. Hill. 1975. Behavior of Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb discharged from a wastewater treatment plant into an estuarine environment. Water Research 9:631–636.
Hemond, H. F. and J. Benoit. 1988. Cumulative impacts on water quality functions of wetlands. Environmental Management 12:639–653.
Hirata, S. 1985. Phosphorus and metals bound to organic matter in coastal sediments—An investigation of complexes of P, Cu, Zn, Fe, Mn, Ni, Co and Ti by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry with sephadex gel chromatography. Marine Chemistry 16:23–46.
Hirner, A. V., K. Kritsotakis, and H. J. Tobschall. 1990. Metal-organic associations in sediments—I. Comparison of unpolluted recent and ancient sediments and sediments affected by anthropogenic pollution. Applied Geochemistry 5:491–505.
Horowitz, A. J. 1991. A Primer on Sediment-Trace Element Chemistry. Lewis Publishers. Chelsea, Michigan.
Howard-Williams, C. 1985. Cycling and retention of nitrogen and phosphorus in wetlands: A theoretical and applied perspective. Freshwater Biology 15:391–431.
Jackson, S. T., R. P. Futyma, and D. A. Wilcox. 1988. A paleoecological test of a classical hydrosere in the Lake Michigan dunes. Ecology 69:928–936.
Johnston, C. A., G. D. Bubenzer, G. B. Lee, F. W. Madison, and J. R. McHenry. 1984. Nutrient trapping by sediment deposition in a seasonally flooded lakeside wetland. Journal of Environmental Quality 13:283–290.
Krom, M. D. and R. A. Berner. 1983. A rapid method for the determination of organic and carbonate carbon in geological samples. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 53:660–663.
Leck, M. A. and K. J. Gravelline. 1979. The seed bank of a freshwater tidal marsh. American Journal of Botany 66:1006–1015.
Leck, M. A., R. L. Simpson. 1987. Seed bank of a freshwater tidal wetland: Turnover and relationship to vegetation change. American Journal of Botany 74:360–370.
Murphy, J. and J. P. Riley. 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27:31–36.
Nriagu, J. O. and R. D. Coker. 1980. Trace metals in humic and fulvic acids from Lake Ontario sediments. Environmental Science and Technology 14:443–446.
Odum, W. E. 1988. Comparative ecology of tidal freshwater and salt marshes. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 19:147–176.
Odum, W. E., T. J. Smith, J. K. Hoover, and C. C. McIvor. 1984. The ecology of tidal freshwater marshes of the United States East Coast: A community profile. United States Fish and Wildlife Service, FWS/OBS-83-17.
Orson, R. A., R. L. Simpson, and R. E. Good. 1990. Rates of sediment accumulation in a tidal freshwater marsh. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 60:859–869.
Orson, R. A., R. L. Simpson, and R. E. Good. 1992a. A mechanism for the accumulation and retention of heavy metals in tidal freshwater marshes of the upper Delaware river estuary. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 34:171–186.
Orson, R. A., R. L. Simpson, and R. E. Good. 1992b. The paleoecological development of a late Holocene, tidal freshwater marsh of the upper Delaware River estuary. Estuaries 15:130–146.
Rashid, M. A. 1974. Absorption of metals on sedimentary and peat humic acids. Chemical Geology 13:115–123.
Roberts, W. P. and J. W. Pierce. 1976. Deposition in upper Patuxent estuary, Maryland, 1968–1969. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 4:267–280.
Shapiro, J., W. T. Edmondson, and D. E. Allison. 1971. Changes in the chemical composition of sediments of Lake Washington, 1958–1970. Limnology and Oceanography 16:437–452.
Simpson, R. L., R. E. Good, R. Walker, and B. R. Frasco. 1983. The role of Delaware river freshwater tidal wetlands in the retention of nutrients and heavy metals. Journal of Environmental Quality 12:41–48.
Sommers, L. E. and D. W. Nelson. 1972. Determination of total phosphorus in soils: A rapid perchloric acid digestion procedure. Proceedings Soil Science Society of America 26:902–904.
Vijayachandran, P. K. and R. D. Harter. 1975. Evaluation of phosphorus adsorption by a cross-section of soil types. Soil Science 119:119–126.
Watts, W. A. and T. C. Winter. 1966. Plant macrofossils from Kirchner Marsh Minnesota—A paleoecological study. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America 77:1339–1359.
Whigham, D. F. and R. L. Simpson. 1976. The potential use of freshwater tidal marshes in the management of water quality in the Delaware River, p. 173–186. In J. Tourbier and R. W. Pierson (eds.), Biological Control of Water Pollution. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Whigham, D. F. and R. L. Simpson. 1980. The effect of sewage effluent on the structure and function of a freshwater tidal marsh ecosystem. United States Department of the Interior, Office of Water Research Technology. Technical Report No. B-60-NJ.
Whigham, D. F., R. L. Simpson, R. E. Good, and F. A. Sickels. 1989. Decomposition and nutrient-metal dynamics of litter in freshwater tidal wetlands, p. 167–188. In R. R. Sharitz and J. W. Gibbons (eds.), Freshwater Wetlands and Wildlife. United States Department of Energy, Office of Scientific and Technical Information, Oak Ridge, Tennessee.
Williams, A. W. 1981. The Chesapeake Beach Railway. Calvert County Historical Society Inc., Prince Frederick, Maryland.
Wolaver, T. G., J. C. Zieman, R. Wetzei, and K. L. Webb. 1983. Tidal exchange of nitrogen and phosphorus between a mesohaline vegetated marsh and the surrounding estuary in the lower Chesapeake Bay. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 16:321–332.
Wolman, M. G. 1967. A cycle of sedimentation and erosion in urban river channels. Geografiska Annaler 49A:385–395.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, H., Brush, G.S. Nutrient and metal accumulation in a freshwater tidal marsh. Estuaries 17, 345–360 (1994). https://doi.org/10.2307/1352668
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1352668