Abstract
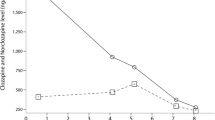
We report on two cases of drug-drug interactions between ciprofloxacin and clozapine. The first case was a 46-year-old male patient receiving a daily dose of clozapine 900 mg. He was admitted to hospital with urosepsis and was treated with a 5-day course of ciprofloxacin and amoxicillin. Two days after completion of antibacterial therapy, the patient developed symptoms of rhabdomyolysis. Clozapine therapy was discontinued and measurement of the patient’s clozapine plasma concentration 1 day after cessation of clozapine therapy and 3 days after cessation of ciprofloxacin treatment showed that it was in excess of recommended therapeutic levels. The second patient was a 58-year-old male patient treated with a daily dose of clozapine 300 mg. He was admitted to hospital because of delirium and suspected urinary tract infection or pneumonia. Treatment with ciprofloxacin was initiated. Measurement of clozapine plasma concentrations prior to and 3 days after commencement of ciprofloxacin showed that clozapine concentrations doubled over that time period. We suggest that inhibition of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes 1A2 and 3A4 by ciprofloxacin resulted in delayed clozapine metabolism and elevated clozapine plasma concentrations. This might cause severe adverse effects. We advise using another antibacterial agent or reducing the clozapine dose and monitoring clozapine levels when this antipsychotic agent is used in combination with ciprofloxacin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertilsson L, Carrillo JA, Dahl ML, et al. Clozapine disposition covaries with CYP1A2 activity determined by a caffeine test. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1994 Nov; 38(5): 471–3
Taylor D. Pharmacokinetic interactions involving clozapine. Br J Psychiatry 1997 Aug; 171: 109–12
Raaska K, Neuvonen PJ. Ciprofloxacin increases serum clozapine and N-desmethylclozapine: a study in patients with schizophrenia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2000 Nov; 56(8): 585–9
Granfors MT, Backman JT, Neuvonen M, et al. Ciprofloxacin greatly increases concentrations and hypotensive effect of tizanidine by inhibiting its cytochrome P450 lA2-mediated presystemic metabolism. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004 Dec; 76(6): 598–606
Fuhr U, Anders EM, Mahr G, et al. Inhibitory potency of quinolone antibacterial agents against cytochrome P450IA2 activity in vivo and in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1992 May; 36(5): 942–8
Hiemke C, Dragicevic A, Grunder G, et al. Therapeutic monitoring of new antipsychotic drugs. Ther Drug Monit 2004 Apr; 26(2): 156–60
Sambhi RS, Puri R, Jones G. Interaction of clozapine and ciprofloxacin: a case report. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2007 Sep; 63(9): 895–6
Horn JR, Hansten PD, Chan LN. Proposal for a new tool to evaluate drug interaction cases. Ann Pharmacother 2007 Apr; 41(4): 674–80
Rosenthal SH, Porter KA, Coffey B. Pain insensitivity in schizophrenia: case report and review of the literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 1990 Sep; 12(5): 319–22
Dworkin RH. Pain insensitivity in schizophrenia: a neglected phenomenon and some implications. Schizophr Bull 1994; 20(2): 235–48
Iqbal MM, Rahman A, Husain Z, et al. Clozapine: a clinical review of adverse effects and management. Ann Clin Psychiatry 2003 Mar; 15(1): 33–48
Huerta-Alardin AL, Varon J, Marik PE. Bench-to-bedside review: rhabdomyolysis — an overview for clinicians. Crit Care 2005 Apr; 9(2): 158–69
Koren W, Koren E, Nacasch N, et al. Rhabdomyolysis associated with clozapine treatment in a patient with decreased calcium-dependent potassium permeability of cell membranes. Clin Neuropharmacol 1998 Jul; 21(4): 262–4
Meltzer HY, Cola PA, Parsa M. Marked elevations of serum creatine kinase activity associated with antipsychotic drug treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 1996 Oct; 15(4): 395–405
Karagianis JL, Phillips LC, Hogan KP, et al. Clozapine-associated neuroleptic malignant syndrome: two new cases and a review of the literature. Ann Pharmacother 1999 May; 33(5): 623–30
Nicholson TE, Renton KW. The role of cytokines in the depression of CYP1A activity using cultured astrocytes as an in vitro model of inflammation in the central nervous system. Drug Metab Dispos 2002 Jan; 30(1): 42–6
Brownlowe K, Sola C. Clozapine toxicity in smoking cessation and with ciprofloxacin. Psychosomatics 2008 Mar; 49(2): 176
Acknowledgements
No sources of funding were used to assist in the preparation of this report. The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brouwers, E.E.M., Söhne, M., Kuipers, S. et al. Ciprofloxacin Strongly Inhibits Clozapine Metabolism. Clin. Drug Investig. 29, 59–63 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2165/0044011-200929010-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/0044011-200929010-00006