Summary
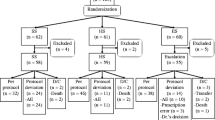
Because of the frequency of penicillin allergies in children receiving β-lactam antibacterial agents, the macrolides are frequently chosen as alternatives in patients with group A β-haemolytic streptococcal (GABHS) infections. Spiramycin, amacrolide widely used in paediatrics, achieving remarkably high tonsillar tissue concentrations, was evaluated in this study in comparison with penicillin V (Phenoxymethylpenicillin). 298 children aged 1.5 to 14 years with acute tonsillitis and a positive rapid antigen test for GABHS were randomised to receive either a 5-day course of spiramycin 100 000 IU/kg twice daily or a 7-day course of penicillin V 25 000 IU/kg 3 times daily. Clinical and bacteriological assessments were recorded at inclusion (day 1), at the end of the treatment visit (days 8 to 12), and at the follow-up visit (days 25 to 35). GABHS isolated during the study were analysed by total DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Of the 237 children with a positive GABHS culture at day 1,210 (88.6%) were evaluable for complete clinical and bacteriological efficacy at the end of treatment. Clinical efficacy was evident in 96.1% (98 of 102) for spiramycin and in 98.1% (106 of 108) for penicillin V. Bacteriological eradication was achieved in 79.4% (81 of 102) for spiramycin and in 89.8% (97 of 108) for penicillin V. Three failures occurred in the spiramycin group. In intent-to-treat analysis, the success rate (clinical cure and bacteriological eradication) for spiramycin was 77.9% (116 of 149) and that for penicillin V was 83.9% (125 of 149). At the follow-up visit, 182 children were evaluable for efficacy. Clinical cure with or without asymptomatic carriage of GABHS was observed in 97.7% (86 of 88) for spiramycin and in 89.4% (89 of 94) for penicillin V. Three relapses and 1 reinfection occurred in the penicillin V group. Adverse events, mainly gastrointestinal, occurred in 10.7% of spiramycin patients versus 12.8% of penicillin V patients. These results show that a 5-day treatment regimen with spiramycin twice daily is effective and well tolerated in GABHS tonsillitis, and is an alternative to penicillin V when necessary in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bass JW. Antibiotic management of group A streptococcal pharyngotonsillitis. Paediatr Infect Dis J 1991; 10: S43–S49
Bisno AL. Group A streptococcal infections and acute rheumatic fever. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 783–93
Gehanno P, Chiche D. Traitement des angines streptocoque beta hemolytique du groupe A par le cefuroxime axetil pendant 4 jours: etude comparative la penicilline V pendant 10 jours. Med Mal Infect 1991; 21: 66–70
Portier H, Houriez-Bernard S, Kazmierczack A, et al. Five days josamycin l g b.i.d. vs 10 days Peni V 1 MIU t.i.d. for streptococcal pharyngitis/tonsillitis in adults and children over 8 years [abstract 1678]. 32nd ICAAC, 1992, Anaheim, USA
Pichichero ME. Cephalosporins are superior to penicillin for treatment of streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis: is the difference worth it? Paediatr Infect Dis J 1993; 12(4): 268–74
Pichichero ME, Gooch WM, Rodriguez W, et al. Effective short-course treatment of acute group A β-hemolytic streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis. Ten days of penicillin V vs 5 days or 10 days of Cefpodoxime therapy in children. Arch Paediatr Adolesc Med 1994; 148: 1053–60
Aujard Y, Boucot I, Brahimi N, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of four day cefuroxime-axetil and ten day penicillin treatment of beta-haemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis in children. Paediatr Infect Dis J 1995; 14: 295–300
Thabaut A. Les macrolides en 1992: structure et classification, activite antibacterienne, pharmacocinetique. La lettre de l’Infeciologue 1992; 18: 585–9
Bingen E, Denamure E, Lambert-Zechovsky N, et al. DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism differentiates recurrence from relapse in treatment failures of Streptococcus pyogenes pharyngitis. J Med Microbiol 1992; 37: 162–4
Graff-Lonnevig V, Hedlin G, Lindfors A, et al. Penicillin allergy: a rare paediatric condition? Arch Dis Child 1988; 63: 1342–6
Dajani AS. Current status of nonsuppurative complications of Group A streptococci. Paediatr Infect Dis J 1991; 10: S25–S27
Quie PG. Development of effective programs for control of epidemic streptococcal infections. Paediatr Infect Dis J 1991; 10: S7–S10
Lundberg C, Nord CE. Streptococcal throat infection: still a complex clinical problem. Scand J Infect Dis 1988; Suppl. 57: 7–11
Cohen R, Estrangin E, Lecompte MD, et al. Epidemiologie bacterienne des angines en pratique pediatrique de ville. Presse Med 1994; 23: 1753–7
Fyllingen G, Arnesen AR, Biermann Ch, et al. Phenoxymethylpenicillin two or three times daily for tonsillitis with beta-haemolytic streptococci group A: a blinded, randomised and controlled clinical study. Scand J Infect Dis 1991; 23: 553–8
Weippl G. Multicentre comparison of azithromycin versus erythromycin in the treatment of pediatric pharyngitis or tonsillitis caused by group A streptococci. J Antimicrob Chemother 1993; 31 Suppl. E: 95–101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03256926.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gendrel, D., Bourrillon, A., Bingen, E. et al. Five-Day Spiramycin vs Seven-Day Penicillin V in the Treatment of Streptococcal Tonsillitis in Children. Clin. Drug Invest. 13, 338–344 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199713060-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199713060-00006