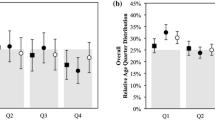
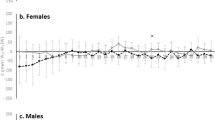
Summary
The general physiological profile of the successful wrestler is of one having high anaerobic power (mean range of 6.1 to 7.5 W/kg for arms; mean range of 11.5 to 19.9 W/kg for legs); high anaerobic capacity (range for arms 4.8 to 5.2 W/kg; range for legs 7.4 to 8.2 W/kg); high muscular endurance; average to above average aerobic power (range 52 to 63 ml/kg/min); average pulmonary function (range 1.90 to 2.02 L/kg/min for V̇Emax); normal flexibility; a high degree of leanness (range 3.7 to 13.0% fat) excluding heavyweights; and a somatotype that emphasises mesomorphy. Training methods include wrestling, and nonwrestling activities for increasing strength and power (i.e. resistance training), and to improve cardiovasular fitness (i.e. endurance training). Unfortunately, data on the isolated effects of wrestling on fitness and the type of training programme most effective for success in wrestling are scarce. The practice of weight loss is commonly used by wrestlers to enhance performance. Rapid weight loss has profound adverse effects on the wrestler’s physiology but little effect on strength or anaerobic power performance as measured in the laboratory. In contrast, muscular endurance appears to be impaired by the rapid weight loss. Current research on weight loss and performance in wrestlers has taken 2 directions: (a) towards nutritional treatments to prevent suboptimal muscular endurance, and (b) towards the development of programmes to estimate minimal weight based on body composition techniques and thereby prevent weight reductions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AAHPER. Nutrition for athletics: a handbook for coaches, p. 26, American Association for Health, Physical Education, and Recreation, Washington, DC, 1971
Ahlman K, Karvonen MJ. Weight reduction by sweating in wrestlers, and its effects on physical fitness. Journal of Sports Medicine 1: 58–62, 1961
Allen TE, Smith DP, Miller DK. Hemodynamic response to subaximal exercise after dehydration and rehydration in high school wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports 9: 159–163, 1977
American College of Sports Medicine. Position paper on weight loss in wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports 8: XI–XIII, 1976
Bar-Or O. The Wingate anaerobic test: an update on methodology, reliability and validity. Sports Medicine 4: 381–394, 1987
Bar-Or O, Dotan R, Rothstein A, Karlsson J, Tesch P. Anaerobic capacity and muscle fiber type distribution in man. International Journal of Sports Medicine 1: 82–85, 1980
Berger RA. Effect of varied weight programs on strength. Research Quarterly 33: 168–181, 1962
Bergh U, Thortensson A, Sjodin B, Hulten B, Piehl K, et al. Maximal oxygen uptake and muscle fiber types in trained and untrained humans. Medicine and Science in Sports 10: 151–154, 1978
Blimkie CJR, Roache P, Hay JT, Bar-Or O. Anaerobic power of arms in teenage boys and girls: relationship to lean tissue. European Journal of Applied Physiology 57: 677–683, 1988
Bock W, Fox EL, Bowers R. The effects of acute dehydration upon cardio-respiratory endurance. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness 7: 67–72, 1967
Boileau RA, McKeown BC, Ryner WF. Cardiovascular and metabolic contributions to the maximal aerobic power of the arms and legs. International Journal of Sports Cardiology 1: 67–75, 1984
Boileau RA, Slaughter MH, Horswill CA. Body composition of the young athlete, In Klish WJ & Ketchmer N (Eds) Body composition measurements in infants and children: Report of the 98th Ross Conference on Pediatric Research, pp. 104–111, Robb Laboratories, Columbus, 1989
Brodie DA, Eston RG, Coxon AY, Kreitzman SN, Stockdale HR, Howard AN. Effect of changes of water and electrolytes on the validity of conventional methods of measuring fat-free mass. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism 35: 89–97, 1991
Buschschluter S. Games blood-letting. Swimming Technique 13: 99, 1977
Cahill GF. Starvation in man. In Albrink MJ (Ed.) Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism, Vol. 5, pp. 397–415, WB Saunders, London, 1976
Caldwell JE, Ahonen E, Nousiainen U. Differential effects of sauna-, diuretic-, and exercise-induced hypohydration. Journal of Applied Physiology 57: 1018–1023, 1984
Cisar CJ, Johnson GO, Fry AC, Housh TJ, Hughes RA, et al. Preseason body composition, build, and strength as predictors of high school wrestling success. Journal of Applied Sport Science Research 1: 66–70, 1987
Clarke DH, Vaccaro P, Andersen NM. Physiological alterations in 7- to 9-year old boys following a season of competitive wrestling. Research Quarterly of Exercise and Sport 55: 318–322, 1984
Clarke KC: Predicting certified weight of young wrestlers: a field study of the Tcheng-Tipton method. Medicine and Science in Sports 6: 52–57, 1974
Claremont AD, Costill DL, Fink W, Van Handel P. Heat tolerance following diuretic induced dehydration. Medicine and Science in Sports 8: 239–243, 1976
Claremont AD, Nagle F, Reddan WD, Brooks GA. Comparison of metabolic, temperature, heart rate and ventilatory responses to exercise at extreme ambient temperatures (0° and 35°C). Medicine and Science in Sports 7: 150–154, 1975
Cohen CR, Allen HD, Spain J, Marx GR, Wolfe RW, et al. Cardiac structure and function of elite high school wrestlers. American Journal of Diseases of Childhood 141: 576–81, 1987
Committee on Dietary Allowances, Food and Nutrition Board, National Research Council. Recommended dietary allowances, 10th ed., National Academy of Sciences, Washington DC., 1989
Committee on Medical Aspects of Sports. Wrestling and weight control. Journal of the American Medical Association 201: 131–133, 1973
Costill DL, Cote R, Fink W. Muscle water and electrolytes following varied levels of dehydration in man. Journal of Applied Physiology 40: 6–11, 1976
Costill DL, Coyle EF, Fink WF, Lesmes GR, Witzmann FA. Adaptations in skeletal muscle following strength training. Journal of Applied Physiology 46: 96–99, 1979
Costill DL, Flynn MG, Kirwan JP, Houmard JA, Mitchell JB, et al. Effects of repeated days of intensified training on muscle glycogen and swimming performance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 20: 249–254, 1988
Costill DL, Sparks KE. Rapid fluid replacement following thermal dehydration. Journal of Applied Physiology 34: 299–303, 1973
Coyle EF, Costill DL, Lemes GR. Leg extension power and muscle fiber composition. Medicine and Science in Sports 11: 12–15, 1979
Croyle PH, Place RA, Hilgenberg AD. Massive pulmonary embolism in a high school wrestler. Journal of the American Medical Association 241: 827–828, 1979
de Garay AL, Levine L, Lindsay Carter JE. Genetic and anthropological studies of Olympic athletes, Academic Press, New York, 1974
DiPrampero PE, Limas FP, Sassi G. Maximal muscular power, aerobic and anaerobic, in 116 athletes performing at the XIXth Olympic games in Mexico. Ergonomics 13: 665–674, 1970
Dudley GA, Djamil R. Incompatibility of endurance- and strength-training modes of exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 59: 1446–1451, 1985
Dudley GA, Fleck SJ. Strength and endurance training: are they mutually exclusive? Sports Medicine 4: 79–85, 1987
Fahey TD, Akka L, Rolph R. Body composition and V̇O2max of exceptional weight-trained athletes. Journal of Applied Physiology 39: 559–561, 1975
Farris EJ. The blood picture of athletes as affected by intercollegiate sports. American Journal of Anatomy 23: 223–275, 1943
Fielding RA, Costill DL, Fink WJ, King DS, Kovaleski JE, et al. Effects of pre-exercise carbohydrate feedings on muscle glycogen use during exercise in well-trained runners. European Journal of Applied Physiology 56: 225–229, 1987
Foster C, Costill DL, Fink WJ. Effects of pre-exercise feedings on endurance performance. Medicine and Science in Sports 11: 1–5, 1979
Freischlag J. Weight loss, body composition, and health of high school wrestlers. Physician and Sportsmedicine 12 (1): 121–126, 1984
Gale JB, Flynn KW. Maximal oxygen consumption and relative body fat of high-ability wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports 6: 232–234, 1974
Girandola RN, Wisewell RA, Romero G. Body composition changes resulting from fluid ingestion and dehydration. Research Quarterly 48: 299–303, 1977
Grassi M, Messina B, Fraioli A, Schietroma M, Di Giacomo ML, et al. Effects of bicarbonate-alkaline earth water (Sangemini) on some parameters of blood chemistry in wrestlers after exertion. Journal of Sports Medicine 23: 102–106, 1983
Gunderson HK, Mcintosh MK. An increased incidence of overweight, obesity and indicators of chronic disease among ex-collegiate wrestlers. Abstract. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 90: A121, 1990
Hansen NC. Wrestling with ‘making weight’. Physician and Sportsmedicine 6 (4): 106–111, 1978
Herbert WG, Ribisl PM. Effects of dehydration upon physicial working capacity of wrestlers under competitive conditions. Research Quarterly 43: 416–422, 1972
Hickner RC, Horswill C, Welker J, Scott JR, Costill DL. Test development for study of physical performance in wrestlers following weight loss. International Journal of Sports Medicine 12: 557–562, 1991
Hickson RC. Interference of strength development by simultaneously training for strength and endurance. European Journal of Applied Physiology 45: 255–263, 1980
Horstman DH, Horvath SM. Cardiovascular adjustments to progressive dehydration. Journal of Applied Physiology 35: 501–504, 1973
Horswill CA, Lohman TG, Slaughter MH, Boileau, RA, Wilmore JH. Estimation of minimal weight of adolescent males using multicomponent models. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 22: 528–532, 1990b
Horswill CA, Park SH, Roemmich JN. Changes in the protein nutritional status of adolescent wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 22: 599–604, 1990c
Horswill CA. An investigation of the correlation between success in college wrestlers and the physiological capacities: maximum aerobic power, maximum anaerobic power, and dynamic endurance. Master’s thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison, unpublished, 1979
Horswill CA, Hickner RC, Scott JR, Costill DL, Gould D. Weight loss, dietary carbohydrate modifications and high intensity, physical performance. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 22: 470–476, 1990a
Horswill CA, Scott JR, Galea P. Comparison of maximum aerobic power, maximum anaerobic power, and skinfold thickness of elite and nonelite junior wrestlers. International Journal of Sports Medicine 10: 165–168, 1989
Horswill CA, Scott J, Galea P, Park SH. Physiological profile of elite junior wrestlers. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 59: 257–261, 1988
Housh TJ, Hughes RJ, Johnson GO, Housh DJ, Wagner LL, et al. Age-related increases in the shoulder strength of high school wrestlers. Pediatric Exercise Science 2: 65–72, 1990
Housh TJ, Johnson GO, Housh DJ, Muscular power of high school wrestlers. Pediatric Exercise Science 3: 43–48, 1991
Housh TJ, Johnson GO, Hughes RJ, Cisar CJ, Thorland WG. Yearly changes in the body composition and muscular strength of high school wrestlers. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 59: 240–243, 1988
Housh TJ, Johnson GO, Hughes RA, Housh DJ, Hughes RJ, et al. Isokinetic strength and body composition of high school wrestlers across age. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 21: 105–109, 1989
Housh TJ, Johnson GO, Kennedy KB, McDowell SL, Hughes RA, et al. Validity of anthropometric estimates of body composition in high school wrestlers. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 60 (3): 239–245, 1989
Houston ME, Marin DA, Green HJ, Thomson JA. The effect of rapid weight loss on physiological function in wrestlers. Physician and Sportsmedicine 9 (11): 73–78, 1981
Houston ME, Sharratt MT, Bruce RW. Glycogen depletion and lactate responses in freestyle wrestling. Canadian Journal of Applied Sports Science 8: 79–82, 1983
Hultman E, Bergstrom J, Roch-Norlund AE. Glycogen storage in human skeletal muscle. In Pernow B & Saltin B (Eds) Advances in experimental medicine and biology, Vol. 11, pp. 273–288, Plenum Press, New York, 1971
Hursh LM. Food and water restriction in the wrestler. Journal of the American Medical Association 241: 915–916, 1979
Inbar O, Bar-Or O. Anaerobic characteristics in male children and adolescents. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 18 (3): 264–269, 1986
Ivy JL, Lee MC, Brozinick JT, Reed MJ. Muscle glycogen storage after different amounts of carbohydrate ingestion. Journal of Applied Physiology 65: 2018–2023, 1988
Jacobs I. The effects of thermal dehydration on performance on the Wingate anaerobic test. International Journal of Sports Medicine 1: 21–24, 1980
Jauhiainen M, Laitinen M, Penttila I, Nousiainen U, Ahonen E. Lipids and apolipoproteina a-I, b and c-II and different weight loss programs (weight lifters, wrestlers, boxers and judokas). International Journal of Biochemistry 17: 167–174, 1985
Johnson GO, Cisar CJ. Basic conditioning principles for high school wrestlers. Physician and Sportsmedicine 15 (1): 153–159, 1987
Katch FI, Michael ED. Body composition of high school wrestlers according to age and wrestling weight category. Medicine and Science in Sports 3: 190–194, 1971
Keller LF. The relation of’quickness of bodily movement’ to success in athletics. Research Quarterly 13: 146–155, 1942
Kelly JM, Gorney BA, Kalm KK. The effects of a collegiate wrestling season on body composition, cardiovascular fitness and muscular strength and endurance. Medicine and Science in Sports 10: 119–124, 1978
Kent G. A pictorial history of wrestling, pp 9–29, Spring Books, Middlesex, 1968
Klinzing JE, Karpowicz W. The effects of rapid weight loss and rehydration on a wrestling performance test. Journal of Sports Medicine 26: 149–156, 1986
Kono I, Kitao H, Matsuda M, Haga S, Fukushima H, et al. Weight reduction in athletes may adversely affect the phagocytic function of monocytes. Physician and Sportsmedicine 16 (7): 56–65, 1988
Kroll W. An anthropometrical study of some Big Ten varsity wrestlers. Research Quarterly 25: 307–312, 1954
Kroll W. Selected factors associated with wrestling success. Research Quarterly 29: 396–406, 1958
Landwer GE, Johnson GO, Hammer RW. Weight control for high school wrestlers. Journal of Sports Medicine 3: 88–94, 1975
Leighton JR. Flexibility characteristics of three specialized skill groups of champion athletes. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 38: 580–583, 1957
Mason EF, Chernigoy FA, Cadwell RE, Burke JP. Clinical study of mild renal ischaemia. Surgery, Gynecology and Obstetrics 119: 293–301, 1964
Maude PJ, Shultz BB. Norms for the Wingate anaerobic test with comparison to another similar test. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 60: 144–151, 1989
McDermott WV, Bartlett MK, Culver PJ. Acute pancreatitis after prolonged fast and subsequent surfeit. New England Journal of Medicine 254: 379–380, 1956
McMurray RG, Proctor CR, Wilson WL. Effect of caloric deficit and dietary manipulation on aerobic and anaerobic exercise. International Journal of Sports Medicine 12(2): 167–172, 1991
Melby CL, Schmidt WD, Corrigan D. Resting metabolic rate in weight-cycling collegiate wrestlers compared with physicially active, noncyling control subjects. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 52: 409–414, 1990
Mendez J, Vollrath W, Druckemiller M. Body composition among college wrestlers and sedentary students with emphasis on 3-methylhistidine excretion and calculation of muscle mass. In Knuttgen HG, et al. (Eds) Biochemistry of exercise, Vol. 13, pp. 373–377, Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1983
Mnatzakanian PA, Vaccaro P. Effects of 4% thermal dehydration and rehydration on hematologic and urinary profile of college wrestlers. Annals of Sports Medicine 2: 41–46, 1984
Morgan WP. Psychological effect of weight reduction in the college wrestler. Medicine and Science in Sports 2: 24–27, 1970
Morganroth J, Maron BJ, Henry WL, Epstein SE. Comparative left ventricular dimensions in trained athletes. Annals of Internal Medicine 82: 521–524, 1975
Nagle FJ, Morgan WP, Hellickson RO, Serfass RC, Alexander JF. Spotting success traits in Olympic contenders. Physician and Sportsmedicine 3 (12): 31–34, 1975
Oppliger RA, Nielsen DH, Vance CG. Wrestler’s minimal weight: anthropometry, bioimpedance, and hydrostatic weighing compared. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 23: 247–253, 1991
Oppliger RA, Tipton CM. Iowa wrestling study: cross-validation of the Tcheng-Tipton minimal weight prediction formulas forhigh school wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 20: 310–316, 1988
Park SH, Roemmich JN, Horswill CA. A season of wrestling and weight loss by adolescent wrestlers: effect on anaerobic arm power. Journal of Applied Sport Science Research 4: 1–4, 1990
Randle PJ, Hales CN, Garland PB, Newsholme EA. The glucose fatty-acid cycle: its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 2: 785–789, 1963
Rasch PJ. Indices of body build of United States free style wrestlers. Journal of the Association of Physical and Mental Rehabilitation 12: 91–94, 1958
Rasch PJ, Brandt JWA. Measurement of pulmonary function in United States freestyle wrestlers. Research Quarterly 28: 279–287, 1957
Rasch PJ, Faires LB, Hunt MB. Effects of a combative sport (amateur wrestling) on the kidneys. Research Quarterly 28: 54–59, 1958
Rasch PJ, Pierson WJ, O’Connell ER, Hunt MB. Response time of amateur wrestlers. Research Quarterly 32: 416–419, 1961
Rasch PJ, Pierson WR, O’Connell ER, Hunt MB. Effect of training for amateur wrestling on total proportional strength scores. Research Quarterly 32: 201–207, 1961
Ribisl PM, Herbert WG. Effects of rapid weight reduction and subsequent rehydration upon the physical working capacity of wrestlers. Research Quarterly 41: 536–541, 1970
Roby FB, Kempema JM, Lohman TG, Williams DP, Tipton CM. Can the same equation be used to predict minimal wrestling weight in hispanic and non-hispanic wrestlers? Abstract no. 171. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 23: S29, 1991
Roemmich JN, Park SH, Horswill CA. Effects of weight loss on selected hormones in the adolescent wrestler. Abstract no. 218. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 21: S37, 1989
Roemmich JN, Sinning WE, Roemmich SR. Seasonal changes in anaerobic power, strength and body composition of adolescent wrestlers. Abstract no. 170. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 23: S29, 1991
Sady SP, Thomson WH, Savage M, Petratis M. The body composition and physical dimensions of 9- to 12-year-old experienced wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 14: 244–248, 1982
Sady SP, Thomson WH, Berg K, Savage M. Physiological characteristics of high-ability prepubescent wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 16: 72–76, 1984
Saltin B, Astrand PO. Maximal oxygen uptake in athletes. Journal of Applied Physiology 23: 353–358, 1967
Sawka MN, Toner MM, Francesconi RP, Pandolf KB. Hypohydration and exercise: effects of heat acclimation, gender, and environment. Journal of Applied Physiology 55: 1147–1153, 1983
Schwane JA, Johnson SR, Vandenakker CB, Armstrong RB. Delayed-onset muscular soreness and plasma CPK and LDH activities after downhill running. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 15: 51–56, 1983
Seals DR, Mullin JP. V̇O2max in variable type exercise among well-trained upper body athletes. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 53: 58–63, 1982
Serfass RC, Stull GA, Alexander JF, JLwing JL. The effects of rapid weight loss and attempted rehydration on strength and endurance of the handgripping muscle in college wrestlers. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 55: 46–52, 1984
Sharratt MT. Wrestling profile. Clinics in Sports Medicine 3 (1): 273–289, 1984
Sharratt MT, Taylor AW, Song TMK. A physiological profile of elite Canadian freestyle wrestlers. Canadian Journal of Applied Sports Science 11: 100–105, 1986
Shavers LG. Effects of a season of varsity wrestling on selected physiological parameters. Journal of Sports Medicine 14: 139–145, 1974
Shetty PS, Jung RT, Watrasiuncz KE, James WPT. Rapid-turn-over transport proteins: an index of subclinical protein-energy malnutrition. Lancet 4: 230–232, 1979
Short SH, Short WR. Four-year study of university athletes’ dietary intake. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 82: 632–645, 1983
Silva JM, Schultz BB, Haslam RW, Murray D. A psychophysiological assessment of elite wrestlers. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 52: 348–358, 1981
Singer RN, Weiss SA. Effects of weight reduction on selected anthropometric, physical, and performance measures of wrestlers. Research Quarterly 39: 361–369, 1968
Sinning WE. Body composition assessment of college wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports 6: 139–145, 1974
Sinning WE, Wilensky NF, Meyers EJ. Post-season body composition changes and weight estimation in high-school wrestlers. In Brockhoff J (Ed.) Physical education sports and the sciences, pp. 137–153, Microform Publications, Eugene, 1976
Smith FR, Suskind R, Thanangkul O. Plasma vitamin A, retinol binding protein, and prealbumin in protein-calorie malnutrition. III. Response to varying dietary treatments. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 28: 732–738, 1975
Smith NJ. Nutrition in children’s sports. In Micheli LJ (Ed.) Pediatric and adolescent sports medicine, pp. 134–143, Little, Brown and Co., Boston, 1984
Song TMK, Cipriano N. Effects of seasonal training on physical and physiological function on elite varsity wrestlers. Journal of Sports Medicine 24: 123–130, 1984
Song TMK, Garvie GT. Anthropometric, flexibility, strength, and physiological measures of Canadian wrestlers and comparison of Canadian and Japanese Olympic wrestlers. Canadian Journal of Applied Sport Science 5: 1–8, 1980
Steen SN, Brownell KD. Patterns of weight loss and regain in wrestlers: has the tradition changed? Medicine and Science in sports Exercise 22: 762–768, 1990
Steen SN, McKinney S. Nutrition assessment of college wrestlers. Physician and Sportsmedicine 14 (11): 100–116, 1986
Steen SN, Oppliger RA, Brownell KD. Metabolic effects of repeated weight loss and regain in adolescent wrestlers. Journal of the American Medical Association 260: 47–50, 1988
Stine G, Ratliff R, Shierman G, Grana WA. Physical profile of the wrestlers at the 1977 NCAA Championships. Physician and Sportsmedicine 7 (11): 98–105, 1979
Strauss RH, Lanese RR, Leizman DJ. Illness and absence among wrestlers, swimmers, and gymnasts at a large university. American Journal of Sports Medicine 16: 653–655, 1988
Strauss RH, Lanese RR, Malarkey WB. Weight loss in amateur wrestlers and its effect on serum testosterone levels. Journal of the American Medical Association 254: 3337–3338, 1985
Tanner JM. The physique of the Olympic athlete, George Allen and Unwin Ltd, London, 1964
Taylor AW. A physiological analysis of the effects of two training programs. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness 11: 252–256, 1971
Taylor AW. Physiological effects of wrestling in adolescents and teenagers. Journal of Sports Medicine 3: 76–84, 1975
Taylor AW, Brassard L, Proteau RD. A physiological profile of Canadian Greco-Roman wrestlers. Canadian Journal of Applied Sports Science 4: 131–134, 1979
Tcheng TK, Tipton CM. Iowa Wrestling Study: anthropometric measurements and the prediction of a ‘minimal’ body weight for high school wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports 5: 1–10, 1973
Tesch P, Karlsson J, Sjodin B. Muscle fiber type distribution in trained and untrained muscles of athletes. In Komi PV (Ed.) Exercise and sport biology, Vol. 12, pp. 79–83, Human Kinetics, Champaign, 1982
Tiidus PM, Ianuzzo CD. Effects of intensity and duration of muscular exercise on delayed soreness and serum enzyme activities. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 15: 461–465, 1983
Tipton CM, Tcheng TK. Iowa Wrestling Study. Weight loss in high school students. Journal of the American Medical Association 214: 1269–1274, 1970
Tipton CM, Tcheng TK, Paul WD. Evaluation of the Hall method for determining minimum wrestling weight. Journal of the Iowa Medical Society 59: 571–574, 1969
Tsopanakis C, Kotsarellis D, Tsopanakis AD. Lipoprotein and lipid profiles of elite athletes in Olympic sports. International Journal of Sports Medicine 7: 316–321, 1986
Tuttle WW. The effect of weight loss by dehydration and the withholding of food on the physiologic responses of wrestlers. Research Quarterly 14: 158–166, 1943
Vaccaro P, Zauner CW, Cade JR. Changes in body weight, hematocrit and plasma protein concentration due to dehydration and rehydration in wrestlers. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness 16: 45–53, 1976
Walberg JL, Leidy MK, Sturgill DJ, Hinkle DE, Ritchey SJ, et al. Macronutrient content of a hypoenergy diet affects nitrogen retention and muscle function in weight lifters. International Journal of Sports Medicine 9: 261–266, 1988
Webster S, Rutt R, Weltman A. Physiological effects of a weight loss regimen practiced by college wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 22: 229–234, 1990
Weissinger E, Housh TJ, Johnson GO, Evans SA. Weight loss behavior in high school wrestling: wrestler and parent perceptions. Pediatric Exercise Science 3: 64–73, 1991
Widerman PM, Hagen RD. Bodyweight loss in a wrestler preparing for competition: a case report. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 14: 413–418, 1982
Wilmore JH, Costill DL. Training for sport and activity, 3rd ed., Wm C. Brown Publishers, Dubuque, 1988
Woods ER, Wilson CD, Masland RP. Weight control methods in high school wrestlers. Journal of Adolescent Health Care 9: 394–397, 1988
Zambraski EJ, Foster DT, Gross PM, Tipton CM. Iowa wrestling study: weight loss and urinary profiles of collegiate wrestlers. Medicine and Science in Sports 8: 105–108, 1976
Zambraski EJ, Tipton CM, Jordan HR, Palmer WK, Tcheng TK. Iowa: wrestling study: urinary profiles of state finalists prior to competition. Medicine and Science in Sports 6: 129–132, 1974
Zambraski EJ, Tipton CM, Tcheng TK, Jordan HR, Vailas AC, et al. Iowa wrestling study: changes in the urinary profiles of wrestlers prior to and after competition. Medicine and Science in Sports 7: 217–220, 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horswill, C.A. Applied Physiology of Amateur Wrestling. Sports Medicine 14, 114–143 (1992). https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-199214020-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-199214020-00004