New Bis-1,3,4-Thiadiazoles Based on Fumaric Acid: Preparation, Structure Elucidation, Antibacterial Activities, and Quantum-Chemical Studies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2022.7822Keywords:
Bis-1, 3, 4-thiadiazoles, Fumaric acid, Antibacterial activity, Spectroscopic methods, DFT.Abstract
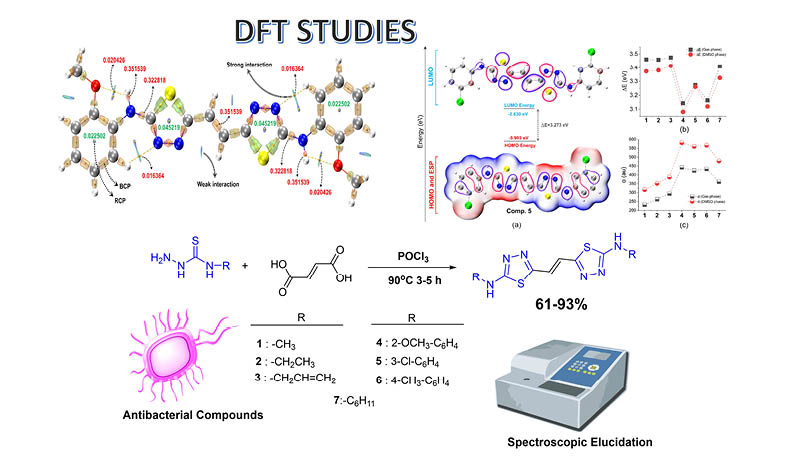
New bis-1,3,4-thiadiazoles (1-7) were obtained by the reaction of fumaric acid and N-(alkyl/aryl/cyclic)thiosemicarbazides in the presence of phosphorous oxychloride. The structures of all compounds were elucidated by FT-IR, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR and elemental methods. Antibacterial activity of the compounds was studied for eight selected bacteria. Compounds (2-7) exhibited effect on K.pneumoniae. However, none of the compounds effect on P.aeruginosa, S. epidermidis, S. Kentucky, S. macrescens. Self-consistent reaction force (SCRF) calculations were performed in DMSO medium to examine solvent energies using CPCM and SMD models. 6-31G(d) and 6-311++G(2d,2p) basis sets were used for DFT calculations. Besides electronic parameters such as electronegativity, electrophilicity and spectroscopic examinations of the compounds, QTAIM, local electron affinities, and Fukui analyzes were also performed. Theoretical approaches supporting the experimental observations revealing that compounds containing aromatic and cyclic groups exhibit stronger antibacterial behavior than compounds containing aliphatic groups are detailed.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 HALİT MUĞLU, Hasan Yakan, Ghaith Alabed Ibrayke Elefkhakry, Ergin Murat Altuner, M. Serdar Çavuş

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
