Association of serum chemerin and inflammatory factors with type 2 diabetes macroangiopathy and waist-to-stature ratio
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4002Keywords:
Type 2 diabetes, T2DM, macroangiopathy, chemerin, inflammatory factor, glycolipid metabolismAbstract
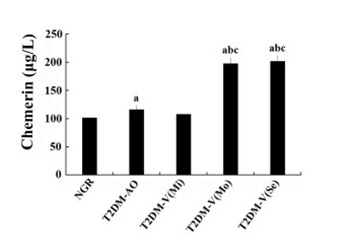
Chemerin is an adipocytokine that participates in glycolipid metabolism; however, its association with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) with lower extremity macroangiopathy (T2DM-V) has rarely been reported. This study explored the association of chemerin and inflammatory factors with body fat parameters, glucolipid metabolism, and insulin resistance (IR) in T2DM and T2DM-V. Patients were classified into normal glucose regulation (NGR), T2DM, and T2DM-V groups. Serum chemerin, glucolipid metabolic parameters, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, interleukin (IL)-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, and fasting insulin levels were measured along with HOMA-IR, body mass index (BMI), and waist-to-stature ratio (WSR). Serum chemerin, TGF-β, IL-6, and MCP-1 levels were significantly higher in T2DM groups than in NGR group, and BMI, WSR, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), 2hPG, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), triglycerides (TG), and HOMA-IR were higher in T2DM-V subgroups with moderate or severe lower extremity macroangiopathy than in NGR group, simple T2DM group, and T2DM-V subgroup with mild macroangiopathy. FPG, 2hPG, HbA1c, TG, and HOMA-IR were higher in T2DM-V subgroup with severe macroangiopathy than in T2DM-V with moderate macroangiopathy (p < 0.05). In all groups, serum chemerin levels were positively correlated with BMI, WSR, FPG, 2hPG, HbA1c, fasting insulin, aspartate transaminase, TG, TGF-β, IL-6, and HOMA-IR (p < 0.05) and negatively correlated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-c] (p < 0.05). Multiple stepwise regression analysis showed that 2hPG, HbA1c, and HDL-c were independent predictors of serum chemerin levels (β = -0.768, -0.122, -0.115, and 3.261, respectively; p < 0.01). Collectively, chemerin, factors associated with obesity, pathological and physiological changes in glucolipid metabolism, and inflammatory factors may promote the development of T2DM macroangiopathy.
Downloads