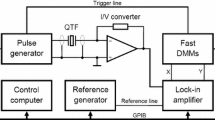
Abstract
This paper presents the design, fabrication, and characterization of a quartz tuning fork temperature sensor based on a new ZY-cut quartz crystal bulk acoustic wave resonator vibrating in a flexural mode. Design and performance analysis of the quartz tuning fork temperature sensor were conducted and the thermal sensing characteristics were examined by measuring the resonance frequency shift of this sensor caused by an external temperature. Finite element method is used to analyze the vibratory modes and optimize the structure of the sensor. The sensor prototype was successfully fabricated and calibrated in operation from 0 to 100 °C with the thermo-sensitivity of 70×10−6/°C. Experimental results show that the sensor has high thermo-sensitivity, good stability, and good reproducibility. This work presents a high-precision low-power temperature sensor using the comprehensive thermal characterization of the ZY-cut quartz tuning fork resonator.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beeby, S.P., Ensell, G., White, N.M., 2000. Microengineered silicon double-ended tuning fork resonators. Eng. Sci. Educ. J., 9(6):265–271. [doi:10.1049/esej:20000606]
Benes, E., Gröschl, M., Burger, W., Schmid, M., 1995. Sensors based on piezoelectric resonators. Sens. Actuat. A, 48(1): 1–21. [doi:10.1016/0924-4247(95)00846-2]
Castellanos-Gomez, A., Agrait, N., Rubio-Bollinger, G., 2011. Force-gradient-induced mechanical dissipation of quartz tuning fork force sensors used in atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy, 111(3):186–190. [doi:10.1016/j.ultramic.2010.11.032]
Clubb, D.O., Buu, O.V.L., Bowley, R.M., Nyman, R., Owers-Bradley, J.R., 2004. Quartz tuning fork for viscometers for helium liquids. J. Low Temp. Phys., 136(1–2):1–13. [doi:10.1023/B:JOLT.0000035368.63197.16]
Ctistis, G., Frater, E.H., Huisman, S.R., Korterik, J.P., Herek, J.L., Vos, W.L., Pinkse, P.W.H., 2011. Controlling the quality factor of a tuning-fork resonance between 9 and 300 K for scaning-probe microscopy. J. Phys. D, 44(37): 375502. [doi:10.1088/0022-3727/44/37/375502]
Dinger, R.J., 1982. The Torsional Tuning Fork as a Temperature. 36th Annual Symp. on Frequency Control, p.265–269. [doi:10.1109/FREQ.1982.200581]
EerNisse, E.P., Wiggins, R.B., 2001. Review of thickness-shear mode quartz resonator sensors for temperature and pressure. IEEE Sens. J., 1(1):79–87. [doi:10.1109/JSEN.2001.923590]
EerNisse, E.P., Ward, R.W., Wiggins, R.B., 1988. Survey of quartz bulk resonator sensor technologies. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control, 35(3):323–330. [doi:10.1109/58.20453]
Friedt, J.M., Carry, E., 2007. Introduction to the quartz tuning fork. Am. J. Phys., 75(5):415–422. [doi:10.1119/1.2711826]
Gil, M., Manzaneque, T., Hernando-García, J., Ababenh, A., Seidel, H., Rojas, J.L., 2011. Piezoelectric Micro-Scale Tuning Fork Resonators for Sensing Application. 16th Int. Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conf., p.1496–1499. [doi:10.1109/TRANSDUCERS.2011.5969682]
Guo, Z., Lin, L., Zhao, Q., Yang, Z., Xie, H., Yan, G., 2010. A lateral-axis microelectromechanical tuning-fork gyro-scope with decoupled comb drive operating at atmospheric pressure. J. Microelectromech. Syst., 19(3): 458–468. [doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2010.2046477]
Hammond, D.L., Adams, C.A., Schmidt, P., 1964. A Linear Quartz Crystal Temperature Sensing Element. 19th Annual ISA Conf, p.1–8.
He, J., Chen, Z., Lin, J., Dai, J., 2003. A new low-cost high-performance quartz tuning-fork temperature sensor. Sens. Rev., 23(2):134–142. [doi:10.1108/02602280310468242]
Jayapandian, J., Swarrup, J.S., Sheela, O.K., Ravi, U., 2012. PSoC-based embedded design and quartz tuning fork for low-temperature measurement system. J. Lab. Autom., 17(2):144–154. [doi:10.1177/2211068211426552]
Lee, S., 2002. Fabrication of an array of surface mount device 32.768 kHz quartz tuning fork-type crystals: photolithography and selective etching of an array of quartz tuning fork resonators with subsequent photoresist spray coating. Vacuum, 65(2):161–168. [doi:10.1016/S0042-207X(01)00477-8]
Lee, S., Moon, Y., Yoon, J., Chung, H., 2004. Analytical and finite element method design of quartz tuning fork resonator and experimental test samples manufactured using photolithography 1-significant design parameters affecting static capacitance C 0. Vacuum, 75(1):57–69. [doi:10.1016/j.vacuum.2003.12.156]
Pisani, M.B., Ren, K.L., Kao, P., Tadigadapa, S., 2011. Application of micromachined Y-cut-quartz bulk acoustic wave resonator for infrarared sensing. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 20(1):288–296. [doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2010.2100030]
Ren, K.L., Pisani, M.B., Kao, P., Tadigadapa, S., 2010. Micromachined Quartz Resonator-Based High Performance Thermal Sensors. IEEE Sensors, p.2197–2201. [doi:10.1109/ICSENS.2010.5690612]
Rychen, J., Ihn, T., Studerus, P., Herrmann, A., Ensslin, K., Hug, H.J., Schendel, P.J.A., Guntherodt, H.J., 2000. Operation characteristic of piezoelectric quartz tuning fork in high magnetic fields at helium temperatures. Rev. Sci. Instrum., 71(4):1695–1697. [doi:10.1063/1.1150521]
Setter, N., Damjanovic, D., Eng, L., Fox, G., Gevorgian, S., Hong, S., Kingon, A., Kohlstedt, H., Park, N.Y., Stephenson, G.B., et al., 2006. Ferroelectric thin films: review of materials, properties, and applications. J. Appl. Phys., 100(5):051606. [doi:10.1063/1.2336999]
Smith, W.L., Spencer, W.J., 1963. Quartz crystal thermometer for measureing temperature deviation in the 10−3 to 10−6 °C range. Rev. Sci. Instrum., 34(3):268–270. [doi:10.1063/1.1718326]
Söderkvist, J., 1997. Using FEA to Treat Piezoelectric Low-Frequency Resonators. IEEE Frequency Control Symp., p.634–642. [doi:10.1109/FREQ.1997.638737]
Spassov, L., 1992. Piezoelectric quartz resonators as highly sensitive temperature sensors. Sens. Actuat. A, 30(1–2): 67–72. [doi:10.1016/0924-4247(92)80198-C]
Spassov, L., Yossiffov, E., Georgiev, V., Vergov, L., 1997. A rotated Y-cut quartz resonator with linear temperature-frequency characteristic. Sens. Actuat. A, 58(3):185–189. [doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(97)01390-3]
Tadigadapa, S., Mateti, K., 2009. Sensors: state-of-the-art and perspectives. Meas. Sci. Technol., 20(9): 092001. [doi:10.1088/0957-0233/20/9/092001]
Trolier-McKinstry, S., Muralt, P., 2004. Thin film piezoelectrics for MEMS. J. Electroceram., 12(1–2):7–17. [doi:10.1023/B:JECR.0000033998.72845.51]
Tsow, F., Tao, N., 2007. Microfabricated tuning fork temperature and infrared sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett., 90(17): 174102. [doi:10.1063/1.2731313]
Ueda, T., Kohsaka, F., Iino, T., Yamazaki, D., 1986. Temperature Sensor Using Quartz Tuning Fork Resonator. 40th Annual Symp. on Frequency Control, p.224–229. [doi:10.1109/FREQ.1986.200946]
Vig, J.R., Filler, R.L., Kim, Y., 1996. Uncooled IR imaging array based on quartz microresonators. J. Microelectromrch. Syst., 5(2):131–137. [doi:10.1109/84.506201]
Wade, W.H., Slutsky, L.J., 1962. Quartz crystal thermometer. Rev. Sci. Instrum., 33(2):212–213. [doi:10.1063/1.1746550]
Wakatsuki, N., Kagawa, Y., Suzuki, K., Haba, M., 2003. Temperature-frequency characteristics simulation of piezoelectric resonators and their equivalent circuits based on three-dimensional finite element modelling. Int. J. Numer. Model., 16(6):479–492. [doi:10.1002/jnm.514]
Wu, X., Xie, L.Q., Xing, J., Pei, T.D., Wang, H.X., Su, J.B., 2012. A z-axis quartz tuning fork micromachined gyroscope based on shear stress detection. IEEE Sens. J., 12(5):1246–1552. [doi:10.1109/JSEN.2011.2163626]
Zeisel, D., Menzi, H., Ullrich, L., 2000. A precise and robust quartz sensor based on tuning fork technonlogy for (SF6)-gas density control. Sens. Actuat. A, 80(3):233–236. [doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(99)00345-3]
Zhou, X., Jing, T., Zhang, J., Wang, X., Zhu, Z., 2007. Humidity sensor based on quartz tuning fork coated with solgel-derived nanocrystalline zinc oxid thin film. Sens. Actuat. B, 123(1):299–305. [doi:10.1016/j.snb.2006.08.034]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Project (No. 11551074) supported by the Science Research Fund of Heilongjiang Provincial Education Department, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Li, X., Duan, Jh. et al. High-precision low-power quartz tuning fork temperature sensor with optimized resonance excitation. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 14, 264–273 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C12MNT05
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C12MNT05