Abstract
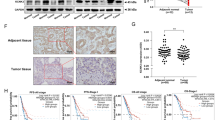
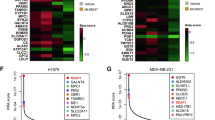
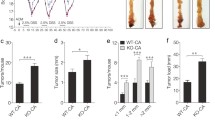
Up-frameshift 1 (UPF1), as the most critical factor in nonsense-mediated messenger RNA (mRNA) decay (NMD), regulates tumor-associated molecular pathways in many cancers. However, the role of UPF1 in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) amino acid metabolism remains largely unknown. In this study, we found that UPF1 was significantly correlated with a portion of amino acid metabolic pathways in LUAD by integrating bioinformatics and metabolomics. We further confirmed that UPF1 knockdown inhibited activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and Ser51 phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α), the core proteins in amino acid metabolism reprogramming. In addition, UPF1 promotes cell proliferation by increasing the amino-acid levels of LUAD cells, which depends on the function of ATF4. Clinically, UPF1 mRNA expression is abnormal in LUAD tissues, and higher expression of UPF1 and ATF4 was significantly correlated with poor overall survival (OS) in LUAD patients. Our findings reveal that UPF1 is a potential regulator of tumor-associated amino acid metabolism and may be a therapeutic target for LUAD.
概要
目的
UPF1是调节无义介导的mRNA降解的核心因子,参与多种肿瘤进展相关分子通路的调节,其在肺腺癌氨基酸代谢中的作用尚不清楚。
方法和结果
本研究通过结合生物信息学和代谢组学,分析发现UPF1与肺腺癌中部分氨基酸代谢通路显著相关,证实UPF1敲低后可显著抑制氨基酸代谢重编程核心蛋白ATF4的表达及eIF2α-Ser51位点的磷酸化水平,且UPF1通过调控ATF4蛋白增加肺腺癌细胞的氨基酸水平进而促进细胞增殖。在临床患者样本数据库中,肺腺癌组织中UPF1的mRNA水平表达异常,UPF1和ATF4均高表达的肺腺癌患者有着较差的总生存期。
结论
本研究表明,UPF1是肿瘤氨基酸代谢重编程的潜在调控因子,可作为肺腺癌治疗的新靶点。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Wahab AF, Mahmoud W, Al-Harizy RM, 2019. Targeting glucose metabolism to suppress cancer progression: prospective of anti-glycolytic cancer therapy. Pharmacol Res, 150:104511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104511
Adams CM, 2007. Role of the transcription factor ATF4 in the anabolic actions of insulin and the anti-anabolic actions of glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem, 282(23):16744–16753. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M610510200
Ameri K, Harris AL, 2008. Activating transcription factor 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 40(1):14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2007.01.020
Bai XP, Ni J, Beretov J, et al., 2021. Activation of the eIF2α/ATF4 axis drives triple-negative breast cancer radioresistance by promoting glutathione biosynthesis. Redox Biol, 43:101993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.101993
B’chir W, Maurin AC, Carraro V, et al., 2013. The eIF2α/ATF4 pathway is essential for stress-induced autophagy gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res, 41(16):7683–7699. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt563
Boroughs LK, DeBerardinis RJ, 2015. Metabolic pathways promoting cancer cell survival and growth. Nat Cell Biol, 17(4):351–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3124
Cao YH, 2019. Adipocyte and lipid metabolism in cancer drug resistance. J Clin Invest, 129(8):3006–3017. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI127201
Chang L, Li CC, Guo T, et al., 2016. The human RNA surveillance factor UPF1 regulates tumorigenesis by targeting Smad7 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 35:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0286-2
Chen BL, Wang HM, Lin XS, et al., 2021. UPF1: a potential biomarker in human cancers. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 26(5):76–84. https://doi.org/10.52586/4925
Chen PH, Cai L, Huffman K, et al., 2019. Metabolic diversity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cell, 76(5):838–851.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.08.028
Dehecq M, Decourty L, Namane A, et al., 2018. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay involves two distinct Upf1-bound complexes. EMBO J, 37(21):e99278. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201899278
Dias AS, Almeida CR, Helguero LA, et al., 2019. Metabolic crosstalk in the breast cancer microenvironment. Eur J Cancer, 121:154–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2019.09.002
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al., 2015. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer, 136(5):E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Georgoudaki AM, Prokopec KE, Boura VF, et al., 2016. Reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages by antibody targeting inhibits cancer progression and metastasis. Cell Rep, 15(9):2000–2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.084
Guo X, Wang AM, Wang W, et al., 2021. HRD1 inhibits fatty acid oxidation and tumorigenesis by ubiquitinating CPT2 in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Oncol, 15(2):642–656. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12856
Gwinn DM, Lee AG, Briones-Martin-Del-Campo M, et al., 2018. Oncogenic KRAS regulates amino acid homeostasis and asparagine biosynthesis via ATF4 and alters sensitivity to L-asparaginase. Cancer Cell, 33(1):91–107.E6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.12.003
Hai T, Curran T, 1991. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 88(9):3720–3724. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720
Han SH, Cao DD, Sha J, et al., 2020. LncRNA ZFPM2-AS1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by interacting with UPF1 to destabilize ZFPM2. Mol Oncol, 14(5): 1074–1088. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12631
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA, 2011. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell, 144(5):646–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Kawauchi K, Araki K, Tobiume K, et al., 2008. p53 regulates glucose metabolism through an IKK-NF-κB pathway and inhibits cell transformation. Nat Cell Biol, 10(5):611–618. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1724
Krishnamoorthy GP, Davidson NR, Leach SD, et al., 2019. EIF1AX and RAS mutations cooperate to drive thyroid tumorigenesis through ATF4 and c-MYC. Cancer Discov, 9(2):264–281. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0606
Kurosaki T, Popp MW, Maquat LE, 2019. Quality and quantity control of gene expression by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 20(7):406–420. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0126-2
Lee JV, Carrer A, Shah S, et al., 2014. Akt-dependent metabolic reprogramming regulates tumor cell histone acetylation. Cell Metab, 20(2):306–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.06.004
Li XZ, Yan XH, 2019. Sensors for the mTORC1 pathway regulated by amino acids. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 20(9):699–712. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900181
Li L, Geng Y, Feng R, et al., 2017. The human RNA surveillance factor UPF1 modulates gastric cancer progression by targeting long non-coding RNA MALAT1. Cell Physiol Biochem, 42(6):2194–2206. https://doi.org/10.1159/000479994
Li ZY, Zhang HF, 2016. Reprogramming of glucose, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism for cancer progression. Cell Mol Life Sci, 73(2):377–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2070-4
Lieu EL, Nguyen T, Rhyne S, et al., 2020. Amino acids in cancer. Exp Mol Med, 52(1):15–30. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-0375-3
Liu C, Karam R, Zhou YQ, et al., 2014. The UPF1 RNA surveillance gene is commonly mutated in pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma. Nat Med, 20(6):596–598. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3548
Lykke-Andersen S, Jensen TH, 2015. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: an intricate machinery that shapes transcriptomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 16(11):665–677. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm4063
Mossmann D, Park S, Hall MN, 2018. mTOR signalling and cellular metabolism are mutual determinants in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 18(12):744–757. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0074-8
Newman AC, Maddocks ODK, 2017. One-carbon metabolism in cancer. Br J Cancer, 116(12): 1499–1504. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.118
Nicholson P, Yepiskoposyan H, Metze S, et al., 2010. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human cells: mechanistic insights, functions beyond quality control and the double-life of NMD factors. Cell Mol Life Sci, 67(5):677–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0177-1
Pei CL, Fei KL, Yuan XY, et al., 2019. LncRNA DANCR aggravates the progression of ovarian cancer by down-regulating UPF1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 23(24): 10657–10663. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201912_19763
Peng YY, Yang H, Li S, 2021. The role of glycometabolic plasticity in cancer. Pathol Res Pract, 226:153595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2021.153595
Popp MWL, Maquat LE, 2013. Organizing principles of mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Annu Rev Genet, 47:139–165. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-111212-133424
Sneeggen M, Guadagno NA, Progida C, 2020. Intracellular transport in cancer metabolic reprogramming. Front Cell Dev Biol, 8:597608. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.597608
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al., 2021. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin, 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tabe Y, Lorenzi PL, Konopleva M, 2019. Amino acid metabolism in hematologic malignancies and the era of targeted therapy. Blood, 134(13):1014–1023. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019001034
Tajan M, Hennequart M, Cheung EC, et al., 2021. Serine synthesis pathway inhibition cooperates with dietary serine and glycine limitation for cancer therapy. Nat Commun, 12:366. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20223-y
Tsun ZY, Possemato R, 2015. Amino acid management in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 43:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.08.002
Ulanovskaya OA, Zuhl AM, Cravatt BF, 2013. NNMT promotes epigenetic remodeling in cancer by creating a metabolic methylation sink. Nat Chem Biol, 9(5):300–306. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1204
Vettore L, Westbrook RL, Tennant DA, 2020. New aspects of amino acid metabolism in cancer. Br J Cancer, 122(2): 150–156. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-019-0620-5
Wang XK, Lai QH, He J, et al., 2019. Lncrna SNHG6 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration in colorectal cancer cells by activating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway via targeting UPF1 and inducing EMT via regulation of ZEB1. Int J Med Sci, 16(1):51–59. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.27359
Xia LZ, Oyang LD, Lin JG, et al., 2021. The cancer metabolic reprogramming and immune response. Mol Cancer, 20:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01316-8
Yan M, Qi H, Xia T, et al., 2019. Metabolomics profiling of metformin-mediated metabolic reprogramming bypassing AMPKα. Metabolism, 91:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.010
Yu H, Li SB, 2020. Role of LINC00152 in non-small cell lung cancer. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 21(3):179–191. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900312
Zhang H, You Y, Zhu ZL, 2017. The human RNA surveillance factor Up-frameshift 1 inhibits hepatic cancer progression by targeting MRP2/ABCC2. Biomed Pharmacother, 92: 365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.090
Zhang MF, Chen H, Qin P, et al., 2021. UPF1 impacts on mTOR signaling pathway and autophagy in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Aging, 13(17):21202–21215. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203421
Zhong ZB, Wu YJ, Luo JN, et al., 2020. Knockdown of long noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 inhibits migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells by upregulating UPF1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 24(16):8246. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202008_22587
Zhou L, Dong C, Xu Z, et al., 2021. NEDD8-conjugating enzyme E2 UBE2F confers radiation resistance by protecting lung cancer cells from apoptosis. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 22(11):959–965. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100170
Zhu JJ, Thompson CB, 2019. Metabolic regulation of cell growth and proliferation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 20(7): 436–450. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0123-5
Zhu W, Zhou BL, Rong LJ, et al., 2020. Roles of PTBP1 in alternative splicing, glycolysis, and oncogensis. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 21(2): 122–136. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900422
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81803886, 81774078, and 21907093). We thank members of the Dr. Hailong PIAO laboratory (Group 1821, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, China) for helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lei FANG, Huan QI, and Peng WANG conceived the project, and designed and performed most of experiments and the data analysis. Hailong PIAO and Chundong GU supervised the project. Lei FANG and Shiqing WANG performed the establishment of animal models. Lei FANG, Huan QI, and Tianjiao LI provided significant intellectual input. Lei FANG, Huan QI, and Tian XIA wrote the manuscript with input from all other authors. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Lei FANG, Huan QI, Peng WANG, Shiqing WANG, Tianjiao LI, Tian XIA, Hailong PIAO, and Chundong GU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. All animal care and experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care Ethics and Use Committee of Dalian Medical University (No. AEE19015).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, L., Qi, H., Wang, P. et al. UPF1 increases amino acid levels and promotes cell proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma via the eIF2α-ATF4 axis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 23, 863–875 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200144
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200144
Key words
- Up-frameshift 1 (UPF1)
- Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4)
- Amino acid metabolism
- Lung adenocarcinoma