Abstract
Objective
To develop a risk scoring model for screening for undiagnosed type 2 diabetes in Chinese population.
Methods
A total of 5348 subjects from two districts of Jinan City, Shandong Province, China were enrolled. Group A (2985) included individuals from east of the city and Group B (2363) from west of the city. Screening questionnaires and a standard oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) were completed by all subjects. Based on the stepwise logistic regression analysis of Group A, variables were selected to establish the risk scoring model. The validity and effectiveness of this model were evaluated in Group B.
Results
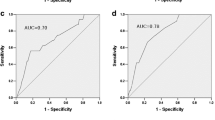
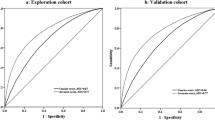
Based on stepwise logistic regression analysis performed with data of Group A, variables including age, body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, heart rate, family history of diabetes, and history of high glucose were accepted into the risk scoring model. The risk for having diabetes increased along with aggregate scores. When Youden index was closest to 1, the optimal cutoff value was set up at 51. At this point, the diabetes risk scoring model could identify diabetes patients with a sensitivity of 83.3% and a specificity of 66.5%, making the positive predictive value 12.83% and negative predictive value 98.53%. We compared our model with the Finnish and Danish model and concluded that our model has superior validity in Chinese population.
Conclusions
Our diabetes risk scoring model has satisfactory sensitivity and specificity for identifying undiagnosed diabetes in our population, which might be a simple and practical tool suitable for massive diabetes screening.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baan, C.A., Ruige, J.B., Stolk, R.P., Witteman, J.C., Dekker, J.M., Heine, R.J., Feskens, E.J., 1999. Performance of a predictive model to identify undiagnosed diabetes in a health care setting. Diabetes Care, 22(2):213–219. [doi:10.2337/diacare.22.2.213]
Bergmann, A., Li, J., Wang, L., Schulze, J., Bornstein, S.R., Schwarz, P.E., 2007. A simplified Finnish diabetes risk score to predict type 2 diabetes risk and disease evolution in a German population. Horm. Metab. Res., 39(9): 677–682. [doi:10.1055/s-2007-985353]
Claudi, T., Midthjell, K., Holmen, J., Fougner, K., Kruger, O., Wiseth, R., 2000. Cardiovascular disease and risk factors in persons with type 2 diabetes diagnosed in a large population screening: the Nord-Trøndelag Diabetes Study, Norway. J. Intern. Med., 248(6):492–500. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2000.00759.x]
Dong, J.J., Lou, N.J., Xin, Y., Xing, H.Y., Mou, Y.R., Wang, Q., LIAO, L., 2009. Evaluation of various questionnaires for screening diabetes mellitus in Chinese population. Chin. J. Endocrinol. Metab., 25(1):64–65 (in Chinese).
Fuller, J.H., Shipley, M.J., Rose, G., Jarrett, R.J., Keen, H., 1980. Coronary-heart-disease risk and impaired glucose tolerance: the Whitehall study. Lancet, 315(8183): 1373–1376. [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(80)92651-3]
Gao, W.G., Dong, Y.H., Pang, Z.C., Nan, H.R., Wang, S.J., Ren, J., Zhang, L., Tuomilehto, J., Qiao, Q., 2010. A simple Chinese risk score for undiagnosed diabetes. Diabet. Med., 27(3):274–281. [doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.02943.x]
Glümer, C., Carstensen, B., Sandbæk, A., Lauritzen, T., Jørgensen, T., Johnsen, K.B., 2004. A Danish diabetes risk score for targeted screening. Diabetes Care, 27(3): 727–733. [doi:10.2337/diacare.27.3.727]
Harris, M.I., 1993. Undiagnosed NIDDM: clinical and public health issues. Diabetes Care, 16(4):642–652.
Hong, J., Gu, W.Q., Zhang, Y.F., Yang, Y.S., Shen, C.F., Xu, M., Li, X.Y., Wang, W.Q., Ning, G., 2007. The interplay of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction involves the development of type 2 diabetes in Chinese obeses. Endocrine, 31(2):93–99. [doi:10.1007/s12020-007-0002-2]
Jia, W.P., Pang, C., Chen, L., Bao, Y.Q., Lu, J.X., Lu, H.J., Tang, J.L., Wu, Y.M., Zuo, Y.H., Jiang, S.Y., Xiang, K.S., 2007. Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in a Chinese adult population: the Shanghai Diabetes Studies, a cross-sectional 3-year follow-up study in Shanghai urban communities. Diabetologia, 50(2):286–292. [doi:10.1007/s00 125-006-0503-1]
Ko, G., So, W., Tong, P., Ma, R., Kong, A., Ozaki, R., Chow, C., Cockram, C., Chan, J., 2010. A simple risk score to identify southern Chinese at high risk for diabetes. Diabet. Med., 27(6):644–649. [doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.02993.x]
Lawrence, J.M., Bennett, P., Young, A., Robinson, A.M., 2001. Screening for diabetes in general practice: cross sectional population study. BMJ, 323(7312):548–551. [doi:10.1136/bmj.323.7312.548]
Lindström, J., Tuomilehto, J., 2003. The diabetes risk score: a practical tool to predict type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetes Care, 26(3):725–731. [doi:10.2337/diacare.26.3.725]
Ma, X.J., Jia, W.P., Hu, C., Zhou, J., Lu, H.J., Zhang, R., Wang, C.R., Wu, S.H., Xiang, K.S., 2008. Genetic characteristics of familial type 2 diabetes pedigrees: a preliminary analysis of 4468 persons from 715 pedigrees. Natl. Med. J. China, 88(36):2541–2543 (in Chinese).
Midthjell, K., Kruger, O., Holmen, J., Tverdal, A., Claudi, T., Bjorndal, A., Magnus, P., 1999. Rapid changes in the prevalence obesity and known diabetes in an adult Norwegian population: the Nord-Trøndelag Health Surveys: 1984–1986 and 1995–1997. Diabetes Care, 22(11): 1813–1820. [doi:10.2337/diacare.22.11.1813]
Park, P.J., Griffin, S.J., Sargeant, L., Wareham, N.J., 2002. The performance of a risk score in predicting undiagnosed hyperglycemia. Diabetes Care, 25(6):984–988. [doi:10.2337/diacare.25.6.984]
Rathmann, W., Martin, S., Haastert, B., Icks, A., Holle, R., Löwel, H., Giani, G., 2005. Performance of screening questionnaires and risk scores for undiagnosed diabetes. Arch. Intern. Med., 165(4):436–441. [doi:10.1001/ archinte.165.4.436]
Ruige, J.B., Bouter, L.M., Neeling, J.N., Henine, R.J., Kositense, P.J., 1997. Performance of an NIDDM screening questionnaire based on symptoms and risk factors. Diabetes Care, 20(4):491–497. [doi:10.2337/diacare.20.4.491]
Schulze, M.B., Hoffmann, K., Boeing, H., Linseisen, J., Rohrmann, S., Möhlig, M., Pfeiffer, A.F., Spranger, J., Thamer, C., Häring, H.U., et al., 2007. An accurate risk score based on anthropometric, dietary, and lifestyle factors to predict the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 30(3):510–515. [doi:10.2337/dc06-2089]
Smith, S.M., Holohan, J., McAuliffe, A., Firth, R.G., 2003. Irish diabetes detection programme in general practice. Diabet. Med., 20(9):717–722. [doi:10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00998.x]
Thomas, C., Hyppönen, E., Power, C., 2006. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in midlife estimated from the Cambridge risk score and body mass index. Arch. Intern. Med., 166(6): 682–688. [doi:10.1001/archinte.166.6.682]
Williams, D.R., Wareham, N.J., Brown, D.C., Byrne, C.D., Clark, P.M., Cox, B.D., Cox, L.J., Day, N.E., Hales, C.N., Palmer, C.R., et al., 1995. Undiagnosed glucose intolerance in the community: the Isle of Ely Diabetes Project. Diabet. Med., 12(1):30–35. [doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.1995.tb02058.x]
Yang, W.Y., Lu, J.M., Weng, J.P., Jia, W.P., Ji, L.N., Xiao, J.J., Shan, Z.Y., Liu, J., Tian, H.M., Ji, Q.H., et al., 2010. Prevalence of diabetes among man and women in China. N. Engl. J. Med., 362(12):1090–1101. [doi:10.1056/ NEJMoa0908292]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 963000052) supported by the Science and Technology Department of Shandong Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Jj., Lou, Nj., Zhao, Jj. et al. Evaluation of a risk factor scoring model in screening for undiagnosed diabetes in China population. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 846–852 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000390
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000390