Abstract
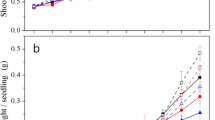
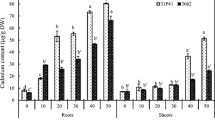
This study was conducted to investigate the combined effects of elevated CO2 levels and cadmium (Cd) on the root morphological traits and Cd accumulation in Lolium multiflorum Lam. and Lolium perenne L. exposed to two CO2 levels (360 and 1 000 μl/L) and three Cd levels (0, 4, and 16 mg/L) under hydroponic conditions. The results show that elevated levels of CO2 increased shoot biomass more, compared to root biomass, but decreased Cd concentrations in all plant tissues. Cd exposure caused toxicity to both Lolium species, as shown by the restrictions of the root morphological parameters including root length, surface area, volume, and tip numbers. These parameters were significantly higher under elevated levels of CO2 than under ambient CO2, especially for the number of fine roots. The increases in magnitudes of those parameters triggered by elevated levels of CO2 under Cd stress were more than those under non-Cd stress, suggesting an ameliorated Cd stress under elevated levels of CO2. The total Cd uptake per pot, calculated on the basis of biomass, was significantly greater under elevated levels of CO2 than under ambient CO2. Ameliorated Cd toxicity, decreased Cd concentration, and altered root morphological traits in both Lolium species under elevated levels of CO2 may have implications in food safety and phytoremediation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arduini, I., Godbold, D.L., Onnis, A., 1995. Influence of copper on root growth and morphology of Pinus pinea L. and Pinus pinaster Ait. seedlings. Tree Physiol., 15(6): 411–415.
Arienzo, M., Adamo, P., Cozzolino, V., 2004. The potential of Lolium perenne for revegetation of contaminated soil from a metallurgical site. Sci. Total Environ., 319(1–3): 13–25. [doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00435-2]
Baryla, A., Carrier, P., Franck, F., Coulomb, C., Sahut, C., Havaux, M., 2001. Leaf chlorosis in oilseed plants (Brassica napus) grown on cadmium-polluted soil: causes and consequences for photosynthesis and growth. Planta, 212(5–6):696–709. [doi:10.1007/s004250000439]
Benavides, M., Gallego, M.S., Tomaro, M.L., 2005. Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol., 17(1):21–34. [doi:10.1590/S1677-04202005000100003]
Bosac, C., Gardner, S.D.L., Taylor, G., Wilkins, D., 1995. Elevated CO2 and hybrid poplar: a detailed investigation of root and shoot growth and physiology of Populus euramericana, ‘Primo’. Forest Ecol. Manag., 74(1–3): 103–116. [doi:10.1016/0378-1127(94)03506-R]
Bowes, G., 1993. Facing the inevitable: plants and increasing atmospheric CO2. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 44(1):309–332. [doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.44.060193.001521]
Caggiano, R., D’Emilio, M., Macchiato, M., Ragosta, M., 2005. Heavy metals in ryegrass species versus metal concentrations in atmospheric particulate measured in an industrial area southern Italy. Environ. Monit. Assess., 102 (1–3): 67–84. [doi:10.1007/s10661-005-1595-7]
Cheng, W.G., Sakai, H., Yagi, K., Hasegawa, T., 2009. Interactions of elevated [CO2] and night temperature on rice growth and yield. Agric. Forest Meteorol., 149(1):51–58. [doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2008.07.006]
Ci, D.W., Jiang, D., Dai, T.B., Jing, Q., Cao, W.X., 2009. Effects of cadmium on plant growth and physiological traits in contrast wheat recombinant inbred lines differing in cadmium tolerance. Chemosphere, 77(11):1620–1625. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.08.062]
Cosio, C., Vollenweider, P., Keller, C., 2006. Localization and effects of cadmium in leaves of a cadmium-tolerant willow (Salix viminalis L.): 1. Macrolocalization and phytotoxic effects of cadmium. Environ. Exp. Bot., 58(1–3):64–74. [doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.06.017]
Daud, M.K., Sun, Y., Dawood, M., Hayat, Y., Variath, M.T., Wu, Y., Raziuddin, Mishkat, U., Salahuddin, Najeeb, U., et al., 2009. Cadmium-induced functional and ultrastructural alterations in roots of two transgenic cotton cultivars. J. Hazard. Mater., 161(1):463–473. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.128]
Day, F.P., Weber, E.P., Hinkle, C.R., Drake, B.G., 1996. Effects of elevated CO2 on fine root length and distribution in an oak-palmetto scrub ecosystem in central Florida. Global Change Biol., 2(2):143–148. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.1996.tb00059.x]
Donnelly, A., Craigon, J., Black, C.R., Colls, J.J., Landon, G., 2001. Does elevated CO2 ameliorate the impact of O3 on chlorophyll content and photosynthesis in potato (Solanum tuberosum)? Physiol. Plant., 111(4):501–511. [doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3054.2001.1110410.x]
Ferris, R., Taylor, G., 1993. Contrasting effects of elevated CO2 on the root and shoot growth of four native herbs commonly found in chalk grassland. New Phytol., 125(4): 855–866. [doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1993.tb03934.x]
Fojtová, M., Fulnečková, J., Fajkus, J., Kovařík, A., 2002. Recovery of tobacco cells from cadmium stress is accompanied by DNA repair and increased telomerase activity. J. Exp. Bot., 53(378):2151–2158. [doi:10.1093/jxb/erf080]
Franzaring, J., Holz, I., Fangmeier, A., 2008. Different responses of Molinia caerulea plants from three origins to CO2 enrichment and nutrient supply. Acta Oecol., 33(2): 176–187. [doi:10.1016/j.actao.2007.10.006]
Geissler, N., Hussin, S., Koyro, H.W., 2009. Elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration ameliorates effects of NaCl salinity on photosynthesis and leaf structure of Aster tripolium L. J. Exp. Bot., 60(1):137–151. [doi:10.1093/jxb/ern271]
Ghosh, M., Singh, S.P., 2005. A comparative study of cadmium phytoextraction by accumulator and weed species. Environ. Pollut., 133(2):365–371. [doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.015]
Greger, M., Ögren, E., 1991. Direct and indirect effects of Cd2+ on photosynthesis in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Physiol. Plant., 83(1):129–135. [doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1991.tb01291.x]
Guo, H.C., Wang, G.H., 2009. Phosphorus status and microbial community of paddy soil with the growth of annual ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) under different phosphorus fertilizer treatments. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B, 10(10):761–768. [doi:10.1631/jzus.B0920101]
Guo, H.Y., Jia, H.X., Zhu, J.G., Wang, X.R., 2006. Influence of the environmental behavior and ecological effect of cropland heavy metal contaminants by CO2 enrichment in atmosphere. Chin. J. Geochem., 25(s1):212. [doi:10.1007/BF02840155]
Högy, P., Fangmeier, A., 2009. Atmospheric CO2 enrichment affects potatoes: 1. aboveground biomass production and tuber yield. Eur. J. Agron., 30(2):78–84. [doi:10.1016/j.eja.2008.07.007]
Horie, T., Baker, J.T., Nakagawa, H., Matsui, T., Kim, H.Y., 2000. Crop Ecosystem Responses to Climate Change: Rice. In: Reddy, K.R., Hodges, H.F. (Eds.), Climate Change and Global Crop Productivity. CAB International, Wallingford, Oxon, UK, p.81–106. [doi:10.1079/9780851994390.0081]
IPCC, 2007. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and NY, USA, p.1–21.
Janssens, I.A., Crookshanks, M., Taylor, G., Ceulemans, R., 1998. Elevated atmospheric CO2 increases fine root production, respiration, rhizosphere respiration and soil CO2 efflux in Scots pine seedlings. Global Change Biol., 4(8):871–878. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2486.1998.00199.x]
Jia, H.X., Guo, H.Y., Yin, Y., Wang, Q., Sun, Q., Wang, X.R., Zhu, J.G., 2007. Responses of rice growth to copper stress under free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE). Chin. Sci. Bull., 52(19):2636–2641. [doi:10.1007/s11434-007-0362-2]
Jia, Y., Tang, S.R., Wang, R.G., Ju, X.H., Ding, Y.Z., Tu, S.X., Smith, D.L., 2010. Effects of elevated CO2 on growth, photosynthesis, elemental composition, antioxidant level, and phytochelatin concentration in Lolium mutiforum and Lolium perenne under Cd stress. J. Hazard. Mater., 180(1–3):384–394. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.043]
Jia, Y.B., Yang, X.E., Feng, Y., Jilani, G., 2008. Differential response of root morphology to potassium deficient stress among rice genotypes varying in potassium efficiency. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B, 9(5):427–434. [doi:10.1631/jzus.B0710636]
Jia, Y.S., Gray, V.M., 2007. The influence N and P supply on the short-term responses to elevated CO2 in faba bean (Vicia faba L). S. Afr. J. Bot., 73(3):466–470. [doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2007.02.189]
Jin, C.W., Du, S.T., Chen, W.W., Li, G.X., Zhang, Y.S., Zheng, S.J., 2009. Elevated carbon dioxide improves plant iron nutrition through enhancing the iron-deficiency-induced responses under iron-limited conditions in tomato. Plant Physiol., 150(1):272–280. [doi:10.1104/pp.109.136721]
Jin, V.L., Evans, R.D., 2010. Elevated CO2 increases plant uptake of organic and inorganic N in the desert shrub Larrea tridentata. Oecologia, 163(1):257–266. [doi:10. 1007/s00442-010-1562-z]
Kimball, B.A., Kobayashi, K., Bindi, M., 2002. Responses of agricultural crops to free-air CO2 enrichment. Adv. Agron., 77:293–368. [doi:10.1016/S0065-2113(02)77017-X]
Kirschbaum, M.U.F., 2004. Direct and indirect climate change effects on photosynthesis and transpiration. Plant Biol., 6(3):242–253. [doi:10.1055/s-2004-820883]
Kiss, Z., Lehoczky, É., Németh, T., 2002. Testing of available heavy metal content of soils in long-term fertilization trials with ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Acta Biol. Szeged., 46:107–108.
Lee-Ho, E., Walton L.J., Reid, D.M., Yeung, E.C., Kurepin, L.V., 2007. Effects of elevated carbon dioxide and sucrose concentrations on Arabidopsis thaliana root architecture and anatomy. Can. J. Bot., 85(3):324–330. [doi:10.1139/B07-009]
Li, T., Yang, X., Lu, L., Islam, E., He, Z., 2009. Effects of zinc and cadmium interactions on root morphology and metal translocation in a hyperaccumulating species under hydroponic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater., 169(1–3):734–741. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.004]
Li, Z.Y., Tang, S.R., Deng, X.F., Wang, R.G., Song, Z.G., 2010. Contrasting effects of elevated CO2 on Cu and Cd uptake by different rice varieties grown on contaminated soils with two levels of metals: implication for phytoextraction and food safety. J. Hazard. Mater., 177(1–3): 352–361. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.039]
Lieffering, M., Kim, H.K., Kobayashi, K., Okada, M., 2004. The impact of elevated CO2 on the elemental concentrations of field-grown rice grains. Field Crops Res., 88(2–3): 279–286. [doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2004.01.004]
Lobell, D.B., Field, C.B., 2008. Estimation of the carbon dioxide (CO2) fertilization effect using growth rate anomalies of CO2 and crop yields since 1961. Global Change Biol., 14(1):39–45. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01476.x]
Loladze, I., 2002. Rising atmospheric CO2 and human nutrition: toward globally imbalanced plant stoichiometry? Trends Ecol. Evol., 17(10):457–461. [doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(02)02587-9]
Long, S.P., Ainsworth, E.A., Rogers, A., Ort, D.R., 2004. Rising atmospheric carbon dioxide: plants FACE the future. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 55(1):591–628. [doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141610]
Marseille, F., Tiffreau, C., Laboudigue, A., Lecomte, P., 2000. Impact of vegetation on the mobility and bioavailability of trace elements in a dredged sediment deposit: a greenhouse study. Agronomie, 20(5):547–556. [doi:10.1051/agro:2000149]
Matamala, R., Schlesinger, W.H., 2000. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on fine root production and activity in an intact temperate forest ecosystem. Global Change Biol., 6(8):967–979. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2486.2000.00374.x]
Moya, T.B., Ziska, L.H., Namuco, O.S., Olszyk, D., 1998. Growth dynamics and genotypic variation in tropical, field-grown paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) in response to increasing carbon dioxide and temperature. Global Change Biol., 4(6):645–656. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2486.1998.00180.x]
Nishizono, H., Ichikawa, H., Suziki, S., Ishii, F., 1987. The role of the root cell wall in the heavy metal tolerance of Athyrium yokoscense. Plant Sci., 101(1):15–20. [doi:10. 1007/BF02371025]
Oksanen, E., Sober, S., Karnosky, D.F., 2001. Impacts of elevated CO2 and/or O3 on leaf ultrastructure of aspen (Populus tremuloides) and birch (Betula papyrifera) in the Aspen FACE experiment. Environ. Pollut., 115(3): 437–446. [doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00233-0]
Ostonen, I., Püttsepp, Ü., Biel, C., Alberton, O., Bakker, M.R., Lõhmus, K., Majdi, H., Metcalfe, D., Olsthoorn, A.F.M., Pronk, A., et al., 2007. Specific root length as an indicator of environmental change. Plant Biosyst., 141(3):426–442. [doi:10.1080/11263500701626069]
Palazzo, A.J., Cary, T.J., Hardy, S.E., Lee, C.R., 2003. Root growth and metal uptake in four grasses grown on zinc-contaminated soils. J. Environ. Qual., 32(3):834–840. [doi:10.2134/jeq2003.0834]
Peng, H.Y., Tian, S.K., Yang, X.E., 2005. Changes of root morphology and Pb uptake by two species of Elsholtzia under Pb toxicity. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B, 6(6):546–552. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2005.B0546]
Phillips, D.L., Johnson, M.G., Tingey, D.T., Catricala, C.E., Hoyman, T.L., Nowak, R.S., 2006. Effects of elevated CO2 on fine root dynamics in a Mojave Desert community: a FACE study. Global Change Biol., 12(1):61–73. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2005.01085.x]
Prior, S.A., Torbert, H.A., Runion, G.B., Rogers, H.H., 2003. Implications of elevated CO2-induced changes in agroecosystem productivity. J. Crop Prod., 8(1/2):217–244. [doi:10.1300/J144v08n01_09]
Pritchard, S.G., Rogers, H.H., 1999. Elevated CO2 and plant structure: a review. Global Change Biol., 5(7):807–837. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2486.1999.00268.x]
Pritchard, S.G., Davis, M.A., Mitchell, R.J., Prior, S.A., Boykin, D.L., Rogers, H.H., Runion, G.B., 2001. Root dynamics in an artificially constructed regenerating longleaf pine ecosystem are affected by atmospheric CO2 enrichment. Environ. Exp. Bot., 46(1):55–69. [doi:10. 1016/S0098-8472(01)00084-3]
Rogers, A., Allen, D.J., Davey, P.A., Morgan, P.B., Ainsworth, E.A., Bernacchi, C.J., Cornic, G., Dermody, O., Heaton, E.A., Mahoney, J., et al., 2004. Leaf photosynthesis and carbohydrate dynamics of soybeans grown throughout their lifecycle under Free-Air Carbon Dioxide Enrichment. Plant Cell Environ., 27(4):449–458. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01163.x]
Rogers, H.H., Peterson, C.M., McCrimmon, J.N., Cure, J.D., 1992. Response of plant roots to elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide. Plant Cell Environ., 15(6):749–752. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.1992.tb01018.x]
Romero-Puertas, M.C., Rodríguez-Serrano, M., Corpas, F.J., del Río, L.A., 2004. Cadmium-induced subcellular accumulation of O2− and H2O2 in pea leaves. Plant Cell Environ., 27(9):1122–1134. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01217.x]
Sabreen, S., Sugiyama, S.I., 2008. Cadmium phytoextraction capacity in eight C3 herbage grass species. Grassl. Sci., 54(1):27–32. [doi:10.1111/j.1744-697X.2008.00101.x]
Sgherri, C.L.M., Quartacci, M.F., Menconi, M., Raschi, A., Navari-Izzo, F., 1998. Interactions between drought and elevated CO2 on alfalfa plants. J. Plant Physiol., 152: 118–124.
Singh, P.K., Tewari, R.K., 2003. Cadmium toxicity induced changes in plant water relations and oxidative metabolism of Brassica juncea L. plants. J. Environ. Biol., 24(1): 107–112.
Tang, S.R., 2006. The Principle and Methods of Phytoremediation of Contaminated Environment. Scientific Press, Beijing, China, p.1–289 (in Chinese).
Tang, S.R., Xi, L., Zheng, J.M., Li, H.Y., 2003. Response to elevated CO2 of Indian mustard and sunflower growing on copper contaminated soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox., 71(5):988–997. [doi:10.1007/s00128-003-0224-9]
Urban, O., 2003. Physiological impacts of elevated CO2 concentration ranging from molecular to whole plant responses. Photosynthetica, 41(1):9–20. [doi:10.1023/A:1025891825050]
Vega, J.M., Garbayo, I., Domínguez, M.J., Vigar, J., 2006. Effect of abiotic stress on photosynthesis and respiration in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: induction of oxidative stress. Enzyme Microb. Tech., 40(1):163–167. [doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.050]
Wang, X., Taub, D.R., 2010. Interactive effects of elevated carbon dioxide and environmental stresses on root mass fraction in plants: a meta-analytical synthesis using pairwise techniques. Oecologia, 163(1):1–11. [doi:10. 1007/s00442-010-1572-x]
Wechsung, G., Wechsung, F., Wall, G.W., Adamsen, F.J., Kimball, B.A., Pinter, P.J.Jr., Lamorte, R.L., Garcia, R.L., Kartschall, T.H., 1999. The effects of free-air CO2 enrichment and soil water availability on spatial and seasonal patterns of wheat root growth. Global Change Biol., 5(5):519–529. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2486.1999.00243.x]
Wu, H.B., Tang, S.R., Zhang, X.M., Guo, J.K., Song, Z.G., Tian, S., Smith, D., 2009. Using elevated CO2 to increase the biomass of a Sorghum vulgare×Sorghum vulgare var. sudanense hybrid and Trifolium pratense L. and to trigger hyperaccumulation of cesium. J. Hazard. Mater., 1170 (2–3): 861–870. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.069]
Yang, L.X., Wang, Y.L., Dong, G.C., Gu, H., Huang, J.Y., Zhu, J.G., Yang, H.J., Liu, G., Han, Y., 2007. The impact of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) and nitrogen supply on grain quality of rice. Field Crops Res., 102(2):128–140. [doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2007.03.006]
Zheng, J.M., Wang, H.Y., Li, Z.Q., Tang, S.R., Chen, Z.Y., 2008. Using elevated carbon dioxide to enhance copper accumulation in Pteridium Revolutum, a copper-tolerant plant, under experimental conditions. Int. J. Phytoremediat., 10(2):161–172. [doi:10.1080/15226510801913934]
Ziska, L.H., Manalo, P.A., Ordonez, R.A., 1996. Intraspecific variation in the response of rice (Oryza sativa L.) to increased CO2 and temperature-growth and yield response of 17 cultivars. J. Exp. Bot., 47(9):1353–1359. [doi:10.1093/jxb/47.9.1353]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Central Public Research Institute Basic Fund for Research and Development (2008-jxh-1), Agro-environmental Protection Institute, Ministry of Agriculture, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Tang, Sr., Ju, Xh. et al. Effects of elevated CO2 levels on root morphological traits and Cd uptakes of two Lolium species under Cd stress. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 313–325 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000181
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000181