Abstract
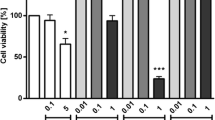
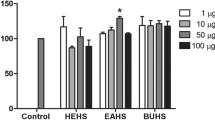
Seaweed has been used in traditional cosmetics and as a herbal medicine in treatments for cough, boils, goiters, stomach ailments, and urinary diseases, and for reducing the incidence of tumors, ulcers, and headaches. Despite the fact that seaweeds are frequently used in the practice of human health, little is known about the role of seaweed in the context of inflammation. This study aimed to investigate the influence of Jeju endemic seaweed on a mouse macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7) under the stimulation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Ethyl acetate extracts obtained from 14 different kinds of Jeju seaweeds were screened for inhibitory effects on pro-inflammatory mediators. Our results revealed that extracts from five seaweeds, Laurencia okamurae, Grateloupia elliptica, Sargassum thunbergii, Gloiopeltis furcata, and Hizikia fusiformis, were potent inhibitors of the production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Based on these results, the anti-inflammatory effects and low cell toxicity of these seaweed extracts suggest potential therapeutic applications in the regulation of the inflammatory response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, S.J., Choi, Y.H., 2007. Methanol extract of the seaweed Gloiopeltis furcata induces G2/M arrest and inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 activity in human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. Phytotherapy Research, 21(1):52–57. [doi:10.1002/ptr.2020]
Blunt, J.W., Copp, B.R., Hu, W.P., Munro, M.H., Northcote, P.T., Prinsep, M.R., 2009. Marine natural products. Natural Product Reports, 26(2):170–244. [doi:10.1039/b805113p]
Choi, H.J., Eun, J.S., Park, Y.R., Kim, D.K., Li, R., Moon, W.S., Park, J.M., Kim, H.S., Cho, N.P., Cho, S.D., et al., 2008. Ikarisoside A inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells via p38 kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathways. European Journal of Pharmacology, 601(1–3):171–188. [doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.09.032]
Dang, H.T., Lee, H.J., Yoo, E.S., Shinde, P.B., Lee, Y.M., Hong, J., Kim, D.K., Jung, J.H., 2008. Anti-inflammatory constituents of the red alga Gracilaria verrucosa and their synthetic analogues. Journal of Natural Products, 71(2):232–240. [doi:10.1021/np070452q]
de Benedetti, F., 2009. Targeting interleukin-6 in pediatric rheumatic diseases. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 21(5):533–537. [doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e32832f1445]
Dokka, S., Shi, X., Leonard, S., Wang, L., Castranova, V., Rojanasakul, Y., 2001. Interleukin-10-mediated inhibition of free radical generation in macrophages. The American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 280(6):L1196–L1202.
Esposito, E., Cuzzocrea, S., 2009. TNF-alpha as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases, ischemia-reperfusion injury and trauma. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 16(24):3152–3167. [doi:10.2174/092986709788803024]
Fonseca, J.E., Santos, M.J., Canhão, H., Choy, E., 2009. Interleukin-6 as a key player in systemic inflammation and joint destruction. Autoimmunity Reviews, 8(7):538–542. [doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2009.01.012]
Iyer, J.P., Srivastava, P.K., Dev, R., Dastidar, S.G., Ray, A., 2009. Prostaglandin E(2) synthase inhibition as a therapeutic target. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets, 13(7):849–865. [doi:10.1517/14728220903018932]
Kang, O.H., Chae, H.S., Choi, J.G., Oh, Y.C., Lee, Y.S., Kim, J.H., Seung, M.J., Jang, H.J., Bae, K.H., Lee, J.H., et al., 2008. Ent-pimara-8(14), 15-dien-19-oic acid isolated from the roots of Aralia cordata inhibits induction of inflammatory mediators by blocking NF-kappaB activation and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. European Journal of Pharmacology, 601(1–3):179–185. [doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.10.012]
Kanwar, J.R., Kanwar, R.K., Burrow, H., Baratchi, S., 2009. Recent advances on the roles of NO in cancer and chronic inflammatory disorders. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 16(19):2373–2394. [doi:10.2174/092986709788682155]
Kim, J.Y., Park, S.J., Yun, K.J., Cho, Y.W., Park, H.J., Lee, K.T., 2008. Isoliquiritigenin isolated from the roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis inhibits LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression via the attenuation of NF-kappaB in RAW 264.7 macrophages. European Journal of Pharmacology, 584(1):175–184. [doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.01.032]
Kim, K.N., Ham, Y.M., Moon, J.Y., Kim, M.J., Kim, D.S., Lee, W.J., Lee, N.H., Hyun, C.G., 2009. In vitro cytotoxic activity of Sargassum thunbergii and Dictyopteris divaricata (Jeju seaweeds) on the HL-60 tumour cell line. International Journal of Pharmacology, 5(5):298–306. [doi:10.3923/ijp.2009.298.306]
Kim, M.M., Rajapakse, N., Kim, S.K., 2009. Anti-inflammatory effect of Ishige okamurae ethanolic extract via inhibition of NF-kappaB transcription factor in RAW 264.7 cells. Phytotherapy Research, 23(5):628–634. [doi:10.1002/ptr.2674]
Kim, S.K., Lee, D.Y., Jung, W.K., Kim, J.H., Choi, I., Park, S.G., Seo, S.K., Lee, S.W., Lee, C.M., Yea, S.S., et al., 2008. Effects of Ecklonia cava ethanolic extracts on airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a murine asthma model: role of suppressor of cytokine signaling. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 62(5):289–296. [doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2007.07.009]
Murakami, A., 2009. Chemoprevention with Phytochemicals Targeting Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase. In: Yoshikawa, T. (Ed.), Food Factors for Health Promotion. Forum of Nutrition, Basel, Karger, Vol. 61, p.193–203. [doi:10.1159/000212751]
O’Connor, D.M., O’Brien, T., 2009. Nitric oxide synthase gene therapy: progress and prospects. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 9(7):867–878. [doi:10.1517/14712590903002047]
Park, J.H., Oh, S.M., Lim, S.S., Lee, Y.S., Shin, H.K., Oh, Y.S., Choe, N.H., Park, J.H., Kim, J.K., 2006. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of the ethanol extract of Rubus coreanus in murine macrophages. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 351(1):146–152. [doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.008]
Radovits, B.J., Kievit, W., Laan, R.F., 2009. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha antagonists in the management of rheumatoid arthritis in the elderly: a review of their efficacy and safety. Drugs and Aging, 26(8):647–664. [doi:10.2165/11316460-000000000-00000]
Rao, P., Knaus, E.E., 2008. Evolution of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibition and beyond. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 11(2):81s–110s.
Samee, H., Li, Z.X., Lin, H., Khalid, J., Guo, Y.C., 2009. Anti-allergic effects of ethanol extracts from brown seaweeds. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B, 10(2):147–153. [doi:10.1631/jzus.B0820185]
Scher, J.U., Pillinger, M.H., 2009. The anti-inflammatory effects of prostaglandins. Journal of Investigative Medicine, 57(6):703–708.
Usami, Y., 2009. Recent synthetic studies leading to structural revisions of marine natural products. Marine Drugs, 7(3):314–330. [doi:10.3390/md7030314]
Yang, E.J., Yim, E.Y., Song, G., Kim, G.O., Hyun, C.G., 2009. Inhibition of nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages by Jeju plant extracts. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 2(4):245–249. [doi:10.2478/v10102-009-0022-2]
Zhang, C., Kim, S.K., 2009. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors (MMPIs) from marine natural products: the current situation and future prospects. Marine Drugs, 7(2):71–84. [doi:10.3390/md7020071]
Zhou, H.Y., Shin, E.M., Guo, L.Y., Zou, L.B., Xu, G.H., Lee, S.H., Ze, K.R., Kim, E.K., Kang, S.S., Kim, Y.S., 2007. Anti-inflammatory activity of 21(alpha,beta)-methyl-melianodiols, novel compounds from Poncirus trifoliata Rafinesque. European Journal of Pharmacology, 572(2–3):239–248. [doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.07.005]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project partially supported by the Jeju Sea-green Program for the Regional Innovation System and the Regional Technology Innovation Program (No. RTI04-02-07) of the Ministry of Knowledge and Economy, Korea
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, EJ., Moon, JY., Kim, MJ. et al. Inhibitory effect of Jeju endemic seaweeds on the production of pro-inflammatory mediators in mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 11, 315–322 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0900364
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0900364
Key words
- Nitric oxide
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
- Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)
- Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)
- Seaweeds
- Pro-inflammatory mediators