Abstract
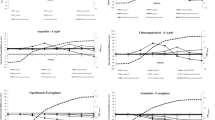
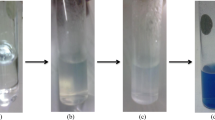
The objective of this study is to propose a more accurate and faster MTT [3-(4,5-dimethyl thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] colorimetric assay (MCA) for quantitative measurement of polypeptide bacteriocins in solutions with nisin as an example. After an initial incubation of nisin and indicator bacterium Micrococcus luteus NCIB 8166 in tubes, MTT was added for another incubation period. After that, nisin was quantified by estimating the number of viable bacteria based on measuring the amount of purple formazan produced by cleavage of yellow tetrazolium salt MTT. Then MCA was compared to a standard agar diffusion assay (ADA). The results suggested a high correlation coefficient (r 2=0.975±0.004) between optical density (OD) and the inhibitory effect of nisin on a bacterial strain Micrococcus luteus NCIB 8166 at a range of 0.125∼32 IU/ml. The MCA described in this study was very quick. Quantification of nisin took only 7∼8 h and the detection limit was at the level of 0.125 IU/ml when compared to 12 IU/ml and 24∼28 h for ADA. The MCA provides an accurate and rapid method for quantification of nisin in solutions and is expected to be used for quantification of other antimicrobial substances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouksaim, M., Fliss, I., Meghrous, J., Simard, R., Lacroix, C., 1998. Immunodot detection of nisin Z in milk and whey using enhanced chemiluminescence. J. Appl. Microbiol., 84(2):176–184. [doi.10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.00315.x]
Bouksaim, M., Lacroix, C., Bazin, R., Simard, R.E., 1999. Production and utilization of polyclonal antibodies against nisin in an ELISA and for immuno-location of nisin in producing and sensitive bacterial strains. J. Appl. Microbiol., 87(4):500–510. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00842.x]
Budde, B.B., Rasch, M., 2001. A comparative study on the use of flow cytometry and colony forming units for assessment of the antibacterial effect of bacteriocins. Int. J. Food Microbiol., 63(1–2):65–72. [doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(00)00399-8]
Daoudi, L., Turcotte, C., Lacroix, C., Fliss, I., 2001. Production and characterization of anti-nisin Z monoclonal antibodies: suitability for distinguishing active from inactive forms through a competitive enzyme immunoassay. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 56(1–2):114–119. [doi:10.1007/s002530000560]
Deegan, L.H., Cotter, P.D., Hill, C., Ross, P., 2006. Bacteriocins: Biological tools for bio-preservation and shelf-life extension. Int. Dairy J., 16(9):1058–1071. [doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2005.10.026]
Delves-Broughton, J., 1990. Nisin and its uses as a food preservative. Food Technol., 44(11):100–117.
Falahee, M.B., Adams, M.R., Dale, J.W., Mornis, B.A., 1990. An enzyme immunoassay for nisin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol., 25(5):590–595.
Giraffa, G., Neviani, E., Veneroni, A., 1990. Use of conductance to detect bacteriocin activity. J. Food Prot., 53(9):772–776.
Hakovirta, J., Reunanen, J., Saris, P.E.J., 2006. Bioassay for nisin in milk, processed cheese, salad dressings, canned tomatoes, and liquid egg products. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 72(2):1001–1005. [doi:10.1128/AEM.72.2.1001-1005.2006]
Howell, T.H., Fiorellini, J.P., Blackburn, P., Projan, S.J., de la Harpe, J., Williams, R.C., 1993. The effect of a mouthrinse based on nisin, a bacteriocin, on developing plaque and gingivitis in beagle dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol., 20(5):335–339. [doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.1993.tb00369.x]
Hu, S.H., 2005. Stability of Drugs. In: Hu, Y.L. (Ed.), Research and Development of Feed Additives from Chinese Materia Medica. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, China, p.72–76 (in Chinese).
Immonen, N., Karp, M., 2007. Bioluminescence-based bioassays for rapid detection of nisin in food. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 22(9–10):1982–1987. [doi:10.1016/j.bios.2006.08.029]
Laridi, R., Kheadr, E.E., Benech, R.O., Vuillemard, J.C., Lacroix, C., Fliss, I., 2003. Liposome encapsulated nisin Z: optimization, stability and release during milk fermentation. Int. Dairy J., 13(4):325–336. [doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(02)00194-2]
Mosmann, T., 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods, 65(1–2):55–63. [doi:10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4]
Parente, E., Brienza, C., Moles, M., Ricciardi, A., 1995. A comparison of methods for the measurement of bacteriocin activity. J. Microbiol. Methods, 22(1):95–108. [doi:10.1016/0167-7012(94)00068-I]
Pongtharangkul, T., Demirci, A., 2004. Evaluation of agar diffusion bioassay for nisin quantification. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 65(3):268–272. [doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1579-5]
Reddy, K.V.R., Yedery, R.D., Aranha, C., 2004. Antimicrobial peptides: premises and promises. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, 24(6):536–547. [doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.09.005]
Reunanen, J., Saris, P.E.J., 2003. Microplate bioassay for nisin in foods, based on nisin-induced green fluorescent protein fluorescence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69(7):4214–4218. [doi:10.1128/AEM.69.7.4214-4218.2003]
Rose, N.L., Sporns, P., McMullen, L.M., 1999. Detection of bacteriocins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/lonization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65(5):2238–2242.
Rossano, R., Del Fiore, A., D’Elia, A., Pesole, G., Parente, E., Riccio, P., 1998. New procedure for the determination of nisin in milk. Biotechnol. Tech., 12(10):783–786. [doi:10.1023/A:1008820803070]
Saravanan, B.C., Sreekumar, C., Bansal, G.C., Ray, D., Rao, J.R., Mishra, A.K., 2003. A rapid MTT colorimetric assay to assess the proliferative index of two Indian strains of Theileria annulata. Vet. Parasitol., 113(3–4):211–216. [doi:10.1016/S0304-4017(03)00062-1]
Skyttä, E., Mattila-Sandholm, T., 1991. A quantitative method for assessing bacteriocins and other food antimicrobials by automated turbidometry. J. Microbiol. Methods, 14(2):77–88. [doi:10.1016/0167-7012(91)90036-P]
Suárez, A.M., Rodriguez, J.M., Hernández, P.E., Azcona-Olivera, J.I., 1996a. Generation of polyclonal antibodies against nisin: immunization strategies and immunoassay development. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 62(6):2117–2121.
Suárez, A.M., Rodriguez, J.M., Morales, P., Hernández, P.E., Azcona-Olivera, J.I., 1996b. Development of monoclonal antibodies to the lantibiotic nisin A. J. Agric. Food Chem., 44(9):2936–2940. [doi:10.1021/jf9602232]
Tramer, J., Fowler, G.G., 1964. Estimation of nisin in food. J. Sci. Food Agric., 15(8):522–528. [doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740150802]
Turcotte, C., Lacroix, C., Kheadr, E., Grignon, L., Fliss, I., 2004. A rapid turbidometric microplate bioassay for accurate quantification of lactic acid bacteria bacteriocins. Int. J. Food Microbiol., 90(3):283–293. [doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00315-5]
Valat, C., Champiat, D., N’Guyen, T.T., Loiseau, G., Raimbault, M., Montet, D., 2003. Use of ATP bioluminescence to determine the bacterial sensitivity threshold to a bacteriocin. Luminescence, 18(5):254–258. [doi:10.1002/bio.735]
Wahlström, G., Saris, P.E.J., 1999. A nisin bioassay based on bioluminescence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65(8):3742–3745.
Wolf, C.E., Gibbons, W.R., 1996. Improved method for quantification of the bacteriocin nisin. J. Appl. Bacteriol., 80(4):453–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (Nos. 2005C22035 and 2005C12015) supported by the Department of Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Cao, Lt. & Hu, Sh. A rapid and accurate 3-(4,5-dimethyl thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide colorimetric assay for quantification of bacteriocins with nisin as an example. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. B 8, 549–554 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0549
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0549