Abstract
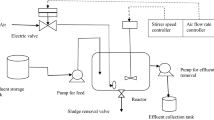
Aerobically activated sludge processing was carried out to treat terylene artificial silk printing and dyeing wastewater (TPD wastewater) in a lab-scale experiment, focusing on the kinetics of the COD removal. The kinetics parameters determied from experiment were applied to evaluate the biological treatability of wastewater. Experiments showed that COD removal could be divided into two stages, in which the ratio BOD/COD (B/C) was the key factor for stage division. At the rapid-removal stage with B/C>0.1, COD removal could be described by a zero order reaction. At the moderate-removal stage with B/C<0.1, COD removal could be described by a first order reaction. Then Monod equation was introduced to indicate COD removal. The reaction rate constant (K) and half saturation constant (K S) were 0.0208–0.0642 L/(gMLSS) h and 0.44–0.59 (gCOD)/L respectively at 20°C–35°C. Activation energy (E a) was 6.05×104 J/mol. By comparison of kinetic parameters, the biological treatability of TPD wastewater was superior to that of traditional textile wastewater, such as papermaking, beer, phenol wastewater, etc. The expected effluent quality strongly related to un-biodegradable COD and kinetics rather than total COD. The results provide useful basis for further scaling up and efficient operation of TPD wastewater treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babuna, F.G., Soyhan, B., Eremektar, G., Orhon, D., 1999. Evaluation of treatability for two textile mill effluents.Water Science and Technology,40(1):145–152.
Cai, Z.C., Zhou, F.F., 1989. Waste treatment in polyester fiber plant by biological contact oxidation process.Synthetic Fiber,18(6):29–32 (in Chinese).
Cheng, S.S., Ho, C.Y., Wu, J.H., 1997. Pilot study of UASB process treating PTA manufacturing wastewater.Water Science and Technology,36(6–7):75–82.
Editorial Board of Environment Protection Bureau of China. 1997. Monitoring and Determination Methods for Water and Wastewater. 3rd ed., China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Guan, B.H., Xu, G.L., Tan, T.E., 2002. Control and effects of pH of printing and dyeing wastewater on activated sludge.Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities,16(3):316–320 (in Chinese).
Guan, B.H., Wu, Z.B., Wu, Z.C., Xu, G.L., Tan, T.E., 2003. Biodegradability of terephthalic acid in terylene artificial silk printing and dyeing wastewater.Journal of Environmental Sciences,15(3):296–301.
Han, H.J., 1986. Study on the biodegradation of terylene dyeing wastewater.Technology of Water Treatment,12(5):289–292 (in Chinese).
Leslie, G., C.P., Henry, C.L., 1989. Biological Wastewater Treatment: Theory and Application. Translated by Li, X.W., Yang, X.K., Zhang, Y.G. China Architecture and Building Press, Beijing, p.216 (in Chinese).
Ma, H.Y., Xie, K.R., Huang, T.Y., Wen, X.Z., 1999. Research on treatment technology of terylene artificial silk printing dyeing wastewater and its application.Environmental Engineering,17(2):22–24 (in Chinese).
Qing, Y.H., Mai, Y.J., Li, P.X., Shi, Z.Y., 1986. Wastewater Engineering Treatment, Disposal and Reuse. 2nd ed., Chemical Industrial Press, Beijing, p.94 (in Chinese).
Tong, H., Bai, Y.Q., 1990. Degradation of TA by microorganism.Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,10(4):464–470 (in Chinese).
Wan, D.B., Pen, J.G., Liu, J.T., Chen, Y.X., Ma, N., 1990. Kinetics of Microbiological Degradation for Terephthalic Acid—A Study on Batch Culture.In: Xu, X.B., Jing, Z.L., Xu, H.X., ed., Environmental Behavior and Ecological Toxicology of Noxious Organic Compounds. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing, p.164–171 (in Chinese).
Wang, G.Q., Jin, Y.X., Shen, Y.S., 1998. Alkali minimization and dyeing wastewater treatment in production of artificial silk fabrics.Environmental Protection,244 (2):21–23, (in Chinese).
Yu, Q.H., Quan, H., 1988. Decontamination of Water Environment and Microbiology of Wastewater Treatment. China Architecture and Building Press, Beijing, p.104 (in Chinese).
Zhao, H.B., 1994. Pilot study on terephthalic acid (PTA) wastewater treatment using an A/O bio-film process.Chinese Journal of Environmental Science,15(6):47–50, 60 (in Chinese).
Zhou, H.F., Zhan, B.J., 1999. Application of anaerobic reduction wastewater in dye house.Environmental Engineering,17(6):18–20 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, Bh., Wu, Zb. & Xu, Gl. Kinetics of aerobically activated sludge on terylene artificial silk printing and dyeing wastewater treatment. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. 5, 441–449 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.0441
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.0441
Key words
- Process kinetics
- Aerobically activated sludge
- COD (chemical oxygen demand)
- Biological treatability
- Printing and dyeing wastewater