Abstract
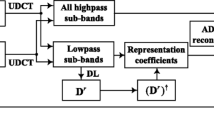
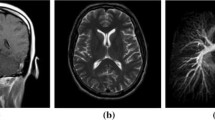
Recently, dictionary learning (DL) based methods have been introduced to compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging (CS-MRI), which outperforms pre-defined analytic sparse priors. However, single-scale trained dictionary directly from image patches is incapable of representing image features from multi-scale, multi-directional perspective, which influences the reconstruction performance. In this paper, incorporating the superior multi-scale properties of uniform discrete curvelet transform (UDCT) with the data matching adaptability of trained dictionaries, we propose a flexible sparsity framework to allow sparser representation and prominent hierarchical essential features capture for magnetic resonance (MR) images. Multi-scale decomposition is implemented by using UDCT due to its prominent properties of lower redundancy ratio, hierarchical data structure, and ease of implementation. Each sub-dictionary of different sub-bands is trained independently to form the multi-scale dictionaries. Corresponding to this brand-new sparsity model, we modify the constraint splitting augmented Lagrangian shrinkage algorithm (C-SALSA) as patch-based C-SALSA (PB C-SALSA) to solve the constraint optimization problem of regularized image reconstruction. Experimental results demonstrate that the trained sub-dictionaries at different scales, enforcing sparsity at multiple scales, can then be efficiently used for MRI reconstruction to obtain satisfactory results with further reduced undersampling rate. Multi-scale UDCT dictionaries potentially outperform both single-scale trained dictionaries and multi-scale analytic transforms. Our proposed sparsity model achieves sparser representation for reconstructed data, which results in fast convergence of reconstruction exploiting PB C-SALSA. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms conventional CS-MRI methods in maintaining intrinsic properties, eliminating aliasing, reducing unexpected artifacts, and removing noise. It can achieve comparable performance of reconstruction with the state-of-the-art methods even under substantially high undersampling factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonso, M.V., Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Figueiredo, M.A.T., 2011. An augmented Lagrangian approach to the constrained optimization formulation of imaging inverse problems. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 20(3):681–695. [doi:10. 1109/TIP.2010.2076294]
Aharon, M., Elad, M., Bruckstein, A., 2006. K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 54(11): 4311–4322. [doi:10.1109/TSP.2006.881199]
Baraniuk, R., 2007. Compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag., 24(4):118–121. [doi:10.1109/MSP.2007.4286571]
Candes, E.J., Donoho, D.L., 2004. New tight frames of curvelets and optimal representations of objects with piecewise C2 singularities. Commun. Pure Appl. Math., 57(2):219–266. [doi:10.1002/cpa.10116]
Candes, E.J., Romberg, J., Tao, T., 2006a. Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 52(2):489–509. [doi:10.1109/TIT.2005.862083]
Candes, E.J., Romberg, J.K., Tao, T., 2006b. Stable signal rcovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun. Pure Appl. Math., 59(8):1207–1223. [doi:10. 1002/cpa.20124]
Chambolle, A., 2004. An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications. J. Math. Imag. Vis., 20(1-2): 89–97. [doi:10.1023/B:JMIV.0000011325.36760.1e]
Chen, C., Huang, J., 2014. The benefit of tree sparsity in accelerated MRI. Med. Image Anal., 18(6):834–842. [doi:10. 1016/j.media.2013.12.004]
Combettes, P.L., Wajs, V.R., 2005. Signal recovery by proximal forward-backward splitting. Multiscale Model. Simul., 4(4):1168–1200. [doi:10.1137/050626090]
Dahl, J., Hansen, P.C., Jensen, S.H., et al., 2010. Algorithms and software for total variation image reconstruction via first-order methods. Numer. Algor., 53(1):67–92. [doi:10. 1007/s11075-009-9310-3]
Donoho, D.L., 2001. Sparse components of images and optimal atomic decompositions. Constr. Approx., 17(3): 353–382. [doi:10.1007/s003650010032]
Donoho, D.L., 2006. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 52(4):1289–1306. [doi:10.1109/TIT.2006.871582]
Eckstein, J., Bertsekas, D.P., 1992. On the Douglas-Rachford splitting method and the proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators. Math. Program., 55(1): 293–318. [doi:10.1007/BF01581204]
Elad, M., 2010. Sparse and Redundant Representations: from Theory to Applications in Signal and Image Processing. Springer, New York, USA. [doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-7011-4]
Elad, M., Aharon, M., 2006. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 15(12):3736–3745. [doi:10.1109/TIP.2006.881969]
Gabay, D., Mercier, B., 1976. A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite element approximation. Comput. Math. Appl., 2(1):17–40. [doi:10. 1016/0898-1221(76)90003-1]
Gho, S.M., Nam, Y., Zho, S.Y., et al., 2010. Three dimension double inversion recovery gray matter imaging using compressed sensing. Magn. Reson. Imag., 28(10): 1395–1402. [doi:10.1016/j.mri.2010.06.029]
Huang, J., Zhang, S., Metaxas, D., 2011. Efficient MR image reconstruction for compressed MR imaging. Med. Image Anal., 15(5):670–679. [doi:10.1016/j.media.2011.06.001]
Kim, Y., Altbach, M.I., Trouard, T.P., et al., 2009. Compressed sensing using dual-tree complex wavelet transform. Proc. Int. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med., 17:2814.
Kim, Y., Nadar, M.S., Bilgin, A., 2012. Wavelet-based compressed sensing using a Gaussian scale mixture model. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 21(6):3102–3108. [doi:10. 1109/TIP.2012.2188807]
Lewicki, M.S., Sejnowski, T.J., 2000. Learning overcomplete representations. Neur. Comput., 12(2):337–365. [doi:10. 1162/089976600300015826]
Lin, L., 1989. A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics, 45(1):255–268. [doi:10. 2307/2532051]
Liu, Y., Cai, J., Zhan, Z., et al., 2015. Balanced sparse model for tight frames in compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS ONE, 10(4):e0119584.1–e0119584.19. [doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119584]
Lustig, M., Donoho, D., Pauly, J.M., 2007. Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med., 58(6):1182–1195. [doi:10.1002/mrm.21391]
Lustig, M., Donoho, D.L., Santos, J.M., et al., 2008. Compressed sensing MRI. IEEE Signal Process. Mag., 25(2):72–82. [doi:10.1109/MSP.2007.914728]
Mallat, S., 2008. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing: the Sparse Way (3rd Ed.). Academic Press, USA.
Nguyen, T.T., Chauris, H., 2010. Uniform discrete curvelet transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 58(7):3618–3634. [doi:10.1109/TSP.2010.2047666]
Ning, B., Qu, X., Guo, D., et al., 2013. Magnetic resonance image reconstruction using trained geometric directions in 2D redundant wavelets domain and non-convex optimization. Magn. Reson. Imag., 31(9):1611–1622. [doi:10.1016/j.mri.2013.07.010]
Ophir, B., Lustig, M., Elad, M., 2011. Multi-scale dictionary learning using wavelets. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process., 5(5):1014–1024. [doi:10.1109/JSTSP.2011.2155032]
Qu, G., Zhang, D., Yan, P., 2002. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett., 38(7): 313–315. [doi:10.1049/el:20020212]
Qu, X., Zhang, W., Guo, D., et al., 2010. Iterative thresholding compressed sensing MRI based on contourlet transform. Inv. Probl. Sci. Eng., 18(6):737–758. [doi:10.1080/17415977.2010.492509]
Qu, X., Guo, D., Ning, B., et al., 2012. Undersampled MRI reconstruction with patch-based directional wavelets. Magn. Reson. Imag., 30(7):964–977. [doi:10.1016/j.mri. 2012.02.019]
Qu, X., Hou, Y., Lam, F., et al., 2014. Magnetic resonance image reconstruction from undersampled measurements using a patch-based nonlocal operator. Med. Image Anal., 18(6):843–856. [doi:10.1016/j.media.2013.09.007]
Rauhut, H., Schnass, K., Vandergheynst, P., 2008. Compressed sensing and redundant dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 54(5):2210–2219. [doi:10.1109/TIT.2008. 920190]
Ravishankar, S., Bresler, Y., 2011. MR image reconstruction from highly undersampled k-space data by dictionary learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., 30(5):1028–1041. [doi:10.1109/TMI.2010.2090538]
Rubinstein, R., Zibulevsky, M., Elad, M., 2010. Double sparsity: learning sparse dictionaries for sparse signal approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process., 58(3): 1553–1564. [doi:10.1109/TSP.2009.2036477]
Rudin, L.I., Osher, S., Fatemi, E., 1992. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D, 60(1-4): 259–268. [doi:10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F]
Trzasko, J., Manduca, A., 2009. Highly undersampled magnetic resonance image reconstruction via homotopic l 0-minimization. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., 28(1):106–121. [doi:10.1109/TMI.2008.927346]
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., et al., 2004. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 13(4):600–612. [doi:10.1109/TIP.2003.819861]
Xydeas, C.S., Petrovic, V., 2000. Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron. Lett., 36(4):308–309. [doi:10.1049/el:20000267]
Zhu, Z., Wahid, K., Babyn, P., et al., 2013. Compressed sensing-based MRI reconstruction using complex doubledensity dual-tree DWT. Int. J. Biomed. Imag., 2013. 907501.1–907501.12. [doi:10.1155/2013/907501]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61175012 and 61201422), the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China (No. 1208RJ-ZA265), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 2011021111-0026), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Nos. lzujbky-2015-108 and lzujbky-2015-197)
ORCID: Min YUAN, http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7855-8678
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, M., Yang, Bx., Ma, Yd. et al. Multi-scale UDCT dictionary learning based highly undersampled MR image reconstruction using patch-based constraint splitting augmented Lagrangian shrinkage algorithm. Frontiers Inf Technol Electronic Eng 16, 1069–1087 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400423
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1400423
Keywords
- Compressed sensing (CS)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Uniform discrete curvelet transform (UDCT)
- Multi-scale dictionary learning (MSDL)
- Patch-based constraint splitting augmented Lagrangian shrinkage algorithm (PB C-SALSA)