Abstract
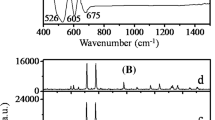
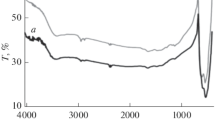
In this paper, we study the synthesis dependence of structural, optical and antimicrobial properties for copper oxide nanoparticles on, synthesized using microwave irradiation CuO(M), co-precipitation CuO(P) and hydrothermal CuO(H) protocols. Structural and morphological properties were studied using XRD, SEM, TEM and SAED techniques. XPS studies confirmed the presence of copper ions in Cu2+ oxidation state, and Raman spectroscopy confirmed the presence of nanostructured phase in all the samples. The synthesized CuO(M), CuO(P) and CuO(H) nanoparticles were investigated for antimicrobial activity against different pathogenic bacteria including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. The result showed that maximum inhibition zone was detected in CuO(M) nanoparticles against Gram-negative bacteria i.e. Klebsiella pneumoniae (20 mm). CuO(H) and CuO(P) nanoparticles have antibacterial inhibition zone of 17 mm and 13 mm against K. pneumoniae and S. aureus, respectively. The CuO(P) and CuO(H) nanoparticles displayed mild antimicrobial activity as compared to the CuO(M) nanoparticles.
Graphic abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and in supplementary file.
References
Y. Liu, Q. Huang, G. Jiang, D. Liu, W. Yu, Cu 2 O nanoparticles supported on carbon nanofibers as a cost-effective and efficient catalyst for RhB and phenol degradation. J. Mater. Res. 32, 3605–3615 (2017)
K. Vishveshvar, M.A. Krishnan, K. Haribabu, S. Vishnuprasad, Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using ixiro coccinea plant leaves and its characterization. BioNanoScience 8, 554–558 (2018)
M. Khan, M.R. Shaik, S.F. Adil, M. Kuniyil, M. Ashraf, H. Frerichs et al., Facile synthesis of Pd@ graphene nanocomposites with enhanced catalytic activity towards Suzuki coupling reaction. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–14 (2020)
K. Gherab, Y. Al-Douri, U. Hashim, M. Ameri, A. Bouhemadou, K.M. Batoo et al., Fabrication and characterizations of Al nanoparticles doped ZnO nanostructures-based integrated electrochemical biosensor. J. Market. Res. 9, 857–867 (2020)
S.M. Boddapati, J.M.R. Saketi, B.R. Mutchu, H.B. Bollikolla, S.F. Adil, M. Khan, Copper promoted desulfurization and CN cross coupling reactions: Simple approach to the synthesis of substituted 2-aminobenzoxazoles and 2, 5-disubstituted tetrazole amines. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 4477–4494 (2020)
S.F. Adil, M.E. Assal, M.R. Shaik, M. Kuniyil, N.M. AlOtaibi, M. Khan et al., A facile synthesis of ZrOx-MnCO3/graphene oxide (GRO) nanocomposites for the oxidation of alcohols using molecular oxygen under base free conditions. Catalysts 9, 759 (2019)
S. Kumar, R. Rani, N. Dilbaghi, K. Tankeshwar, K.-H. Kim, Carbon nanotubes: a novel material for multifaceted applications in human healthcare. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 158–196 (2017)
S. Kumar, W. Ahlawat, G. Bhanjana, S. Heydarifard, M.M. Nazhad, N. Dilbaghi, Nanotechnology-based water treatment strategies. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14, 1838–1858 (2014)
N.D. Mu’azu, N. Jarrah, M. Zubair, M.S. Manzar, T.S. Kazeem, A. Qureshi et al., Mechanistic aspects of magnetic MgAlNi barium-ferrite nanocomposites enhanced adsorptive removal of an anionic dye from aqueous phase. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 24, 715–732 (2020)
S. Saif, A. Tahir, T. Asim, Y. Chen, S.F. Adil, Polymeric nanocomposites of iron-oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) synthesized using terminalia chebula leaf extract for enhanced adsorption of arsenic (V) from water. Colloids Interfaces 3, 17 (2019)
M. Signoretto, F. Menegazzo, A. Di Michele, E. Fioriniello, Effects of support and synthetic procedure for sol-immobilized Au nanoparticles. Catalysts 6, 87 (2016)
M.S. Bakshi, How surfactants control crystal growth of nanomaterials. Cryst. Growth Des. 16, 1104–1133 (2016)
Y. Li, C. Li, B. Wang, W. Li, P. Che, A comparative study on the thermoelectric properties of CoSb3 prepared by hydrothermal and solvothermal route. J. Alloy. Compd. 772, 770–774 (2019)
J.Y. Cheon, S.J. Kim, Y.H. Rhee, O.H. Kwon, W.H. Park, Shape-dependent antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 2773 (2019)
J.J. Lv, M.Y. Li, and Q.X. Zeng, Preparation and characterization of copper oxide and copper nanoparticles. in Advanced Materials Research, 2011, pp. 715–721
N. Dhineshbabu, V. Rajendran, N. Nithyavathy, R. Vetumperumal, Study of structural and optical properties of cupric oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 933–939 (2016)
J.K. Sharma, M.S. Akhtar, S. Ameen, P. Srivastava, G. Singh, Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles with leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea and its dye-sensitized solar cells applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 632, 321–325 (2015)
O. Waser, M. Hess, A. Grntner, P. Novßk, S.E. Pratsinis, Size controlled CuO nanoparticles for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 241, 415–422 (2013)
F. Wang, H. Li, Z. Yuan, Y. Sun, F. Chang, H. Deng et al., A highly sensitive gas sensor based on CuO nanoparticles synthetized via a sol–gel method. RSC Adv. 6, 79343–79349 (2016)
M. Shahmiri, N.A. Ibrahim, F. Shayesteh, N. Asim, N. Motallebi, Preparation of PVP-coated copper oxide nanosheets as antibacterial and antifungal agents. J. Mater. Res. 28, 3109 (2013)
P. Sutradhar, M. Saha, D. Maiti, Microwave synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using tea leaf and coffee powder extracts and its antibacterial activity. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 4, 86 (2014)
C. Boruban, E.N. Esenturk, Synthesis of CuO nanostructures on zeolite-Y and investigation of their CO2 adsorption properties. J. Mater. Res. 32, 3669 (2017)
G. Mustafa, H. Tahir, M. Sultan, N. Akhtar, Synthesis and characterization of cupric oxide (CuO) nanoparticles and their application for the removal of dyes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 12, 6650–6660 (2013)
R. Sankar, R. Maheswari, S. Karthik, K.S. Shivashangari, V. Ravikumar, Anticancer activity of Ficus religiosa engineered copper oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 44, 234–239 (2014)
A. Hussain, M.F. AlAjmi, M.T. Rehman, S. Amir, F.M. Husain, A. Alsalme et al., Copper (II) complexes as potential anticancer and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents: in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–17 (2019)
C.L. Carnes, K.J. Klabunde, The catalytic methanol synthesis over nanoparticle metal oxide catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A 194, 227–236 (2003)
L. Sun, Z. Zhang, Z. Wang, Z. Wu, H. Dang, Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanoparticles from liquid ammonia. Mater. Res. Bull. 40, 1024–1027 (2005)
P. Saravanan, S. Alam, G. Mathur, A liquid−liquid interface technique to form films of CuO nanowhiskers. Thin Solid Films 491, 168–172 (2005)
T. Ahmad, R. Chopra, K. Ramanujachary, S. Lofland, A. Ganguli, Canted antiferromagnetism in copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized by the reverse-micellar route. Solid State Sci. 7, 891–895 (2005)
V.V.T. Padil, M. Černík, Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using gum karaya as a biotemplate and their antibacterial application. Int. J. Nanomed. 8, 889 (2013)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley Publishing, Boston, 1956).
E.E. Kaya, S. Gürmen, A straightforward approach for the synthesis of nanostructured Y2O3 particles: synthesis, morphology, microstructure and crystal imperfection. Phys. E. 115, 113668 (2020)
V. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B. Dole, Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theoret. Appl. Phys. 6, 6 (2012)
G. Rajender, P. Giri, Strain induced phase formation, microstructural evolution and bandgap narrowing in strained TiO2 nanocrystals grown by ball milling. J. Alloy. Compd. 676, 591–600 (2016)
A. Chauhan, R. Verma, S. Kumari, A. Sharma, P. Shandilya, X. Li et al., Photocatalytic dye degradation and antimicrobial activities of pure and Ag-doped ZnO using Cannabis sativa leaf extract. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–16 (2020)
P. Bindu, S. Thomas, Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theoret. Appl. Phys. 8, 123–134 (2014)
Y. Asakuma, M. Miura, Effect of microwave radiation on diffusion behavior of anti-solvent during crystallization. J. Cryst. Growth 402, 32–36 (2014)
Y. Wang, Y. Lü, W. Zhan, Z. Xie, Q. Kuang, L. Zheng, Synthesis of porous Cu2O/CuO cages using Cu-based metal–organic frameworks as templates and their gas-sensing properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 12796–12803 (2015)
R. Mariammal, K. Ramachandran, B. Renganathan, D. Sastikumar, On the enhancement of ethanol sensing by CuO modified SnO2 nanoparticles using fiber-optic sensor. Sens. Actuators B 169, 199–207 (2012)
D.D.M. Prabaharan, K. Sadaiyandi, M. Mahendran, S. Sagadevan, Precipitation method and characterization of cobalt oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 123, 264 (2017)
H. Siddiqui, M. Qureshi, F.Z. Haque, Effect of copper precursor salts: facile and sustainable synthesis of controlled shaped copper oxide nanoparticles. Optik 127, 4726–4730 (2016)
M. Dar, Q. Ahsanulhaq, Y. Kim, J. Sohn, W. Kim, H. Shin, Versatile synthesis of rectangular shaped nanobat-like CuO nanostructures by hydrothermal method; structural properties and growth mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 6279–6284 (2009)
J.D. Rodney, S. Deepapriya, P.A. Vinosha, S. Krishnan, S.J. Priscilla, R. Daniel et al., Photo-Fenton degradation of nano-structured La doped CuO nanoparticles synthesized by combustion technique. Optik 161, 204–216 (2018)
H. Siddiqui, M.R. Parra, F.Z. Haque, Optimization of process parameters and its effect on structure and morphology of CuO nanoparticle synthesized via the sol−gel technique. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 87, 125–135 (2018)
A. Bhaumik, A.M. Shearin, R. Patel, K. Ghosh, Significant enhancement of optical absorption through nano-structuring of copper based oxide semiconductors: possible future materials for solar energy applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 11054–11066 (2014)
J. Irwin, T. Wei, Raman scattering investigation of Cu18O. J. Phys. 3, 299 (1991)
J. Xu, W. Ji, Z. Shen, W. Li, S. Tang, X. Ye et al., Raman spectra of CuO nanocrystals. J. Raman Spectrosc. 30, 413–415 (1999)
M. Rashad, M. Rüsing, G. Berth, K. Lischka, and A. Pawlis, CuO and Co3O4 nanoparticles: synthesis, characterizations, and Raman spectroscopy. J. Nanomater. 2013 (2013)
Z.N. Kayani, M. Umer, S. Riaz, S. Naseem, Characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles fabricated by the sol–gel method. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 3704–3709 (2015)
R. Jana, A. Dey, M. Das, J. Datta, P. Das, P.P. Ray, Improving performance of device made up of CuO nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal over the reflux method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 452, 155–164 (2018)
A. Bhattacharjee, M. Ahmaruzzaman, Microwave assisted facile and green route for synthesis of CuO nanoleaves and their efficacy as a catalyst for reduction and degradation of hazardous organic compounds. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 353, 215–228 (2018)
X. Wu, L. Ye, K. Liu, W. Wang, J. Wei, F. Chen et al., Antibacterial properties of mesoporous copper-doped silica xerogels. Biomed. Mater. 4, 045008 (2009)
K.R. Raghupathi, R.T. Koodali, A.C. Manna, Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 27, 4020–4028 (2011)
J.E. Weckx, H.M. Clijsters, Oxidative damage and defense mechanisms in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris as a result of root assimilation of toxic amounts of copper. Physiol. Plant. 96, 506–512 (1996)
R. Brayner, R. Ferrari-Iliou, N. Brivois, S. Djediat, M.F. Benedetti, F. Fiévet, Toxicological impact studies based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett. 6, 866–870 (2006)
Z. Huang, X. Zheng, D. Yan, G. Yin, X. Liao, Y. Kang et al., Toxicological effect of ZnO nanoparticles based on bacteria. Langmuir 24, 4140–4144 (2008)
A. Abdal Dayem, M.K. Hossain, S.B. Lee, K. Kim, S.K. Saha, G.-M. Yang et al., The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the biological activities of metallic nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 120 (2017)
M. Raffi, S. Mehrwan, T.M. Bhatti, J.I. Akhter, A. Hameed, W. Yawar et al., Investigations into the antibacterial behavior of copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Ann. Microbiol. 60, 75–80 (2010)
J.P. Ruparelia, A.K. Chatterjee, S.P. Duttagupta, S. Mukherji, Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 4, 707–716 (2008)
R. Verma, A. Chauhan, M. Shandilya, X. Li, R. Kumar, S. Kulshrestha, Antimicrobial potential of Ag-doped ZnO nanostructure synthesized by the green method using Moringa oleifera extract. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 103730 (2020)
Acknowledgments
Author K M Batoo is thankful to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for financial support through the project Code (RG-1437-030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest among them.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chauhan, A., Verma, R., Batoo, K.M. et al. Structural and optical properties of copper oxide nanoparticles: A study of variation in structure and antibiotic activity. Journal of Materials Research 36, 1496–1509 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00193-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00193-7