Abstract
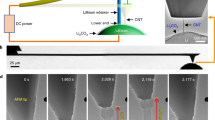
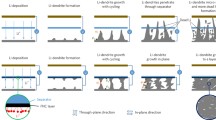
We have quantified lithium dendrite growth in an optically accessible symmetric Li-metal cell, charged under imposed temperatures on the electrode surface. We have found that the dendrite length measure is reduced up to 43% upon increasing anodic temperature of about 50°C. We have deduced that imposing higher temperature on the electrode surface will augment the reduction rate relative to dendritic peaks and therefore lithium holes can draw near with the sharp deposited tips. We have addressed this mechanism via fundamentals of electrochemical transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon J.-M. and M. Armand, Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature, 2001. 414(6861): p. 359–367.
Armand M. and J.M. Tarascon, Building better batteries. Nature, 2008. 451(7179): p. 652–657.
Williard N., {etet al.}, Lessons Learned from the 787 Dreamliner Issue on Lithium-Ion Battery Reliability. Energies, 2013. 6(9): p. 4682–4695.
Xu K., Nonaqueous liquid electrolytes for lithium-based rechargeable batteries. Chemical Reviews-Columbus, 2004. 104(10): p. 4303–4418.
Aryanfar A., {etet al.}, Dynamics of Lithium Dendrite Growth and Inhibition: Pulse Charging Experiments and Monte Carlo Calculations. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2014: p. 1721–1726.
Mayers M.Z., J.W. Kaminski, and T.F. Miller III, Suppression of Dendrite Formation via Pulse Charging in Rechargeable Lithium Metal Batteries. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012. 116(50): p. 26214–26221.
Orsini F., A.D.P., B. Beaudoin, J.M. Tarascon, M. Trentin, N. Langenhuisen, E.D. Beer, P. Notten, In Situ Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) observation of interfaces with plastic lithium batteries. Journal of power sources, 1998. 76: p. 19–29.
Monroe C. and J. Newman, Dendrite growth in lithium/polymer systems - A propagation model for liquid electrolytes under galvanostatic conditions. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003. 150(10): p. A1377–A1384.
Nishida T., {etet al.}, Optical observation of Li dendrite growth in ionic liquid. Electrochimica Acta, 2013.
Monroe C. and J. Newman, The effect of interfacial deformation on electrodeposition kinetics. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2004. 151(6): p. A880–A886.
Aurbach D., {etet al.}, A short review of failure mechanisms of lithium metal and lithiated graphite anodes in liquid electrolyte solutions. Solid State Ionics, 2002. 148(3): p. 405–416.
Liu X.H., {etet al.}, Lithium fiber growth on the anode in a nanowire lithium ion battery during charging. Applied Physics Letters, 2011. 98(18).
Crowther O. and A.C. West, Effect of electrolyte composition on lithium dendrite growth. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2008. 155(11): p. A806–A811.
Schweikert N., {etet al.}, Suppressed lithium dendrite growth in lithium batteries using ionic liquid electrolytes: Investigation by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and in situ Li-7 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Power Sources, 2013. 228: p. 237–243.
Howlett P.C., D.R. MacFarlane, and A.F. Hollenkamp, A sealed optical cell for the study of lithium-electrode electrolyte interfaces. Journal of Power Sources, 2003. 114(2): p. 277–284.
Rosso M., {etet al.}, Onset of dendritic growth in lithium/polymer cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2001. 97-8: p. 804–806.
Seong I.W., {etet al.}, The effects of current density and amount of discharge on dendrite formation in the lithium powder anode electrode. Journal of Power Sources, 2008. 178(2): p. 769–773.
Stone G., {etet al.}, Resolution of the Modulus versus Adhesion Dilemma in Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Rechargeable Lithium Metal Batteries. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2012. 159(3): p. A222–A227.
Brissot C., {etet al.}, In situ concentration cartography in the neighborhood of dendrites growing in lithium/polymer-electrolyte/lithium cells. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1999. 146(12): p. 4393–4400.
Brissot C., {etet al.}, Dendritic growth mechanisms in lithium/polymer cells. Journal of Power Sources, 1999. 81: p. 925–929.
Chazalviel J.N., Electrochemical Aspects of the Generation of Ramified Metallic Electrodeposits. Physical Review A, 1990. 42(12): p. 7355–7367.
Park H.E., C.H. Hong, and W.Y. Yoon, The effect of internal resistance on dendritic growth on lithium metal electrodes in the lithium secondary batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2008. 178(2): p. 765–768.
Diggle J., A. Despic, and J.M. Bockris, The mechanism of the dendritic electrocrystallization of zinc. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1969. 116(11): p. 1503–1514.
Brissot C., {etet al.}, Concentration measurements in lithium/polymer-electrolyte/lithium cells during cycling. Journal of Power Sources, 2001. 94(2): p. 212–218.
Bard A.J., and Larry R. Faulkner, Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications. 1980. 2 New York: Wiley, 1980.
Akolkar R., Modeling dendrite growth during lithium electrodeposition at sub-ambient temperature. Journal of Power Sources, 2014. 246: p. 84–89.
acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support from Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation Grant No. OPP1069500 on environmental sustainability and energy conservation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aryanfar, A., Colussi, A.J. & Hoffmann, M.R. Lithium Dendrite Growth Control Using Local Temperature Variation. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1680, 13–18 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2014.890
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2014.890