Abstract
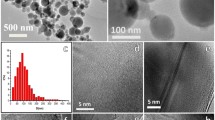
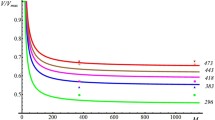
The advantage of aluminum powder as a fuel additive in energetic formulation includes its high volumetric combustion enthalpy and relatively low cost. However, the thermodynamically predicted benefits of aluminum combustion are rarely achieved because of extended ignition delays associated with heterogeneous reactions occurring at the alumina surface which surrounds the aluminum particle. In order to fully exploit aluminum’s high reaction energy, this effort focuses on adjusting its combustion dynamics by modifying its surface and structure. The modification is achieved by cryo-milling aluminum with cyclooctane, which is liquid at room temperature, but solid when cooled by liquid nitrogen. The prepared materials consist of micron-sized, equiaxial, mostly Al particles with a small amount of cyclooctane. Aluminum surface in the prepared sample is coated with a cyclooctane-modified layer with properties significantly different from those of regular alumina. Its oxidation kinetics, as observed from thermo-analytical measurements, is different from that of pure aluminum. The powder ignites at substantially reduced temperatures, produces shorter ignition delays, and higher aerosol burn rates compared to a regular spherical Al powder with similar particle sizes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yetter, R.A., Risha, G.A., and Son, S.F., Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 32 II, pp. 1819–1838 (2009)
Jouet, R. J., et al., Chemistry of Materials, 17, pp.2987–2996 (2005)
Lewis, W. K., et al., The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 114, pp. 6377–6380 (2010)
Dreizin, E.L., Progress in Energy and Combustion Science. 35, pp. 141–167 (2009)
Zhang, S., Schoenitz, M., and Dreizin, E.L., International Journal of Energetic Materials and Chemical Propulsion, in press (2012)
Zhang S., Schoenitz, M., and Dreizin, E.L., Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 71, pp. 1213–1220 (2010)
Zhang, S., Schoenitz, M., and Dreizin, E.L., Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (46), pp. 19653–19659 (2010)
Zhang, S., et al.,Combustion and Flame, 159 (5), pp. 1980–1986 (2012)
Stamatis, D., et al., Combustion Science and Technology, 181(1), pp. 97–116. (2009)
Gill, R.J., Badiola, C., and Dreizin, E.L., Combustion and Flame, 157 (11), pp. 2015–2023 (2010)
Badiola, C., Gill R.J., and Dreizin, E.L., Combustion and Flame, 158, pp. 2064–2070 (2011)
Trunov, M.A., et al., Combustion and Flame, 140(4), pp. 310–318 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Schoenitz, M. & Dreizin, E.L. Nano-structured Aluminum Powders with Modified Protective Surface Layers. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1521, 505 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2013.130
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2013.130