Abstract
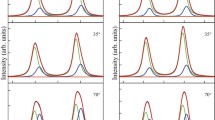
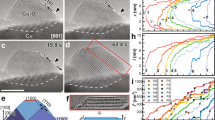
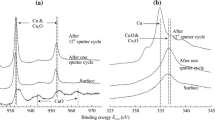
A wide information gap exists between our present atomic-scale knowledge of metal oxidation derived from conventional ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) surface science experiments and the oxidation mechanisms obtained from the growth of bulk oxide thin films under technologically relevant realistic (or near-) atmospheric conditions. To bridge this pressure gap, we present an in-situ transmission electron microscopy (TEM) study of the initial oxidation stage of Cu(100) and Cu-Au(100) surfaces where the oxygen partial pressure varies from 5x10-4 to 150 Torr. For Cu(100), with increasing oxygen partial pressure (pO2), the nucleation density of the oxide islands increases and so does the growth rate of the oxide islands. As the pO2 continues to increase, a transition from epitaxial cube-on-cube Cu2O islands to randomly oriented oxide islands is observed. A kinetic model based on the classic heterogeneous nucleation theory is developed to explain the effect of oxygen partial pressure on the oxide orientation. It is shown that such a transition in the oxide nucleation orientation is related to the effect of oxygen pressure on the nucleation barrier and atom collision rate. The Cu-Au(111) alloy revealed the same oxygen pressure dependency of the oxide nucleation orientation as pure Cu oxidation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Lundgren, J. Gustafson, A. Mikkelsen, J. N. Andersen, A. Stierle, H. Dosch, M. Todorova, J. Rogal, K. Reuter, and M. Scheffler, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 046101 (2004).
J. A. Eastman, P. H. Fuss, L. E. Rehn, P. M. Baldo, G. W. Zhou, D. D. Fong, and L. J. Thompson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 051914 (2005).
K. Lahtonen, M. Hirsimaki, M. Lampimaki, and M. Valden, The Journal of Chemical Physics 129, 124703 (2008).
I. Lyubinetsky, S. Thevuthasan, D. E. McCready, and D. R. Baer, Journal of Applied Physics 94, 7926 (2003).
G. W. Zhou, Phys. Rev. B 81, 195440 (2010).
G. W. Zhou, J. C. Yang, Physical Review Letters 89, 106101 (2002).
G. W. Zhou, J. C. Yang, Applied Surface Science 210/3–4, 165 (2003).
G. W. Zhou, J. C. Yang, Surface Science 531/3, 359 (2003).
G. W. Zhou, J. C. Yang, Applied Surface Science 222, 357–364 (2004).
G. W. Zhou, J. C. Yang, Surface Science 559/2–3, 100–110 (2004).
Langli Luo, Yihong Kang, Zhenyu Liu, Judith C Yang, and Guangwen Zhou, Phys. Rev. B, Accepted on March 2nd, 2011
D. R. Gaskell, “Introduction to Metallurgical Thermodynamics” (Scripta, Washington, D.C., 1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, L., Kang, Y., Liu, Z. et al. Effect of Oxygen Pressure on the Initial Oxidation Behavior of Cu and Cu-Au Alloys. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1318, 706 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.920
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.920