Abstract
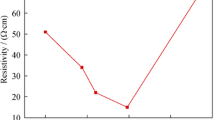
Aluminum-doped zinc oxide films were prepared by atomic layer deposition using diethylzinc, trimethylaluminum, and water. High-purity water was used with low vacuum. The effect of growth temperature on characteristics of the films was investigated. The crystallinity was improved as growth temperature was increased from 180 to 235 °C, with the grain sizes increasing from 32.830 to 47.020 nm. The films possessed high transparency with a 95% transmission window blue shifted with growth temperature. This shift was seen in the energyband gaps which changed from 3.46 to 3.68 eV, leading to a decreased resistivity from 1.52 × 10−5 to 1.28 × 10−5 Ω cm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Jang, J. Kim, U. Ghorpade, H. Shin, M. Gang, S. Park, H. Kim, D. Lee, and J. Kim: Comparison study of ZnO-based quaternary TCO materials for photovoltaic application. J.Alloys Compd 793, 499–504 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.042.
Z. Chen, Y. Liu, W. Zhang, X. Guo, L. Yin, Y. Wang, L. Li, Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, and T. Zhang: Growth of graphene/Ag nanowire/graphene sandwich films for transparent touch-sensitive electrodes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 221, 78 (2019).
D. Ko, B. Gu, J. Cheon, J. Roh, C. Kim, S. Jod, D. Hyun, and J. Kim: Decoupling the contributions to the enhancement of electrical conductivity in transparent silver nanowire/zinc oxide composite electrodes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 223, 634 (2019).
D. Olson, C. Rost, J. Gaskins, C. Szwejkowski, J. Braun, and P. Hopkins: Size effects on the cross-plane thermal conductivity of transparent conducting indium tin oxide and fluorine tin oxide thin films. IEEE Trans. Comp. Pack. Manuf.Technol. 9(1), 51 (2019).
M. Jin, J. Choi, D. Kim, J. Park, C. An, H. Kim, B. Kim, Y. Diao, and H. Jung: Enhanced thermal stability of organic solar cells on nano structured electrode by simple acid etching. Org. Electron. 15, 680 (2014).
D. Solís-Cortés, E. Navarrete-Astorga, J.L. Costa-Krämer, J. Salguero- Fernandez, R. Schrebler, D. Leinen, E.A. Dalchiele, J.R. Ramos-Barrado, and F. Martín: Ga-doped IZO films obtained by magnetron sputtering as transparent conductors for visible and solar applications. Ceram. Int. 45, 5577 (2019).
J. Carlé, M. Helgesen, M. Madsen, E. Bundgaard, and F. Krebs: Upscaling from single cells to modules–fabrication of vacuum- and ITO-free polymer solar cells on flexible substrates with long lifetime. J.Mater. Chem.. 2, 1290 (2014).
F. Khan, S. Baek, A. Mobin, and J. Kim: Enhanced performance of silicon solar cells by application of low-cost sol–gel-derived Al-rich ZnO film. Sol. Energ. 101, 265 (2014).
H. Kumarakurua, D. Cherns, and A. Collins: The growth and conductivity of nanostructured ZnO films grown on Al-doped ZnO precursor layers by pulsed laser deposition. Ceram. Int. 40, 8389 (2014).
K. Kumar, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, and S. Valanarasu: Effect of different solvents on the key structural, optical and electronic properties of sol–gel dip coated AZO nanostructured thin films for optoelectronic applications. J.Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 887 (2018).
A. Jilani, M.S. Abdel-wahab, A.A. Al-ghamdi, A. Dahlan, and I.S. Yahia: Nonlinear optical parameters of nanocrystalline AZO thin film measured at different substrate temperatures. Physica. 481, 97 (2016).
Y. Choi, S. Gong, D. Johnson, S. Golledge, G. Yeom, and H. Park: Characteristics of the electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of Al-doped ZnO thin films deposited by atomic layer deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 269, 92 (2013).
S. George: Atomic layer deposition: an overview. Chem. Rev. 110, 111 (2010).
J.F. Chang and M.H. Hon: The effect of deposition temperature on the properties of Al-doped zinc oxide thin films. Thin Solid Film. 386, 79 (2001).
C. Ahn, S. Lee, and H. Cho: Influence of growth temperature on the electrical and structural characteristics of conductive Al-doped ZnO thin films grown by atomic layer deposition. Thin Solid Film. 545, 106 (2013).
R. Prabua, S. Valanarasua, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, A. Kathalingam, S. Srikumare, and R. Chandramohan: An effect of temperature on structural, optical, photoluminescence and electrical properties of copper oxide thin films deposited by nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 74, 129 (2018).
C. Barret and T.B. Massalki: Structure of Metals: Crystallographic Methods, Principles and Data (Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1980), p. 204.
N. Dasgupta, S. Neubert, W. Lee, O. Trejo, J. Lee, and F. Prinz: Atomic layer deposition of Al-doped ZnO films: effect of grain orientation on conductivity. Chem. Mater. 22, 4769 (2010).
B.E. Warren: X-Ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., London, 1969). p. 18.
A. Barhoumi, G. Leroy, B. Duponchel, J. Gest, L. Yang, N. Waldhoff, and S. Guermazi: Aluminum doped ZnO thin films deposited by direct current sputtering: structural and optical properties. Superlattice. Microstruct. 82, 483 (2015).
M. Steglich, A. Bingel, G. Jia, and F. Falk: Atomic layer deposited ZnO:Al for nanostructured silicon heterojunction solar cells. Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. Cell. 103, 62 (2012).
B. Szyszka: Transparent and conductive aluminum doped zinc oxide films prepared by mid-frequency reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 351, 164 (1999).
V. Balaprakash, P. Gowrisankar, S. Sudha, and R. Rajkumar: Aluminum doped ZnO transparent conducting thin films prepared by sol-gel dip coating technique for solar cells and optoelectronic applications. Mater. Technol. 33, 414 (2018).
T. Gu, E. Hu, S. Guo, Y. Wu, J. Wang, Z. Wang, K. Yua, W. Wei, Y. Zheng, S. Wang, and L. Chen: Ellipsometric study on optical properties of hydrogen plasma-treated aluminum-doped ZnO thin film. Vacuu. 163, 69 (2019).
L. Wen, B. Sahu, H. Kim, and J. Han: Study on the electrical, optical, structural, and morphological properties of highly transparent and conductive AZO thin films prepared near room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 473, 649 (2019).
H. Agura, A. Suzuki, T. Matsushita, T. Aoki, and M. Okuda: Low resistivity transparent conducting Al-doped ZnO films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Film. 445, 263 (2003).
H. Kim, M. Osofsky, S.M. Prokes, O.J. Glembocki, and A. Pique: Optimization of Al-doped ZnO films for low loss plasmonic materials at telecommunication wavelengths. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 171103 (2013).
N.A. Vorobyeva, M.N. Rumyantseva, R.B. Vasiliev, V.F. Kozlovskiy, Y.M. Soshnikova, D.G. Filatova, V.B. Zaytsev, A.V. Zaytseva, and A.M. Gaskov: Doping effects on electrical and optical properties of spin-coated ZnO thin films. Vacuu. 114, 198 (2015).
G. Frank and H. Kostlin: Electrical-properties and defect model of tindoped indium oxide layers. Appl. Phys. Mater. Sci. Process. 27(4), 197 (1982).
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, and A. Vancu: Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi. 15, 627 (1966).
Y. Kim and W. Tai: Electrical and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 4911 (2007).
Y. Xia, P. Wang, S. Shi, M. Zhang, G. Hea, J. Lv, and Z. Suna: Deposition and characterization of AZO thin films on flexible glass substrates using DC magnetron sputtering technique. Ceram. Int. 43(5), 4536 (2017).
N. Benramdane, W.A. Murad, R.H. Misho, M. Ziane, and Z. Kebbab: A chemical method for the preparation of thin films of CdO and ZnO. Mater. Chem. Phys. 48, 119–23 (1997).
H. Zheng, R. Zhang, D. Li, X. Chen, S. Wang, Y. Zheng, M. Li, Z. Hu, N. Dai, and L. Chen: Optical properties of Al-doped ZnO films in the infrared region and their absorption applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13, 149 (2018).
S. Mihaiu, A. Toader, M. Anastasescu, M. Gabor, T. Petrisor, M. Stoica, and M. Zaharescu: Al-doped and undoped zinc oxide films obtained by soft chemistry. Process. Appl. Ceram. 3(1-2), 79 (2009).
J. Hodgson: Optical Absorption and Dispersion in Solids (Chapman and Hall Ltd, London, 1970), p. 9.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) under Grant No. 1059B191200565-ID 893022. Portions of this work were conducted in the Minnesota Nano Center, which is supported by the National Science Foundation through the National Nano Coordinated Infrastructure Network (NNCI) under Award No. ECCS-1542202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at {rs|https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.82|url|}.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güneri, E., Stadler, B. Effect of growth temperature on the key properties of aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films prepared by atomic layer deposition. MRS Communications 9, 1105–1110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.82
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.82