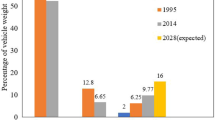
Abstract
Powder metallurgy processing of aluminum alloy based metal matrix composites (MMC) is realized to be a promising alternative as expected to advance rapidly compared to other conventional methods. This paper reviews the extensive development in metal-matrix composite research works with particular focus on aluminum alloys 2xxx series as metal-matrix particulates processed by powder metallurgy route. Effect of reinforcement materials such as SiC and Al2O3 on the mechanical properties of the composites manufactured through conventional methods and powder metallurgy route are compared and presented. The influence of percentage of reinforcement material on the overall properties of the MMC’s as reported by the researchers are presented. Summary on fundamental aspects of manufacturing MMC’s via powder metallurgy route, the effect of mechanical properties, tribological properties, and microstructural properties are presented. Eventually, some advantages of powder metallurgy method are mentioned which may substantiate the claim to consider this as a novel method for near net shape manufacturing.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.K. Lindroos and M.J. Talvitie: Recent advances in metal matrix composites. J Mater. Process. Technol. 53, 273–284 (1995).
J.M. Torralba, C.E. Costa, and F. Velasco: P/M aluminum matrix composites: An overview. J Mater. Process. Technol. 133, 203–206 (2003).
C. Srinivasa: 2014 and 6061 aluminium powder metallurgy composites containing silicon carbide particles/fibres. Mater. Des. 3069 (96), 359–366 (2014).
C. Persson, A. Weiland, L. Hultman, and U. Wahlstro: Internal stress and microstructure of SiC reinforced aluminium alloy 2014. Acta. Metalla. 46 (15), 5271–5281 (2014).
G.S. Marahleh: Strengthening of aluminum by SiC, Al2O3 and MgO. JJMIE 5 (6), 533–541 (2011).
R.S. Mishra, T.R. Bieler, and A.K. Mukherjee: Overview No. 119 — Superplasticity in Powder Metallury Aluminum Alloys and composites. Acta. Metalla. 43 (3), 877–891 (1995).
J. Corrochano, M. Lieblich, and J. Ibáñez: The effect of ball milling on the microstructure of powder metallurgy aluminium matrix composites reinforced with MoSi2 intermetallic particles. Composites, Part A 42 (9), 1093–1099 (2011).
B.S. Ünlü: Investigation of tribological and mechanical properties Al2O3–SiC reinforced Al composites manufactured by casting or P/M method. Mater. Des. 29 (10), 2002–2008 (2008).
N.E. Bekheet, R.M. Gadelrab, M.F. Salah, and A.N.A. El-azim: The effects of aging on the hardness and fatigue behavior of 2024 Al alloy/SiC composites. Mater. Des. 23, 153–159 (2002).
H.K. Durmuş and C. Meriç: Age-hardening behavior of powder metallurgy AA 2014 alloy. Mater. Des. 28 (3), 982–986 (2007).
W. Wai, L. Eugene, and M. Gupta: Characteristics of aluminum and magnesium based nanocomposites processed using hybrid microwave sintering. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energ. 44 (1), 14–27 (2010).
M. Oghbaei and O. Mirzaee: Microwave versus conventional sintering: A review of fundamentals, advantages and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 494 (1–2), 175–189 (2010).
S. Singh, D. Gupta, V. Jain, and A. Sharma: Microwave processing of materials and applications in manufacturing industries: A review. Mater. Manuf. Processes 30, 37–41 (2014).
K. Venkateswarlu, S. Saurabh, V. Rajinikanth, R.K. Sahu, and A.K. Ray: Synthesis of TiN reinforced aluminium metal matrix composites through microwave sintering. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 19 (2), 231–236 (2009).
T. Senthilvelan, S. Gopalakannan, S. Vishnuvarthan, and K. Keerthivaran: Fabrication and characterization of SiC, Al2O3 and B4C reinforced Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy (AA 7075) metal matrix composites: A study. Adv. Mater. Res. 622–623, 1295–1299 (2012).
Y.-C. Kang and S.L.-I. Chan: Tensile properties of nanometric Al2O3 particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 85 (2–3), 438–443 (2004).
S.M.R. Mousavi Abarghouie and S.M.S. Reihani: Aging behavior of a 2024 Al alloy–SiCp composite. Mater. Des. 31 (5), 2368–2374 (2010).
C. Dhadsanadhep, T. Luangvaranunt, J. Umeda, and K. Kondoh: Fabrication of Al/Al2O3 composite by powder metallurgy method from aluminum and rice husk ash. J. Mater. 18 (2), 99–102 (2008).
D.R. Kumar, R. Narayanasamy, and C. Loganathan: Effect of glass and SiC in aluminum matrix on workability and strain hardening behavior of powder metallurgy hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 34, 120–136 (2012).
R. Purohit, R.S. Rana, and C.S. Verma: Fabrication of Al–SiCp composites through powder metallurgy process and testing of properties. Int. J. Eng. Res. & Appl. 2 (3), 420–437 (2012).
S.C. Tjong and Z.Y. Ma: High-temperature creep behaviour of powder-metallurgy aluminium composites reinforced with SiC particles of various sizes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 59, 1117–1125 (1999).
D.P. Bishop, J.R. Cahoon, M.C. Chaturvedi, G.J. Kipouros, and W.F. Caley: On enhancing the mechanical properties of aluminum P/M alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 290, 16–24 (2000).
Z. Shi, J. Yang, J.C. Lee, D. Zhang, H.I. Lee, and R. Wu: The interfacial characterization of oxidized SiC(p)/2014 Al composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 303 (2001), 46–53 (2014).
J.B. Fogagnolo, F. Velasco, M.H. Robert, and J.M. Torralba: Effect of mechanical alloying on the morphology, microstructure and properties of aluminium matrix composite powders. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 342, 131–143 (2003).
M. Rahimian, N. Parvin, and N. Ehsani: Investigation of particle size and amount of alumina on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al matrix composite made by powder metallurgy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527 (4–5), 1031–1038 (2010).
S. Pournaderi, S. Mahdavi, and F. Akhlaghi: Fabrication of Al/Al2O3 composites by in situ powder metallurgy (IPM). Powder Technol. 229, 276–284 (2012).
M. Kok: Production and mechanical properties of Al2O3 particle-reinforced 2024 aluminium alloy composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 161 (3), 381–387 (2005).
M. Yamaguchi, F. Meng, K. Firestein, K. Tsuchiya, and D. Golberg: Powder metallurgy routes toward aluminum boron nitride nanotube composites, their morphologies, structures and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 604, 9–17 (2014).
T. Kobayashi: Strength and fracture of aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 280, 8–16 (2000).
K.S. See and T.A. Dean: The effects of the disposition of SiC particles on the forgeability and mechanical properties of co-sprayed aluminium-based MMCs. J Mater. Process. Technol. 136 (96), 0–9 (1997).
A. Hassani, E. Bagherpour, and F. Qods: Influence of pores on workability of porous Al/SiC composites fabricated through powder metallurgy + mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 591, 132–142 (2014).
Y.Q. Liu, S.H. Wei, J.Z. Fan, Z.L. Ma, and T. Zuo: Mechanical properties of a low-thermal-expansion aluminum/silicon composite produced by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30 (4), 417–422 (2014).
S. Scudino, G. Liu, M. Sakaliyska, K.B. Surreddi, and J. Eckert: Powder metallurgy of Al-based metal matrix composites reinforced with β-Al3Mg2 intermetallic particles: Analysis and modeling of mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 57 (15), 4529–4538 (2009).
V. Umasankar, S. Karthikeyan, and M.A. Xavior: The influence of electroless nickel coated SiC on the interface strength and microhardness of aluminium composites. J. Mater. Env. Sci. 5 (1), 153–158 (2014).
M. Rahimian, N. Ehsani, N. Parvin, and H.R. Baharvandi: The effect of particle size, sintering temperature and sintering time on the properties of Al–Al2O3 composites, made by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209 (14), 5387–5393 (2009).
C.R.A. Chennakesava Reddy and B. Kotiveerachari: Effect of aging condition on structure and the properties of Al-ALLOY/SiC composite. Int. J. Eng. & Technol. 2 (6), 462–465 (2010).
P. Ashwath and M.A. Xavior: The effect of ball milling & reinforcement percentage on sintered samples of aluminium alloy metal matrix composites. Procedia Eng. 97, 1027–1032 (2014).
Y. Sahin and V. Kilicli: Abrasive wear behaviour of SiCp/Al alloy composite in comparison with ausferritic ductile iron. Wear 271 (11–12), 2766–2774 (2011).
D.P. Bishop, X.Y. Li, K.N. Tandon, and W.F. Caley: Dry sliding wear behaviour of aluminum alloy 2014 microalloyed with Sn and Ag. Wear 222, 84–92 (2014).
P. Ravindran, K. Manisekar, P. Rathika, and P. Narayanasamy: Tribological properties of powder metallurgy–Processed aluminium self lubricating hybrid composites with SiC additions. Mater. Des. 45, 561–570 (2013).
P. Ravindran, K. Manisekar, P. Rathika, and P. Narayanasamy: Tribological properties of powder metallurgy — Processed aluminium self lubricating hybrid composites with SiC additions. Mater. Des. 45, 561–570 (2013).
M. Narayan and P. Bai: Dry sliding wear of Al alloy 2024–A12O3 particle composites. Wear 183, 563–570 (1995).
Y. Şahin: Abrasive wear behaviour of SiC/2014 aluminium composite. Tribol. Int. 43 (5–6), 939–943 (2010).
T. Miyajima and Y. Iwai: Effects of reinforcements on sliding wear behavior of aluminum matrix composites. Wear 255 (1–6), 606–616 (2003).
H.G.P. Kumar and M.A. Xavior: Fatigue and wear behavior of Al6061–graphene composites synthesized by powder metallurgy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 69, 415–419 (2015).
R.N. Rao and S. Das: Effect of matrix alloy and influence of SiC particle on the sliding wear characteristics of aluminium alloy composites. Mater. Des. 31 (3), 1200–1207 (2010).
M. Asif, K. Chandra, and P.S. Misra: Development of aluminium based hybrid metal matrix composites for heavy duty applications. J. Min. & Mater. Char. Eng. 10 (14), 1337–1344 (2011).
P. Ravindran, K. Manisekar, R. Narayanasamy, and P. Narayanasamy: Tribological behaviour of powder metallurgy-processed aluminium hybrid composites with the addition of graphite solid lubricant. Ceram. Int. 39, 1169–1182 (2013).
N. Radhika, R. Subramanian, and S.V. Prasat: Tribological behaviour of aluminium/alumina/graphite hybrid metal matrix composite using Taguchi’s techniques. J. Min. & Mater. Char. Eng. 10 (5), 427–443 (2011).
G. Iacob, G. Popescu, and M. Buzatu: Al/Al2O3/Gr hybrid composites. U. P. B. Science Bulletin 75, 117–126 (2013).
T. Miyajima, S. Sasayama, T. Honda, Y. Fuwa, and Y. Iwai: Effects of hardness of counterface on dry sliding wear of aluminum matrix composites against steels. Tribol. Online 7 (1), 24–32 (2012).
A. Canakci and F. Arslan: Abrasive wear behaviour of B4C particle reinforced Al2024 MMCs. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 63 (5–8), 785–795 (2012).
L. Hu, A. Kothalkar, M. O’Neil, I. Karaman, and M. Radovic: Current-activated, pressure-assisted infiltration: A novel, versatile route for producing interpenetrating ceramic–metal composites. Mater. Res. Lett. 2 (3), 124–130 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashwath, P., Xavior, M.A. Processing methods and property evaluation of Al2O3 and SiC reinforced metal matrix composites based on aluminium 2xxx alloys. Journal of Materials Research 31, 1201–1219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.131
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.131