Abstract
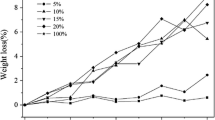
Poly(L-lactide)/poly(para-dioxanone) (PLLA/PPDO) (85/15 w/w) blends with 0, 1, 3, and 5 wt% poly(para-dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDOLLA) as a compatibilizer were prepared by solution coprecipitation. The in vitro hydrolytic degradation (HD) of blend bars with different contents of PDOLLA was studied by immersing the bars in a phosphate buffer solution (PBS) at pH 7.49. To estimate the degradation of blend bars, the weight loss, water absorption, thermal properties, surface morphology, and mechanical properties of blend bars, as well as the pH value changes of the PBS, were studied for 8 wk of HD. By adding 1 and 3 wt% PDOLLA, the weight loss of PLLA/PPDO (85/15 w/w) blends increased from 6.4 to 6.8 and 7.4% after 8 wk of HD, 6.2 and 15.6% increment, respectively, while, the average tensile strength of PLLA/PPDO (85/15 w/w) blends for 2–8 wk of HD increased from 25.8 to 29.0 MPa and 31.0 MPa, 12.4 and 20.2% increment, respectively. Considering their good mechanical properties and HD rate, the PLLA/PPDO (85/15 w/w) blends with 1 and 3 wt% PDOLLA are potential to be used as a medical implant material.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Yang, F. Liu, L. Yang, and S. Li: Hydrolytic and enzymatic degradation of poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-d,l-lactide) random copolymers with shape memory behavior. Eur. Polym. J. 46, 783 (2010).
A. Javadi, Y. Srithep, S. Pilla, J. Lee, S. Gong, and L.S. Turng: Processing and characterization of solid and microcellular PHBV/coir fiber composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 30, 749 (2010).
L.S. Nair and C.T. Laurencin: Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 32, 762 (2007).
H. Liu, F. Chen, B. Liu, G. Estep, and J. Zhang: Super toughened poly(lactic acid) ternary blends by simultaneous dynamic vulcanization and interfacial compatibilization. Macromolecules 43, 6058 (2010).
J.H. Yang, Y.D. Lee, R.S. Tsai, and H.B. Tsai: Enzymatic degradation of poly(l-lactide)/poly(tetramethylene glycol) triblock copolymer electrospun fiber. Mater. Chem. Phys. 133, 1127 (2012).
J.H. Wu, M.S. Yen, M.C. Kuo, and B.H. Chen: Physical properties and crystallization behavior of silica particulates reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 142, 726 (2013).
R.M. Rasal, A.V. Janorkar, and D.E. Hirt: Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35, 338 (2010).
S. Wang, P. Ma, R. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Zhang, and Y. Zhang: Mechanical, thermal and degradation properties of poly(d,l-lactide)/poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate)/poly(ethylene glycol) blend. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 93, 1364 (2008).
B. Meng, J. Tao, J. Deng, Z. Wu, and M. Yang: Toughening of polylactide with higher loading of nano-titania particles coated by poly(ε-caprolactone). Mater. Lett. 65, 729 (2011).
J. Lu, Z. Qiu, and W. Yang: Fully biodegradable blends of poly(l-lactide) and poly(ethylene succinate): Miscibility, crystallization, and mechanical properties. Polymer 48, 4196 (2007).
W.M. Gramlich, M.L. Robertson, and M.A. Hillmyer: Reactive compatibilization of poly(l-lactide) and conjugated soybean oil. Macromolecules 43, 2313 (2010).
M. Shibata, N. Teramoto, and Y. Inoue: Mechanical properties, morphologies, and crystallization behavior of plasticized poly(l-lactide)/poly(butylene succinate-co-l-lactate) blends. Polymer 48, 2768 (2007).
V. Arias, A. Hoglund, K. Odelius, and A.C. Albertsson: Tuning the degradation profiles of poly(l-lactide)-based materials through miscibility. Biomacromolecules 15, 391 (2014).
L. Jiang, M.P. Wolcott, and J. Zhang: Study of biodegradable polylactide/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Biomacromolecules 7, 199 (2006).
R. Gallego, S. López-Quintana, F. Basurto, K. Núñez, N. Villarreal, and J.C. Merino: Synthesis of new compatibilizers to poly(lactic acid) blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 54, 522 (2014).
W. Bai, D. Chen, Z. Zhang, Q. Li, D. Zhang, and C. Xiong: Poly(para-dioxanone)/inorganic particle composites as a novel biomaterial. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part B 90, 945 (2009).
W. Bai, L.F. Zhang, Q. Li, D.L. Chen, and C.D. Xiong: In vitro hydrolytic degradation of poly(para-dioxanone)/poly(d,l-lactide) blends. Mater. Chem. Phys. 122, 79 (2010).
W. Bai, Z.P. Zhang, Q. Li, D.L. Chen, H.C. Chen, N. Zhao, and C.D. Xiong: Miscibility, morphology and thermal properties of poly(para-dioxanone)/poly(D,L-lactide) blends. Polym. Int. 58, 183 (2009).
W. Bai, D. Chen, Q. Li, H. Chen, S. Zhang, X. Huang, and C.D. Xiong: In vitro hydrolytic degradation of poly(para-dioxanone) with high molecular weight. J. Polym. Res. 16, 471 (2008).
X. Xie, W. Bai, D. Chen, C. Xiong, and X. Pang: Effect of poly(para-dioxanone) on the hydrolytic degradation of poly(l-lactide). J. Polym. Environ. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-014-0670-y.
A.P.T. Pezzin, G.O.R. Alberda van Ekenstein, C.A.C. Zavaglia, G. Brinke, and E.A.R. Duek: Poly(para-dioxanone) and poly(l-lactic acid) blends: Thermal, mechanical, and morphological properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 88, 2744 (2003).
A.P.T. Pezzin and E.A.R. Duek: Miscibility and hydrolytic degradation of bioreabsorbable blends of poly(p-dioxanone) and poly(L-lactic acid) prepared by fusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 101, 1899 (2006).
P. Ma, X. Cai, Y. Zhang, S. Wang, W. Dong, M. Chen, and P.J. Lemstra: In-situ compatibilization of poly(lactic acid) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends by using dicumyl peroxide as a free-radical initiator. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 102, 145 (2014).
X. Xie, W. Bai, A. Wu, D. Chen, C. Xiong, C. Tang, and X. Pang: Increasing the compatibility of poly(L-lactide)/poly(para-dioxanone) blends through the addition of poly(para-dioxanone-co-L-lactide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132, 1029 (2015).
L. Zhang, C. Xiong, and X. Deng: Miscibility, crystallization and morphology of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(d,l-lactide) blends. Polymer 37, 235 (1996).
B. Wang, C. Ma, Z.C. Xiong, H.W. Zhou, Q.H. Zhou, and D.L. Chen: Regulating the physical and biological performances of poly(p-dioxanone) by copolymerization with L-phenylalanine. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 130, 2311 (2013).
D. Garlotta: A literature review of poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Environ. 9, 63 (2001).
S.C. Chen, X.L. Wang, Y.Z. Wang, K.K. Yang, Z.X. Zhou, and G. Wu: In vitro degradation of biodegradable blending materials based on poly(p-dioxanone) and poly(vinyl alcohol)-graft-poly(p-dioxanone) with high molecular weights. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 80, 453 (2007).
H.Z. Zhao, J.Y. Hao, C.D. Xiong, and X.M. Deng: Different crystallinity of poly(d,l-lactide-co-p-dioxanone) copolymers acquired by control of chain microstructure. Chin. Chem. Lett. 20, 1506 (2009).
E. Díaz, I. Sandonis, I. Puerto, and I. Ibáñez: In vitro degradation of PLLA/nHA composite scaffolds. Polym. Eng. Sci. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.23806.
S. Zhou, X. Deng, and H. Yang: Biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymers: Characterization and their use as drug carriers for a controlled delivery system. Biomaterials 24, 3563 (2003).
H. Peng, S. Zhou, T. Guo, Y. Li, X. Li, J. Wang, and J. Weng: In vitro degradation and release profiles for electrospun polymeric fibers containing paracetanol. Colloids Surf., B 66, 206 (2008).
X. Deng, S. Zhou, X. Li, J. Zhao, and M. Yuan: In vitro degradation and release profiles for poly- dl -lactide-poly(ethylene glycol) microspheres containing human serum albumin. J. Controlled Release 71, 165 (2001).
Y. Bai, P. Luo, P. Wang, W. Bai, C. Xiong, and C. Tang: Hydrolytic degradation of PPDO/PDLLA blends containing the compatibilizer PLADO. J. Polym. Environ. 21, 1016 (2013).
L. Dai, D. Li, and J. He: Degradation of graft polymer and blend based on cellulose and poly(l-lactide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 130, 2257 (2013).
P. Sriromreun, A. Petchsuk, M. Opaprakasit, and P. Opaprakasit: Standard methods for characterizations of structure and hydrolytic degradation of aliphatic/aromatic copolyesters. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 98, 169 (2013).
P. Wan, C. Yuan, L.L. Tan, Q. Li, and K. Yang: Fabrication and evaluation of bioresorbable PLLA/magnesium and PLLA/magnesium fluoride hybrid composites for orthopedic implants. Compos. Sci. Technol. 98, 36 (2014).
Y. Huang, C. Zhang, Y. Pan, Y. Zhou, L. Jiang, and Y. Dan: Effect of NR on the hydrolytic degradation of PLA. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 98, 943 (2013).
Y.S. Liu, Q.L. Huang, A. Kienzle, W.E.G. Muller, and Q.L. Feng: In vitro degradation of porous PLLA/pearl powder composite scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 38, 227 (2014).
J.L. Atkinson and S. Vyazovkin: Dynamic mechanical analysis and hydrolytic degradation behavior of linear and branched poly(L-lactide)s and poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide)s. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 214, 835 (2013).
Y. Li, S. Li, L. Ji, B. He, and Z. Gu: Studies on the degradation of poly(L-lactide-r-trimethene carbonate) copolymers. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 31, 966 (2013).
S. Mattioli, J.M. Kenny, and I. Armentano: Plasma surface modification of porous PLLA films: Analysis of surface properties and in vitro hydrolytic degradation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 125, E239 (2012).
C.L. Wanamaker, W.B. Tolman, and M.A. Hillmyer: Hydrolytic degradation behavior of a renewable thermoplastic. Biomacromolecules 10, 443 (2009).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51103156) and the West Light Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit http://dx.doi.org/jmr.2015.31.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, X., Bai, W., Tang, C. et al. Effects of poly(para-dioxanone-co-L-lactide) on the in vitro hydrolytic degradation behaviors of poly(L-lactide)/poly(para-dioxanone) blends. Journal of Materials Research 30, 860–868 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.31
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.31