Abstract
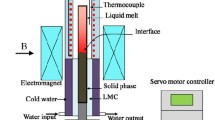
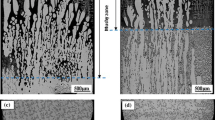
The effect of a strong magnetic field on the solid solubility and the microsegregation during directional solidification of Al-Cu alloy at lower growth speeds (1-10 μm/s) has been investigated experimentally. Results indicate that the magnetic field causes the reduction of the grain boundary and promotes the amalgamation of the grains. Further, measurement results reveal that the magnetic field increases the solid solubility and decreases the microsegregation. It is also found that the value of the solid solubility increases as the magnetic field and the temperature gradient increase. The modification of the solid solubility and the microsegregation under the magnetic field is attributed to the thermoelectric magnetic force acting on the solid and the interdendritic thermoelectric magnetic convection. The present work may initiate a new method to enhance the solid solubility and to eliminate the microsegregation in Al-based alloys via an applied strong magnetic field during directional solidification.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.W. Lan and C.Y. Tu: Three-dimensional analysis of flow and segregation control by slow rotation for Bridgman crystal growth in microgravity. J. Cryst. Growth 1881, 237 (2002).
Z. Li, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, and C. Ravidran: Effect of alloying elements on the segregation and dissolution of CuAl2 phase in Al-Si-Cu 319 alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 38, 1203 (2003).
M. Nishida, Y. Kawamura, and T. Yamamuro: Formation process of unique microstructure in rapidly solidified Mg97Zn1Y2 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 1217, 375 (2004).
J. Loboda-Cackovic: Segregation processes in PdCu(110) and the effects of sulphur impurity on surface composition and microstructure from annealing. Vacuum 48, 913 (1997).
C. Stelian, Y. Delannoy, Y. Fautrelle, and T. Duffar: Solute segregation in directional solidification of GaInSb concentrated alloys under alternating magnetic fields. J. Cryst. Growth 266, 207 (2004).
W.V. Youdelis and R.C. Dorward. Directional solidification of aluminium-copper alloys in a magnetic field. Can. J. Phys. 44, 139 (1966).
W.V. Youdelis and J.R. Cahoon: Diffusion in a magnetic field. Can. J. Phys. 48, 805 (1970).
S. Asai: Recent development and prospect of electromagnetic processing of materials. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 1, 191 (2000).
H. Yasuda, I. Ohnala, Y. Yamamoto, A.S. Wismogroho, N. Takezawa, and K. Kishio: Alignment of BiMn crystal orientation in Bi-20 at% Mn alloys by laser melting under a magnetic field. Mater. Trans., JIM 44, 2550 (2003).
L. Li, Y.D. Zhang, C. Esling, Z.H. Zhao, Y.B. Zuo, H.T. Zhang, and J.Z. Cui: Formation of feathery grains with the application of a static magnetic field during direct chill casting of Al-9.8wt%Zn alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 1063 (2009).
L. Li, Y.D. Zhang, C. Esling, H. Jiang, Z.H. Zhao, Y.B. Zuo, and J.Z. Cui: Crystallographic features of the primary Al3Fe phase in as-cast Al-3.31wt% Fe alloy. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 43, 1108 (2010).
T. Liu, Q. Wang, A. Gao, C. Zhang, C.J. Wang, and J.C. He: Fabrication of functionally graded materials by a semi-solid forming process under magnetic field gradients. Scr. Mater. 57, 992 (2007).
T. Garcin, S. Rivoirard, C. Elgoyhen, and E. Beaugnon: Experimental evidence and thermodynamics analysis of high magnetic field effects on the austenite to ferrite transformation temperature in Fe–C–Mn alloys. Acta Mater. 58, 2026 (2010).
X.W. Zuo, E.G. Wang, H. Han, L. Zhang, and J.C. He: Magnetic properties of Fe–49%Sn monotectic alloys solidified under a high magnetic field. J. Alloys Compd. 92, 621 (2010).
H. Yasuda, I. Ohnaka, Y. Ninomiya, R. Ishii, S. Fujita, and K. Kishio: Levitation of metallic melt by using the simultaneous imposition of the alternating and the static magnetic fields. J. Cryst. Growth 260, 475 (2004).
X.Y. Lu, A. Nagata, K. Watanabe, T. Nojima, K. Sugawara, and S. Kamada: Crystal growth of Bi-2201 phase in high magnetic fields. Physica C 382, 27 (2002).
Q. Wang, C.S. Lou, T. Liu, X.J. Pang, K. Nakajima, and J.C. He: Effects of uniform and gradient high magnetic fields on gravity segregation in aluminum alloys. ISIJ Int. 49, 1094 (2009).
C.J. Wang, Q. Wang, Y.Q. Wang, J. Huang, and J.C. He: Effects of high magnetic fields on the distribution of Si in solidified structures of Al-Si alloy. Acta Phys. Sin. 55, 648 (2006).
T. Liu, Q. Wang, N. Hirota, Y. Liu, S.H. Chen, and J.C. He: In situ control of the distributions of alloying elements in alloys in liquid state using high magnetic field gradients. J. Cryst. Growth 335, 121 (2011).
J. Wang, Y. Fautrelle, and Z.M. Ren: Modification of liquid/solid interface shape in directionally solidifying Al-Cu alloys by a transverse magnetic field. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 213 (2013).
S. Yesilyurt, L. Vujisic, S. Motalkef, F.R. Szofran, and M.P. Volz: A numerical investigation of the effect of thermoelectromagnetic convection (TEMC) on the Bridgman growth of Ge1–xSix. J. Cryst. Growth 207, 278 (1999).
J. Wang, Y. Fautrelle, and Z.M. Ren: Thermoelectric magnetic force acting on the solid during directional solidification under a static magnetic field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 251904 (2012).
P. Lehmann, R. Moreau, D. Camel, and R. Bolcato: A simple analysis of the effect of convection on the structure of the mushy zone in the case of horizontal Bridgman solidification comparison with experimental results. Acta Mater. 46, 4067 (1998).
J.A. Shercliff: Thermoelectric magnetohydrodynamics. J. Fluid Mech. 91, 235 (1979).
X. Li, Z.M. Ren, and Y. Fautrelle: Effect of a high axial magnetic field on the microstructure in a directionally solidified Al-Al2Cu eutectic alloy. Acta Mater. 54, 5349 (2006).
H.D. Brody and M.C. Flemings: Solute redistribution in dendritic solidification. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 236, 615 (1966).
X. Li, Y. Fautrelle, Z.M. Ren, A. Gagnoud, R. Moreau, Y.D. Zhang, and C. Esling: Effect of a high magnetic field on the morphological instability and irregularity of the interface of a binary alloy during directional solidification. Acta Mater. 57, 1689 (2009).
B. Sadigh, T.J. Lenosky, M.J. Caturla, A.A. Quong, and L.X. Benedict: Large enhancement of boron solubility in silicon due to biaxial stress. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 4738 (2002).
S.Q. Hong, Q.Z. Hong, and J.W. Mayer: Effects of grown in stress on the metastable solid solubility limits in Sb implanted Ge0.1Si0.9 alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 2054 (1993).
X. Li, A. Gagnoud, Y. Fautrelle, Z.M. Ren, G.H. Cao, R. Moreau, Y.D. Zhang, and C. Esling: Investigation of thermoelectric magnetic force in solid and its effect on morphological instability in directional solidification. J. Cryst. Growth 324, 217 (2011).
W.J. Boettinger, F. Biancaniello, and S. Coriell: Solutal convection induced macrosegregation the dendrite to composite transition in off-eutectic alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 12, 321 (1981).
S.N. Tewari, R. Shah, and H. Song: Effect of magnetic field on the microstructure and macrosegregation in directionally solidified Pb-Sn alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 25, 1535 (1994).
T. Alboussiere and R. Moreau: Influence of a magnetic-field on the solidification of metallic alloys. C. R. Acad. Sci. 313, 749 (1991).
X. Li, A. Gagnoud, Z.M. Ren, Y. Fautrelle, and R. Moreau: Investigation of thermoelectric magnetic convection and its effect on solidification structure during directional solidification under a low axial magnetic field. Acta Mater. 57, 2180 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Address all correspondence to this author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Gagnoud, A., Ren, Z. et al. Effect of strong magnetic field on solid solubility and microsegregation during directional solidification of Al-Cu alloy. Journal of Materials Research 28, 2810–2818 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.271
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.271