Abstract
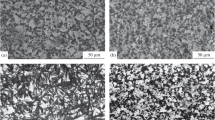
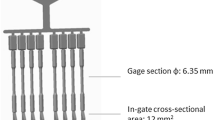
Chips produced by turning a commercial purity magnesium billet were cold compacted and then hot extruded at four different temperatures: 250, 300, 350, and 400 °C. Cast billets, of identical composition, were also extruded as reference material. Chip boundaries, visible even after 49:1 extrusion at 400 °C, were observed to suppress grain coarsening. Although 250 °C extruded chip-consolidated product showed early onset of yielding and lower ductility, fully dense material (extruded at 400 °C) had nearly 40% reduction in grain size with 22% higher yield strength and comparable ductility as that of the reference. The study highlights the role of densification and grain refinement on the compression behavior of chip consolidated specimens.
















Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. Sharma and T. Nakagawa: Recent development in the recycling of machining swarfs by sintering and powder forging. Ann. CIPR. 25, 121 (1977).
M. Mabuchi, K. Kubota, and K. Higashi: Superplasticity in an AZ91 alloy extrusion processed from machined chips. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 12, 1831 (1993).
M. Mabuchi, K. Kubota, and K. Higashi: New recycling process by extrusion for machined chips of AZ91 magnesium and mechanical properties of extruded bars. Mater. Trans. JIM. 36, 1249 (1995).
M. Nakanishi, M. Mabuchi, N. Saito, M. Nakamura, and K. Higashi: Tensile properties of the ZK60 magnesium alloy produced by hot extrusion of machined chip. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 17, 2003 (1998).
M. Samuel: A new technique for recycling aluminium scrap. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 135, 117 (2003).
J. Gronostajski, H. Marciniak, and A. Matuszak: New methods of aluminium and aluminium-alloy chips recycling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 106, 34 (2000).
Z. Sherafat, M.H. Paydar, and R. Ebrahimi: Fabrication of Al7075/Al, two phase material, by recycling Al7075 alloy chips using powder metallurgy route. J. Alloy. Comp. 487, 395 (2009).
Y. Chino, M. Mabuchi, S. Otsuka, K. Shimojima, H. Hosokawa, Y. Yamada, C. Wen, and H. Iwasaki: Corrosion and mechanical properties of recycled 5083 aluminum alloy by solid state recycling. Mater. Trans. 44, 1284 (2003).
Y. Chino, H. Iwasaki, and M. Mabuchi: Solid-state recycling for machined chips of iron by hot extrusion and annealing. J. Mater. Res. 19, 1524 (2004).
P. Luo, H. Xie, M. Paladugu, S. Palanisamy, M.S. Dargusch, and K. Xia: Recycling of titanium machining chips by severe plastic deformation consolidation. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 4606 (2010).
Y. Chino, M. Kobata, K. Shimojima, H. Hosokawa, Y. Yamada, H. Iwasaki, and M. Mabuchi: Blow forming of Mg alloy recycled by solid-state recycling. Mater. Trans. 45, 361 (2004).
M. Nakanishi, M. Mabchi, K. Kubota, and K. Higashi: Relationship between extrusion ratio and mechanical properties of extruded machined-chips of AZ 91 Mg alloy. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder and Powder Metall. 42, 373 (1995).
H. Watanabe, K. Moriwaki, T. Mukai, K. Ishikawa, M. Kohzu, and K. Higashi: Consolidation of machined magnesium alloy chips by hot extrusion utilizing superplastic flow. J. Mater. Sci. 36, 5007 (2001).
Y. Chino, T. Hoshika, and J-S. Lee: Mechanical properties of AZ31 Mg alloy recycled by severe deformation. J. Mater. Res. 21, 754 (2006).
Y. Chino and M. Mabuchi: Deformation characteristics of recycled AZ91 Mg alloy containing oxide contaminants. Mater. Trans. 49, 1093 (2008).
Y. Tao, Z. Ming-yi, H. Xiao-shi, and W. Kun: Recycling of AZ91 Mg alloy through consolidation of machined chips by extrusion and ECAP. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 20, s604 (2010).
T. Peng, Q.D. Wang, Y.K. Han, J. Zheng, and W. Guo: Consolidation behavior of Mg–10Gd–2Y–0.5Zr chips during solid-state recycling. J. Alloys Compd. 503, 253 (2010).
P. Pérez, G. Garcés, and P. Adeva: Influence of texture on the mechanical properties of commercially pure magnesium prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 3969 (2007).
S. Mueller, K. Mueller, and W. Reimers: Modifications of the extrusion process of magnesium alloys for improved mechanical properties. Key Eng. Mater. 367, 9 (2009).
J. Bohlen, S.B. Yi, J. Swiostek, D. Letzig, H.G. Brokmeier, and K.U. Kainer: Microstructure and texture development during hydrostatic extrusion of magnesium alloy AZ31. Scr. Mater. 53, 259 (2005).
S.I. Wright, J. Bingert, T.A. Masaon, and R.J. Larsen: Advanced characterization of twins using automated electron backscatter diffraction. Mater. Sci. Forum. 408, 511 (2002).
S. Mishra, K. Narasimhan, and I. Samajdar: Deformation twinning in AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel: Role of strain and strain path. Mater. Sci. Technol. 23, 1118 (2007).
S.K. Sahoo, V.D. Hiwarkar, I. Samajdar, P. Pant, G.K. Dey, D. Srivastav, R. Tewari, and S. Banerjee: Deformation twinning in zircaloy2. Mater. Sci. Technol. 26, 104 (2010).
M.R. Barnett, Z. Keshavarz, A.G. Beer, and D. Atwell: Influence of grain size on the compressive deformation of wrought Mg-3Al-1Zn. Acta Mater. 52, 5093 (2004).
J.W. Christian and S. Mahajan: Deformation twinning. Prog. Mater. Sci. 39, 1 (1995).
J. Koike, T. Kobayashi, T. Mukai, H. Watanabe, M. Suzuki, K. Maruyama, and K. Higashi: The activity of non-basal slip systems and dynamic recovery at room temperature in fine-grained AZ31B magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 51, 2055 (2003).
J.F. Dorris: Classification of failure modes for unconfined compression tests of multi-year ridge ice. Technical information record, BRC-1285, Project No. 27802.34, Shell Development Company, Texas, USA (1985).
X.X. Wei and K.T. Chau: Finite and transversely isotropic elastic cylinders under compression with end constraint induced by friction. Int. J. Solids Struct. 46, 1953 (2009).
J.B. Rao, S. Kamaluddin, and N.R.M.R. Bhargava: Optical strain measurements and its finite element analysis of cold workability limits of pure aluminium. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2, 1 (2010).
F.K. Chen and C.J. Chen: On the non-uniform deformation of the cylinder compression test. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 122, 192 (2000).
S. Biswas, S.S. Dhinwal, and S. Suwas: Room-temperature equal channel angular extrusion of pure magnesium. Acta Mater. 58, 3247 (2010).
P. Andersson, C.H. Cáceres, and J. Koike: Hall-Petch parameters for tension and compression in cast Mg. Mater. Sci. Forum. 419, 123 (2003).
G. Mann, J.R. Griffiths, and C.H. Cáceres: Hall-Petch parameters in tension and compression in cast Mg-2Zn alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 378, 188 (2004).
D.L. Yin, J.T. Wang, J.Q. Liu, and X. Zhao: On tension–compression yield asymmetry in an extruded Mg–3Al–1Zn alloy. J. Alloys. Compd. 478, 789 (2009).
Y.N. Wang and J.C. Huang: Texture analysis in hexagonal materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 81, 11 (2003).
M. Paramsothy, S.F. Hassan, N. Srikanth, and M. Gupta: Enhancement of compressive strength and failure strain in AZ31 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys. Compd. 482, 73 (2009).
M.R. Barnett, Z. Keshavraz, A.G. Beer, and D. Atwell: Influence of grain size on the compressive deformation of wrought Mg-3Al-1Zn. Acta Mater. 52, 5093 (2004).
M.R. Barnett: Twinning and the ductility of magnesium alloys: Part I: “Tension” twins. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 464, 1 (2007).
Y. Chino, T. Furuta, M. Hakamada, and M. Mabuchi: Influence of distribution of oxide contaminants on fatigue behavior in AZ31 Mg alloy recycled by solid-state processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. 424, 355 (2006).
K. Matsuura, Y. Watanabe, and Y. Hirashima: Use of recycled steel machining chips and aluminium can shreds for synthesizing iron aluminide intermetallic alloys. ISIJ Int. 44, 1258 (2004).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work involved the Institute X-ray Facility and Institute Nanoscience Initiative (INI) facility sponsored by Department of Science and Technology under the Funds for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure in Universities and Higher Educational Institutions (DST-FIST program) at Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore. The authors would also like to acknowledge the use of the National Facility for Texture & OIM (a DST- IRPHA (Intensification of Research in High Priority Areas) facility) at Indian Institute of Technology-Bombay for this study. Adamane R. Anilchandra, would like to thank Mr. Somjeeth Biswas of IISc for the useful discussion during the course of work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anilchandra, A.R., Basu, R., Samajdar, I. et al. Microstructure and compression behavior of chip consolidated magnesium. Journal of Materials Research 27, 709–719 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.411
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.411