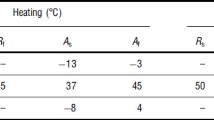
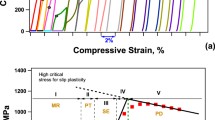
Abstract
Spherical indents in NiTi shape memory alloys can have reversible depth change: deeper depth in the martensitic phase at low temperature and shallower depth in the austenitic phase at high temperature. This is the indentation-induced two-way shape memory effect. After polishing the indents, two-way reversible surface protrusions can occur on the shape memory alloy surfaces upon heating and cooling. The height of the surface protrusion is about the same as the depth of the reversible indent. Further polishing reduces the height of the surface protrusion, which disappears completely when the polished depth is about the length of the contact radius. By comparing finite element analysis and experimental data, we show that the depth at which a protrusion disappears is close to the 10% strain boundary. This suggests that slip-plasticity is responsible for the observed indentation-induced two-way shape memory effect.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.Y. Ni, Y.T. Cheng D.S. Grummon: Microscopic superelastic behavior of a nickel-titanium alloy under complex loading conditions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2811 2003
W.Y. Ni, Y.T. Cheng D.S. Grummon: Recovery of microindents in a nickel-titanium shape-memory alloy: A “self-healing” effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3310 2002
Y.J. Zhang, Y.T. Cheng D.S. Grummon: Indentation stress dependence of the temperature range of microscopic superelastic behavior of nickel-titanium thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 033505 2005
G.A. Shaw, D.S. Stone, A.D. Johnson, A.B. Ellis W.C. Crone: Shape memory effect in nanoindentation of nickel-titanium thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 257 2003
W.Y. Ni, Y.T. Cheng D.S. Grummon: Microscopic shape memory and superelastic effects under complex loading conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 177, 512 2004
K. Otsuka C.M. Wayman: Shape Memory Materials Cambridge University Press New York 1998
Y.J. Zhang, Y.T. Cheng D.S. Grummon: Two-way indent depth recovery in a NiTi shape memory alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 131904 2006
Y.J. Zhang, Y.T. Cheng D.S. Grummon: Shape memory surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 041912 2006
A. Nagasawa, K. Enami, Y. Ishino, Y. Abe S. Nenno: Reversible shape memory effect. Scripta Metall. 8, 1055 1974
H. Scherngell A.C. Kneissl: Generation, development and degradation of the intrinsic two-way shape memory effect in different alloy systems. Acta Mater. 50, 327 2002
R. Stalmans, J. Van Humbeeck L. Delaey: Thermomechanical cycling, 2 way memory and concomitant effects in Cu-Zn-Al alloys. Acta Metall. Mater. 40, 501 1992
Y. Liu, Y. Liu J. Van Humbeeck: Two-way shape memory effect developed by martensite deformation in NiTi. Acta Mater. 47, 199 1998
J.J. Wang, T. Omori, Y. Sutou, R. Kainuma K. Ishida: Two-way shape memory effect induced by cold-rolling in Ti-Ni and Ti-Ni-Fe alloys. Scripta Mater. 52, 311 2005
Y. Liu, Z. Xie, J. Van Humbeeck L. Delaey: Some results on the detwinning process in NiTi shape memory alloys. Scripta Mater. 41, 1273 1999
W.Y. Ni Y.T. Cheng: Modeling conical indentation in homogeneous materials and in hard films on soft substrates. J. Mater. Res. 20, 521 2005
K.L. Johnson: Contact Mechanics Cambridge University Press New York 1985 174–176
L.E. Samuels T.O. Mulhearn: An experimental investigation of the deformed zone associated with indentation hardness impressions. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 5, 125 1957
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Cheng, YT. & Grummon, D.S. Understanding indentation-induced two-way shape memory effect. Journal of Materials Research 22, 2851–2855 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2007.0356
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2007.0356