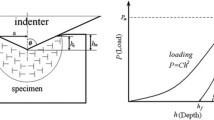
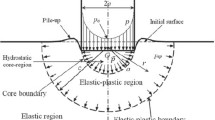
Abstract
Existing indentation models (both analytical models and numerical analysis) show a linear relationship between δr/δm and H/Er, where δr and δm are the residual and maximum indentation depth, and Er and H are the reduced Young’s modulus and hardness of the test material. Based on the analysis of Oliver and Pharr, a new relationship between δr/δm and H/Er has been derived in a different way without any additional assumptions, which is nonlinear, and this has been verified by finite element analysis for a range of bulk materials. Furthermore, this new relationship for residual depth is used to derive an analytical relationship for the radius of the plastic deformation zone Rp in terms of the residual depth, Young’s modulus, and hardness, which has also been verified by finite element simulations for elastic perfectly plastic materials with different work hardening behavior. The analytical model and finite element simulation confirms that the conventional relationship used to determine Rp developed by Lawn et al. overestimates the plastic deformation, especially for those materials with high E/H ratio. The model and finite element analysis demonstrate that Rp scales with δr, which is sensible given the self-similarity of the indentations at different scales, and that the ratio of Rp/δr is nearly constant for materials with different E/H, which contradicts the conventional view.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic-modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, F.R. Brotzen: On the generality of the relationship among contact stiffness, contact area, and elastic-modulus during indentation. J. Mater. Res. 7, 613 (1992).
S.V. Hainsworth, H.W. Chandler, T.F. Page: Analysis of nanoindentation load-displacement loading curves. J. Mater. Res. 11, 1987 (1996).
X. Li, D. Diao, B. Bhushan: Fracture mechanisms of thin amorphous carbon films in nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 45, 4453 (1997).
J. Malzbender, G. de With, J. den Toonder: Elastic modulus, indentation pressure and fracture toughness of hybrid coatings on glass. Thin Solid Films 366, 139 (2000).
J. Chen, S.J. Bull: Assessment of the toughness of thin coatings using nanoindentation under displacement control. Thin Solid Films 494, 1 (2006).
Y.T. Cheng, C.M. Cheng: Relationships between hardness, elastic modulus, and the work of indentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 614 (1998).
Y.T. Cheng, Z. Li, C.M. Cheng: Scaling relationships for indentation measurements. Philos. Mag. A 82, 1821 (2002).
J. Malzbender, G. de With: Energy dissipation, fracture toughness and the indentation load–displacement curve of coated materials. Surf. Coat. Technol. 135, 60 (2000).
B.R. Lawn, A.G. Evans, D.B. Marshall: Elastic/plastic indentation damage in ceramics: The median/radial crack system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 63, 574 (1980).
P.J. Burnett, D.S. Rickerby: The mechanical properties of wear-resistant coatings. 1. Modeling of hardness behaviour. Thin Solid Films 148, 41 (1987).
A.E. Giannakopoulos, S. Suresh: Determination of elastoplastic properties by instrumented sharp indentation. Script Mater. 40, 1191 (1999).
S. Harvey, H. Huang, S. Venkataraman, W.W. Gerberich: Microscopy and microindentation mechanics of single-crystal Fe-3 wt% Si: Part I. Atomic force microscopy of a small indentation. J. Mater. Res. 8, 1291 (1993).
I.N. Sneddon: The relation between load and penetration in the axisymmetric Boussinesq problem for a punch of arbitrary profile. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
B.R. Lawn, V.R. Howes: Elastic recovery at hardness indentations. J. Mater. Sci. 16, 2745 (1981).
M. Sakai: Energy principle of the indentation-induced inelastic surface deformation and hardness of brittle materials. Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 1751 (1993).
M. Sakai, S. Shimizu, T. Ishikawa: The indentation load-depth curve of ceramics. J. Mater. Res. 14, 1471 (1999).
M. Sakai: Simultaneous estimate of elastic/plastic parameters in depth-sensing indentation tests. Scripta Mater. 51, 391 (2004).
S.J. Bull: Interface engineering and graded films: Structure and characterization. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 19, 1404 (2001).
S.J. Bull, E. G-Berasetegui, T. F. Page: Modelling of the indentation response of coatings and surface treatments. Wear 256, 857 (2004).
G.M. Pharr, A. Bolshakov: Understanding nanoindentation unloading curves. J. Mater. Res. 17, 2660 (2002).
J. Malzbender, G. de With: The use of the loading curve to assess soft coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 127, 265 (2000).
W.C. Oliver: Alternative technique for analyzing instrumented indentation data. J. Mater. Res. 16, 3202 (2001).
J. Malzbender, G. de With, J. den Toonder: The P-h2 relationship in indentation. J. Mater. Res. 15, 1209 (2000).
Y. Bao, L. Liu, Y. Zhou: Assessing the elastic parameters and energy-dissipation capacity of solid materials: A residual indent may tell all. Acta Mater. 53, 4857 (2005).
J. Malzbender: Comment on the determination of mechanical properties from the energy dissipated during indentation. J. Mater. Res. 20, 1090 (2005).
J. Alkorta, J.M. Martinez-Esnaola, J.G. Sevillano: Comments on “Comment on the determination of mechanical properties from the energy dissipated during indentation” by J. Malzbender [J. Mater. Res. 20, 1090 (2005)]. J. Mater. Res. 21, 302 (2006).
J. Menčik, M.V. Swain: Microindentation tests with pointed indenters. Mater. Forum 18, 277 (1994).
J. Liu, M.C. Mwanza, P.A.S Reed, S. Syngellakis: ANSYS Application Note. (ANSYS Inc., Canonsburg, PA, 2002).
ANSYS 8.0 Documentation, ANSYS Inc., Canonsburg, PA.
S. Soare: Design of a rotating sensor for stress measurement in metallisation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Newcastle Upon Tyne (2004).
A. Bolshakov, G.M. Pharr: Influences of pileup on the measurement of mechanical properties by load and depth-sensing indentation techniques. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1049 (1998).
K.L. Johnson: The correlation of indentation experiments. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 18, 115 (1970).
M. Li, W. Chen, N. Liang, L. Wang: A numerical study of indentation using indenters of different geometry. J. Mater. Res. 19, 73 (2004).
Y.T. Cheng, C.M. Cheng: Scaling approach to conical indentation in elastic-plastic solids with work hardening. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 1284 (1998).
D.B. Marsh: Plastic flow in glass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 279, 420 (1963).
L.J. Vandeperre, F. Giuliani, W.J. Clegg: Effect of elastic surface deformation on the relation between hardness and yield strength. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3704 (2004).
W. Yu, J.P. Blanchard: An elastic-plastic indentation model and its solutions. J. Mater. Res. 11, 2358 (1996).
D. Tabor: Hardness of Metals. (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1951).
J. Chen and S.J. Bull: (in preparation).
J.C. Hay, A. Bolshakov, G.M. Pharr: A critical examination of the fundamental relations used in the analysis of nanoindentation data. J. Mater. Res. 14, 2296 (1999).
M. Troyon, L. Huang: About the correction factor for contact area in nanoindentation measurements. J. Mater. Res. 20, 610 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Bull, S.J. A critical examination of the relationship between plastic deformation zone size and Young’s modulus to hardness ratio in indentation testing. Journal of Materials Research 21, 2617–2627 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0323
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0323