Abstract
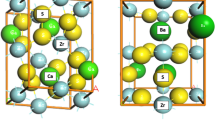
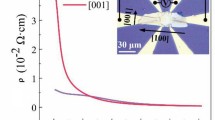
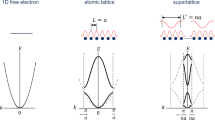
In recent years, LAST-m (AgPbmSbTem+2) and related materials have emerged as potential high performance high temperature thermoelectrics. These compounds are obtained by starting from PbTe, and replacing pairs of Pb2+ ions by (Ag1+, Sb3+) pairs. One example is LAST-18. When optimally doped, this compound has thermoelectric figure of merit ZT=1.7 at 700K. This large ZT is most likely due to very low lattice thermal conductivity, caused by phonon scattering from nanostructures. These nanostructures involve clustering and ordering of Ag, Sb, and Pb ions. Possible origins of this atomic ordering and how the presence of nanostructures affects the electronic structure near the band gap region are discussed. The temperature (T) dependence of electrical conductivity σ (∼T2.2 in the range 300K <T< 900K) in n-type PbTe is analyzed in terms of the T-dependence of different physical quantities contributing to transport. We find that the dominant contribution comes from the explicit T-dependence of relaxation time rather than its energy dependence. The T-dependence of chemical potential is also significant in the concentration range of interest. Electronic thermal conductivity for constant field (κel,E) and for constant current (κel,J) are found to differ considerably at high temperatures and the Weidemann-Franz (WF) law κel,J = LoσT, where Lo =2x10−8WΩ/K is the Lorentz number, overstimates κel,J by nearly 60% at 800K for carrier concentration n=5x1019/cm3. As a result, one tends to underestimate the lattice contribution κlatt = κexp - κel,J. We give theoretical values of effective Lorentz number L = κel.J/σT for different n and T.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Uher, Chemistry, Physics, and Materials Science of Thermoelectric Materials: Beyond Bismuth Telluride”, Edited by M. G. Kanatzidis, S. D. Mahanti, and T. P. Hogan, Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York (2003), p. 121.
T. C. Harman et al., Science 297, 2229 (2002).
K. F. Hsu et al., Science 303, 818 (2004).
K. Takahata and I. Terasaki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41, 763 (2002).
J. M. Ziman, Principles of The Theory of Solids (Camb. Univer Press, NY 1964), p 179.
K. Hoang, K. Desai, and S. D. Mahanti, Phys. Rev. B 72, 064102 (2005).
E. Quarez et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 9177 (2005); P. F. P. Poudeu et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 3835 (2006).
K. Hoang, Atomic and Electronic Structures of Novel Ternary and Quaternary Narrow Band-Gap Semiconductors, Ph. D. Thesis, Michigan State University (2007).
K. Hoang, et al., Phys. Rev. Letters 99, 156403 (2007).
D. Bilc et al., Phys. Rev. Letters 93, 146403 (2004).
H. Hazama, U. Mizutani, and R. Asahi, Phys. Rev. B 73, 115108 (2006).
B. A. Volkov, L. I. Ryabova, and D. R. Khokhlov, Phys.-Usp. 45, 819 (2002).
S. Ahmad, K. Hoang, and S. D. Mahanti, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 056403 (2006); 96, 169907(E)(2006).
S. Ahmad et al., Phys. Rev. B 74, 155205 (2006).
G. D. Mahan and J. O. Sofo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93, 7436 (1996).
M.-K. Han et al., (to be submitted to Chemistry of Materials).
J. Sootman et al (unpublished).
B. A. Effimova et al., Soviet Physics – Semiconductors 4, 1653 (1971).
D. Bilc, S. D. Mahanti, and M. G. Kanatzidis, Phys. Rev. B 74, 125202 (2006).
S. Ahmad, Defect Structure and Transport Properties of Narrow Gap Semiconductor PbTe and Related Ststems, Ph. D. Thesis, Michigan State University (2007); Also see C.M.Bhandari and D. D. M. Rowe , J. Phys. D; Appl. Phys. 18, 873 (1985).
J. R. Drabble and H. J. Goldsmid, International Series of Monographs on Semiconductors: Thermal Conduction in Semiconductors, Vol. 4 (Pergammon Press, 1961).
P. Hohenberg and W. Kohn, Phys. Rev. 136, B864 (1964); W. Kohn and L. J. Sham, Phys. Rev. 140, A1133 (1965).
J. P. Perdew and Y. Wang, Phys. Rev. B 45, 13244 (1992).
W. G. Aulber, L. Jonsson, and J. W. Wilkins, Solid State Physics 54, 1 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahanti, S.D., Hoang, K. & Ahmad, S. Atomic Ordering, Electronic Structure, and Transport Properties of LAST-m Systems. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1044, 406 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1044-U04-06
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1044-U04-06