Abstract
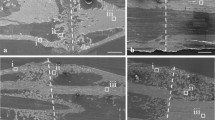
Accumulation of microdamage during fatigue can lead to increased fracture susceptibility in bone. Current techniques for imaging microdamage in bone are inherently destructive and two-dimensional. A non-destructive, three-dimensional technique is needed to measure the spatial density of microdamage accumulation. Therefore, the objective of this study was to image microdamage accumulation in cortical bone during fatigue using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) with a barium sulfate (BaSO4) contrast agent. Bovine cortical bone beams were loaded under four-point bending fatigue. Two symmetric notches were machined on the tensile surface in order to generate damage at the stress concentrations during loading. Specimens were loaded to a specified number of cycles or until one notch fractured, such that the other notch exhibited accumulated microdamage just prior to fracture. Microdamage ahead of the notch was stained by precipitation of BaSO4 and imaged using micro-CT. Reconstructed images showed a distinct region of bright voxels around the notch tip or along propagating cracks due to the presence of BaSO4, which was verified by backscattered electron imaging and energy dispersive spectroscopy. The stained region exhibited a characteristic kidney shape perpendicular to the notch tip, which was correlated to principal strain contours calculated by finite element analysis. The area of stained regions was positively correlated with the number of loading cycles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.S.S. Jee, in Bone Mechanics Handbook, edited by S. C. Cowin (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2001) pp. 1.1–1.2.
D.B. Burr, M.R. Forwood, D.P. Fyhrie, R.B. Martin, M.B. Schaffler and C.H. Turner, J Bone Miner Res. 12, 6–15 (1997).
R.B. Martin, Calcif Tissue Int. 73, 101–107 (2003).
M.B. Schaffler, E.L. Radin and D.B. Burr, Bone. 10, 207–214 (1989).
K.J. Jepsen and D.T. Davy, J Biomechanics. 30, 891–894 (1997).
R.B. Martin and D.B. Burr, J Biomechanics. 15, 137–139 (1982).
D.B. Burr, R.B. Martin, M.B. Schaffler and E.L. Radin, J Biomechanics. 18, 189–200 (1985).
S. Mori and D.B. Burr, Bone. 14, 103–109 (1993).
D.B. Burr and T. Stafford, Clin Orthop Rel Res. 260, 305–308 (1990).
T.C. Lee, T.L. Arthur, L.J. Gibson and W.C. Hayes, J Orthop Res. 18, 322–325 (2000).
F.J. O’Brien, D. Taylor and T.C. Lee, J Biomechanics. 35, 523–526 (2002).
F.J. O’Brien, D. Taylor and T.C. Lee, J Biomechanics. 36, 973–980 (2003).
M.B. Schaffler, W. Pitchford, K. Choi and J.M. Riddle, Bone. 15, 483–488 (1994).
P. Zioupos and J.D. Currey, J Biomechanics. 27, 993–5 (1994).
F.J. O’Brien, D. Taylor, G.R. Dickson, and T.C. Lee, J Anat. 197, 413–420 (2000).
J. Li, M.A. Miller, G.D. Hutchins and D.B. Burr, Trans Orthop Res Soc. 30, 33 (2005).
H. Leng, J.J. VanDersarl, G.L. Niebur and R.K. Roeder, Trans Orthop Res Soc. 30, 665 (2005).
D.B. Masse, X. Wang, R.K. Roeder and G.L. Niebur, Trans Orthop Res Soc. 30, 35 (2005).
R.K. Nalla, J.H. Kinney and R.O. Ritchie, Nature Mater. 2, 164–168 (2003).
R.K. Nalla, J.J. Kruzic, J.H. Kinney and R.O. Ritchie, Bone. 35, 1240–1246 (2004).
O.S. Sobelman, J.C. Gibeling, S.M. Stover, S.J. Hazelwood, O.C. Yeh, D.R. Shelton and R.B. Martin, J Biomechanics. 37, 1295–1303 (2004).
D.T. Reilly and A.H. Burstein, J Bone Joint Surg. 56, 1001–1022 (1974).
J.D. Currey, in Bone Mechanics Handbook, edited by S. C. Cowin (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2001) pp. 19.1–19.4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leng, H., Wang, X., Niebur, G. et al. Fatigue Microdamage in Bovine Cortical Bone Imaged by Micro-Computed Tomography Using a Barium Sulfate Contrast Agent. MRS Online Proceedings Library 898, 904 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-0898-L09-04
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-0898-L09-04