Abstract
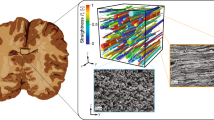
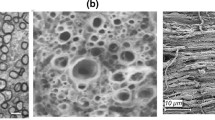
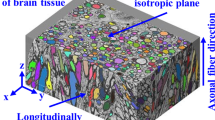
The atypical mechanical behavior of white matter and its influence on the mechanical properties of brain tissue necessitate adoption of a mutli-scale model of white matter for accurate computational analysis. Herein, we present a micromechanical analysis coupled with finite elements into a biomechanical interacting model of white matter. A representation of the white matter of central nervous system is identified and its microstructure is generated. The geometric descriptions of the axon and the surrounding matrix are obtained from neurofilament immunohistochemistry images. Consecutively, linear elastic material constitutive models are applied to describe the behavior of axons and their surrounding matrix subjected to small deformations. This model facilitates determination of the tissue’s stress and strain fields, and enables an understanding of the effects of axon undulation on local fields. The fundamental nature of the model enables future scale-up for structural tissue analysis and predictions of axon damage at the microscale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.S. Margulies, D.F. Meaney, L.E. Bilston, L.E. Thibault, N.G. Campeau, and S.J. Riederer, in Proceedings of International IRCOBI Conference on the Biomechanics of Impacts, Verona, Italy, 1992.
T.A. Gennarelli, L.E. Thibault, R. Tipperman, G. Tomei, R. Sergot, M. Brown, W.L. Maxwell, D.I. Graham, J.H. Adams, A. Irvine, L.M. Gennarelli, A.C. Duhaime, R. Boock, and J. Greenberg, Journal of Neurosurgery 71, 244 (1987).
L. Voo, S. Kumaresan, F. Pintar, N. Yoganandan, and A. Sances, Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 34, 375 (1996).
A.C. Bain and D.F. Meaney, Journal of Biomechanical Engineering 122, 615 (2000).
M.T. Prange and S.S. Margulies, Journal of Biomechanical Engineering 124, 244 (2002).
F.A. Pintar, S. Kumaresan, N. Yoganandan, A. Yang, B. Stemper, and T.A. Gennarelli, Biomed Sci Instrum, 429 (2001).
J.T. Maikos, Z. Qian, D. Metaxas, and D.I. Shreiber, Journal of Neurotrauma 25, 795 (2008).
L. Zhang, K.H. Yang, and A.I. King, Journal of Biomechanical Engineering 126, 226 (2004).
Q. Zhu, M. Prange, and S. Margulies, Developmental Neuroscience 28, 388 (2006).
T. El Sayed, A. Mota, F. Fraternali, and M. Ortiz, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 197, 4692 (2008).
H. Hao and D.I. Shreiber, Journal of Biomechanical Engineering 129, 511 (2007).
D.I. Shreiber, H. Hao, and R.A. Elias, Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology 8, 311 (2009).
G. Karami, N. Grundman, N. Abolfathi, A. Naik, and M. Ziejewski, Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2, 243 (2009).
A.C. Bain, D.I. Shreiber, and D.F. Meaney, Transactions of the ASME 125, 798 (2003).
R. Bernal, P.A. Pullarkat, and F. Melo, Physical Review Letters 99, 018301 (2007).
Y. Pan, L. Iorga, and A.A. Pelegri, Composites Science and Technology 68, 2792 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Y., Pelegri, A.A. & Shreiber, D.I. Simulation of the Mechanical Behavior of White Matter Using a Micromechanics Finite Element Method. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1301, 87–92 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.565
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.565