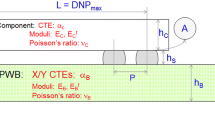
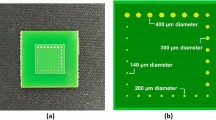
Abstract
A single printed circuit board includes thousands, sometimes even hundreds of thousands, of solder joints. The failure of even a single solder joint is usually enough to compromise the functionality of an electronic device or system. PbSn solder had been the standard ma te rial for these joints until various regulations around the world began to limit Pb use. SnAgCu and related alloys are quickly replacing PbSn, but much still needs to be understood and controlled. None of the paradigms for understanding the mechanical response of PbSn alloys is applicable to lead-free alloys. Much of the surprising behavior of SnAgCu solder arises from the complex and fascinating nature of its solidification behavior. In this ar ticle, the impact of solidification on the microstruc ture and therefore the mechanical properties of these solder joints will be addressed in the context of microelectronics proc essing. The need for better simulations of SnAgCu solder behavior will also be examined. Notably, modelers will have to account for a variety of new parameter dependencies not previously considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.J. Puttlitz, K.A. Stalter, Eds. Handbook of Lead - Free Solder Technology for Microelectronic Assemblies (Marcel Dekker, New York, 2004), and related Internet links: IPC Compliance Web Site, http://leadfree.ipc.org/RoHS_3–2-1–4.asp; EC Environment Policy, Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment, http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/weee_index.htm; U.K. Department of Trade and Industry Web Site, EC Directive on Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment, http://www.dti.gov.uk/innovation/sustainability/weee/page30269.html; Grace Compliance Specialist Web Site, http://www.graspllc.com/China%20RoHS.php/.
K.W. Moon et al., J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1122 (2000).
J.-P. Clech, MicroMater. Nanomater. 3, 144 (2004).
R. Darveaux, K. Banerji, A. Mawer, G. Dody, in Ball Grid Array Technology, J.H. Lau, ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1995) pp. 379–442.
L.P. Lehman et al., J. Electron. Mater. 33 (12), 1429 (2004).
A.U. Telang, T.R. Bieler, JOM 57, 44 (2005).
A.U. Telang, T.R. Bieler, S. Choi, K.N. Subramanian, J. Mater. Res. 17, 2204 (2002).
D.R. Frear, J. Met. 48, 49 (1996).
D.G. House, E.V. Vernon, Br. J. Appl. Phys. 11, 254 (1960).
J.A. Rayne, B.S. Chandrasekhar, Phys. Rev. 120, 1658 (1960).
K.N. Subramanian, J.G. Lee, J. Mater. Sci.–Mater. Electron. 15, 235 (2004).
S.B. Park, R. Dhakal, L.P. Lehman, E.J. Cotts, in Proc. ASME InterPACK (San Francisco, CA, 2005).
D.R. Frear, J.W. Jang, J.K. Lin, C. Zhang, J. Met. 53, 28 (2001).
D.W. Henderson et al., J. Mater. Res. 19 (6), 1608 (2004).
Special Issue on Lead - Free Solders and Processing Issues in Microelectronics Packaging, J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1359 (2003).
K. Zeng, K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 38, 55 (2002).
A. Zribi et al., J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1157 (2001).
M.A. Matin, E.W.C. Coenen, W.P. Vellinga, M.G.D. Geers, Scripta Mater. 53, 927 (2005).
T.R. Bieler et al., Proc. 56th Electronic Components Technology Conf. (2006) p. 6.
L.P. Lehman et al., Proc. 55th Electronic Components Technology Conf. (2005) p. 674–681.
W.C. Luoa et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A 396, 385 (2005).
K. Kim, K. Suganuma, J. Kim, C. Hwang, J. Met. 56, 39 (2004).
A.U. Telang et al., J. Electron. Mater. 33 (12), 1412 (2004).
F. Ochoa, X. Deng, N. Chawla, J. Electron. Mater. 33 (12), 1596 (2004).
K.P. Wu, N. Wade, S. Yamada, K. Miyahara, Z. Metallkd. 95 (3), 185 (2004).
Q. Xiao, L. Nguyen, W.D Armstrong, Proc. 54th Electronic Components Technology Conf. (2004) p. 1325–1332.
R.L.J.M. Ubachs, P.J.G. Schreurs, M.G.D. Geers, IEEE Trans. Components Packaging Technologies 27 (4), 635 (2004).
S. Jadhav, T.R. Bieler, K.N. Subramanian, J.P. Lucas, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1197 (2001).
S. Choi et al., J. Met. 53, 22 (2001).
A.U. Telang, T.R. Bieler, M.A. Crimp, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 421 (1–2), 22 (2006).
J. Weertman, Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Eng. 218, 207 (1960).
M.D. Mathew, Y. Hang, S. Movva, K.L. Murty, Metall. Mater. Trans. 01.36A (1), 99 (2005).
R. Kinyanjui, L.P. Lehman, L. Zavalij, E. Cotts, J. Mater. Res. 20, 2914 (2005).
K.S. Kim, S.H. Huh, K. Suganuma, J. Alloys Compd. 352, 226 (2002).
F. Ochoa, X. Deng, N. Chawla, J. Electron. Mater. 33 (12), 1596 (2004).
K.P. Wu, N. Wade, S. Yamada, K. Miyahara, Z. Metallkd. 95 (3), 185 (2004).
I. Dutta, D. Pan, R.A. Marks, S.G. Jadhav, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 410–11, 48 (2005).
S.K. Kang et al., in Proc. 54th Electronic Components Technology Conf. (2004) p. 661–667.
J.G. Lee, K.N. Subramanian, Soldering Surf. Mount Technol. 17 (1), 33 (2005).
S.K. Kang et al., J. Electron. Mater. 35 479 (2006).
I.E. Anderson, J.L. Harringa, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1485 (2004).
J.C. Gong, C.Q. Liu, P.P. Conway, V.V. Silberschmidt, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 427 (1–2), 60 (2006).
R. Darveaux, K. Banerji, IEEE Trans. Components, Hybrids, Manuf. Technol., 15 (6), 1013 (December 1992).
Y. Wei et al., J. Electron. Packaging 126 367 (2004).
J. Gong, C. Liu, P.P. Conway, V.V. Silberschmidt, Comput. Mater. Sci. (2007) in press, http://www.sciencedirect.com.
H. Rhee, K.N. Subramanian, Soldering Surf. Mount Technol., 18 (1), 19 (2006).
C. Kanchanomai, Y. Miyashita, Y. Mutoh, S.L. Mannan, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 345 90 (2003).
S. Terashima, K. Takahama, M. Nozaki, M. Tanaka, Mater. Trans. JIM 45 (4), 1383 (2004).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borgesen, P., Bieler, T., Lehman, L.P. et al. Pb-Free Solder: New Materials Considerations for Microelectronics Processing. MRS Bulletin 32, 360–365 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2007.236
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2007.236