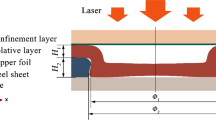
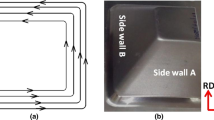
Abstract
In the present study, gradient microstructure and texture development in wedge-based severe plastic burnishing of oxygen-free high conductivity copper was investigated. Microstructural response and evolution of crystallographic texture in severe surface plastic deformation was shown to be controllable in terms of both magnitude and gradient through control of the incident wedge angle and burnishing parameters. Equiaxed ultra-fined grains and micro/nanoscale elongated grains were produced in the subsurface region, which is indicative of dynamic recrystallization at large strains in the subsurface. Subsurface regions exhibited a significant fraction of shear texture components along the 〈110〉 partial fibers. Texture evolution simulated using the visco-plastic self-consistent framework revealed variations in strain level controlling different mechanisms for rotation of these partial fibers from their ideal orientation. Controllability of subsurface properties and microstructure for such materials is briefly discussed. These results allude to fundamental limits in material processing by severe shear using scalable deformation configurations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.Q. Deng, A. Godfrey, W. Liu, and N. Hansen: A gradient nanostructure generated in pure copper by platen friction sliding deformation. Scr. Mater. 117, 41 (2016).
X.C. Liu, H.W. Zhang, and K. Lu: Strain-induced ultrahard and ultrastable nanolaminated structure in nickel. Science 342, 337 (2013).
Y. Guo, C. Saldana, W. Dale Compton, and S. Chandrasekar: Controlling deformation and microstructure on machined surfaces. Acta Mater. 59, 4538 (2011).
Z. Pu, S. Yang, G.L. Song, O.W. Dillon, D.A. Puleo, and I.S. Jawahir: Ultrafine-grained surface layer on Mg–Al–Zn alloy produced by cryogenic burnishing for enhanced corrosion resistance. Scr. Mater. 65, 520 (2011).
H.W. Huang, Z.B. Wang, X.P. Yong, and K. Lu: Enhancing torsion fatigue behaviour of a martensitic stainless steel by generating gradient nanograined layer via surface mechanical grinding treatment. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 1200 (2013).
K. Lu: Making strong nanomaterials ductile with gradients. Science 345, 1455 (2014).
X. Wu, P. Jiang, L. Chen, F. Yuan, and Y.T. Zhu: Extraordinary strain hardening by gradient structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111, 7197 (2014).
Y. Guo, W.D. Compton, and S. Chandrasekar: In situ analysis of flow dynamics and deformation fields in cutting and sliding of metals. Proc. R. Soc. A 471, 2178 (2015).
T.G. Murthy, C. Saldana, M. Hudspeth, and R.M. Saoubi: Deformation field heterogeneity in punch indentation. Proc. R. Soc. A 470, 1 (2014).
W.L. Li, N.R. Tao, and K. Lu: Fabrication of a gradient nano-micro-structured surface layer on bulk copper by means of a surface mechanical grinding treatment. Scr. Mater. 59, 546 (2008).
T.S. Wang, J. Yang, C.J. Shang, X.Y. Li, B. Lv, M. Zhang, and F.C. Zhang: Sliding friction surface microstructure and wear resistance of 9SiCr steel with low-temperature austempering treatment. Surf. Coating. Technol. 202, 4036 (2008).
S. Basu and M.R. Shankar: Spatial confinement-induced switchover in microstructure evolution during severe plastic deformation at micrometer length scales. Acta Mater. 79, 146 (2014).
S. Basu, Z. Wang, R. Liu, and C. Saldana: Enhanced subsurface grain refinement during transient shear-based surface generation. Acta Mater. 116, 114 (2016).
T.L. Brown, C. Saldana, T.G. Murthy, J.B. Mann, Y. Guo, L.F. Allard, A.H. King, W.D. Compton, K.P. Trumble, and S. Chandrasekar: A study of the interactive effects of strain, strain rate and temperature in severe plastic deformation of copper. Acta Mater. 57, 5491 (2009).
A. Mahato, Y. Guo, N.K. Sundaram, and S. Chandrasekar: Surface folding in metals: A mechanism for delamination wear in sliding. Proc. R. Soc. A 470, 20140297 (2014).
I.J. Beyerlein and L.S. Tóth: Texture evolution in equal-channel angular extrusion. Prog. Mater. Sci. 54, 427 (2009).
C.F. Gu, L.S. Tóth, M. Arzaghi, and C.H.J. Davies: Effect of strain path on grain refinement in severely plastically deformed copper. Scr. Mater. 64, 284 (2011).
S. Basu and M. Ravi Shankar: Crystallographic textures resulting from severe shear deformation in machining. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46, 801 (2014).
D. Sagapuram, M. Efe, W. Moscoso, S. Chandrasekar, and K.P. Trumble: Controlling texture in magnesium alloy sheet by shear-based deformation processing. Acta Mater. 61, 6843 (2013).
H.A. Bruck, S.R. McNeill, M.A. Sutton, and W.H. Peters: Digital image correlation using Newton–Raphson method of partial differential correction. Exp. Mech. 29, 261 (1989).
P. Lava, S. Cooreman, and D. Debruyne: Study of systematic errors in strain fields obtained via DIC using heterogeneous deformation generated by plastic FEA. Optic Laser. Eng. 48, 457 (2010).
R.A. Lebensohn and C.N. Tomé: A self-consistent anisotropic approach for the simulation of plastic deformation and texture development of polycrystals: Application to zirconium alloys. Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 2611 (1993).
S. Li, I.J. Beyerlein, C.T. Necker, D.J. Alexander, and M. Bourke: Heterogeneity of deformation texture in equal channel angular extrusion of copper. Acta Mater. 52, 4859 (2004).
N. Fang: Tool-chip friction in machining with a large negative rake angle tool. Wear 258, 890 (2005).
C. Saldana, S. Basu, Z. Wang, and G.W. Woodruff: Deformation heterogeneity and texture in surface severe plastic deformation of copper. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 472, 20150486 (2016).
D.A. Hughes and N. Hansen: Microstructure and strength of nickel at large strains. Acta Mater. 48, 2985 (2000).
S. Abolghasem, S. Basu, and M.R. Shankar: Quantifying the progression of dynamic recrystallization in severe shear deformation at high strain rates. J. Mater. Res. 28, 2056 (2013).
S. Basu, Z. Wang, and C. Saldana: Anomalous evolution of microstructure and crystallographic texture during indentation. Acta Mater. 105, 25 (2016).
W. Polkowski, P. Jóźwik, M. Polański, and Z. Bojar: Microstructure and texture evolution of copper processed by differential speed rolling with various speed asymmetry coefficient. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 564, 289 (2013).
W.N. Findley and R.M. Reed: The influence of extreme speeds and rake angles in metal cutting. J. Eng. Ind. 85, 49 (1963).
W.H. Huang, L. Chang, P.W. Kao, and C.P. Chang: Effect of die angle on deformation texture of copper processed by equal channel angular extrussion. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 307, 113 (2001).
A. Gholinia, P. Bate, and P.B. Prangnell: Modelling texture development during equal channel angular extrusion of aluminium. Acta Mater. 50, 2121 (2002).
H. Beladi, P. Cizek, and P.D. Hodgson: Dynamic recrystallization of austenite in Ni–30% Fe model alloy: Microstructure and texture evolution. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 40, 1175 (2009).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported in part by NSF CMMI 1254818 and Third Wave Systems (via DOE subcontract DE-EE0005762).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Basu, S., Murthy, T.G. et al. Gradient microstructure and texture in wedge-based severe plastic burnishing of copper. Journal of Materials Research 33, 1046–1056 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.58
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.58