Abstract
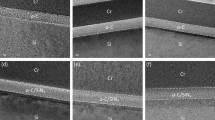
The structure of ultrathin amorphous carbon (a-C) films synthesized by filtered cathodic vacuum arc (FCVA) deposition was investigated by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, electron energy loss spectroscopy, and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Results of the plasmon excitation energy shift and through-thickness elemental concentration show a multilayered a-C film structure comprising an interface layer consisting of C, Si, and, possibly, SiC, a buffer layer with continuously increasing sp3 fraction, a relatively thicker layer (bulk film) of constant sp3 content, and an ultrathin surface layer rich in sp2 hybridization. A detailed study of the C K-edge spectrum indicates that the buffer layer between the interface layer and the bulk film is due to the partial backscattering of C+ ions interacting with the heavy atoms of the silicon substrate. The results of this study provide insight into the minimum thickness of a-C films deposited by FCVA under optimum substrate bias conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Robertson: Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 37, 129 (2002).
O.R. Monteiro: Thin film synthesis by energetic condensation. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 31, 111 (2001).
I.G. Brown: Cathodic arc deposition of films. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 28, 243 (1998).
A.A. Voevodin and M.S. Donley: Preparation of amorphous diamond-like carbon by pulsed laser deposition: A critical review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 82, 199 (1996).
M.K. Fung, K.H. Lai, C.Y. Chan, I. Bello, C.S. Lee, S.T. Lee, D.S. Mao, and X. Wang: Mechanical properties and corrosion studies of amorphous carbon on magnetic disks prepared by ECR plasma technique. Thin Solid Films 368, 198 (2000).
R. Hauert: An overview on the tribological behavior of diamond-like carbon in technical and medical applications. Tribol. Int. 37, 991 (2004).
A. Erdemir and C. Donnet: Tribology of diamond-like carbon films: Recent progress and future prospects. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39, R311 (2006).
H.-S. Zhang and K. Komvopoulos: Synthesis of ultrathin carbon films by direct current filtered cathodic vacuum arc. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 083305 (2009).
J. Díaz, G. Paolicelli, S. Ferrer, and F. Comin. Separation of the sp3 and sp2 components in the C1s photoemission spectra of amorphous carbon films. Phys. Rev. B 54, 8064 (1996).
N. Yasui, H. Inaba, K. Furusawa, M. Saito, and N. Ohtake: Characterization of head overcoat for 1 Tb/in2 magnetic recording. IEEE Trans. Magn. 45, 805 (2009).
J. Zhu, J. Han, X. Han, H.I. Schlaberg, and J. Wang: sp3-rich deposition conditions and growth mechanism of tetrahedral amorphous carbon films deposited using filtered arc. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 013512 (2008).
A.C. Ferrari and J. Robertson: Raman spectroscopy of amorphous, nanosrtructured, diamond-like carbon, and nanodiamond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 362, 2477 (2004).
A.C. Ferrari and J. Robertson: Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 61, 14095 (2000).
D.S. Knight and W.B. White: Characterization of diamond films by Raman spectroscopy. J. Mater. Res. 4, 385 (1989).
S. Oswald and R. Reiche: Binding state information from XPS depth profiling: Capabilities and limits. Appl. Surf. Sci. 179, 307 (2001).
P.R. Poudel, P.P. Poudel, B. Rout, M. El Bouanani, and F.D. McDaniel: An XPS study to investigate the dependence of carbon ion fluences in the formation of buried SiC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 283, 93 (2012).
M.P. Siegal, P.N. Provencio, D.R. Tallant, R.L. Simpson, B. Kleinsorge, and W.I. Milne: Bonding topologies in diamondlike amorphous-carbon films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2047 (2000).
C.A. Davis, G.A.J. Amaratunga, and K.M. Knowles: Growth mechanism and cross-sectional structure of tetrahedral amorphous carbon thin films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 3280 (1998).
C.A. Davis, K.M. Knowles, and G.A.J. Amaratunga: Cross-sectional structure of tetrahedral amorphous carbon thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 76-77, 316 (1995).
E. Riedo, F. Comin, J. Chevrier, F. Schmithusen, S. Decossas, and M. Sancrotti: Structural properties and surface morphology of laser-deposited amorphous carbon and carbon nitride films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 125, 124 (2000).
Y. Lifshitz, S.R. Kasi, J.W. Rabalais, and W. Eckstein: Subplantation model for film growth from hyperthermal species. Phys. Rev. B 41, 10468 (1990).
G.M. Pharr, D.L. Callahan, S.D. McAdams, T.Y. Tsui, S. Anders, A. Anders, J.W. Ager III, I.G. Brown, C.S. Bhatia, S.R.P. Silva, and J. Robertson: Hardness, elastic modulus, and structure of very hard carbon films produced by cathodic-arc deposition with substrate pulse biasing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 779 (1996).
J. Robertson: Requirements of ultrathin carbon coatings for magnetic storage technology. Tribol. Int. 36, 405 (2003).
J. Robertson: Ultrathin carbon coatings for magnetic storage technology. Thin Solid Films 383, 81 (2001).
E. Byon and A. Anders: Ion energy distribution functions of vacuum arc plasmas. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 1899 (2003).
H.-S. Zhang and K. Komvopoulos: Direct-current cathodic vacuum arc system with magnetic-field mechanism for plasma stabilization. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 073905 (2008).
N. Wang and K. Komvopoulos: Incidence angle effect of energetic carbon ions on deposition rate, topography, and structure of ultrathin amorphous carbon films deposited by filtered cathodic vacuum arc. IEEE Trans. Magn. 48, 2220 (2012).
D. Wan and K. Komvopoulos: Transmission electron microscopy and electron energy loss spectroscopy analysis of ultrathin amorphous carbon films. J. Mater. Res. 19, 2131 (2004).
D.B. Williams and C.B. Carter: Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Textbook for Materials Science (Springer, New York, 2009). Chapter 37, pp. 679–681.
R.F. Egerton: Electron Energy-Loss Spectroscopy in the Electron Microscope, 3rd ed. (Springer, New York, 2011). Chapter 3, pp. 111–229.
R.F. Egerton: Electron energy-loss spectroscopy in the TEM. Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 016502 (2009).
V. Olevano and L. Reining: Excitonic effects on the silicon plasmon resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5962 (2001).
D.R. McKenzie, D. Muller, and B.A. Pailthorpe: Compressive-stress-induced formation of thin-film tetrahedral amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 773 (1991).
A. Duarte-Moller, F. Espinosa-Magana, R. Martinez-Sanchez, M. Avalos-Borja, G.A. Hirata, and L. Cota-Araiza: Study of different forms of carbon by analytical electron microscopy. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 104, 61 (1999).
S.D. Berger, D.R. McKenzie, and P.J. Martin: EELS analysis of vacuum arc-deposited diamond-like films. Philos. Mag. Lett. 57, 285 (1988).
J.J. Cuomo, J.P. Doyle, J. Bruley, and J.C. Liu: Sputter deposition of dense diamond-like carbon films at low temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 58, 466 (1991).
R.J. Iwanowski, K. Fronc, W. Paszkowicz, and M. Heinonen: XPS and XRD study of crystalline 3C-SiC grown by sublimation method. J. Alloys Compd. 286, 143 (1999).
D. Wan and K. Komvopoulos: Tetrahedral and trigonal carbon atom hybridization in thin amorphous carbon films synthesized by radio-frequency sputtering. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 9891 (2007).
S. Tanuma, C.J. Powell, and D.R. Penn: Calculations of electron inelastic mean free paths II. Data for 27 elements over the 50-2000 eV range. Surf. Interface Anal. 17, 911 (1991).
W.H. Gries: A universal predictive equation for the inelastic mean free pathlengths of X-ray photoelectrons and Auger electrons. Surf. Interface Anal. 24, 38 (1996).
Acknowledgment
This research was funded by the Computer Mechanics Laboratory (CML) and the UCB-KAUST Academic Excellence Alliance (AEA) Program. TEM and XPS studies were performed at the National Center for Electron Microscopy and the Molecular Foundry, respectively, of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., Komvopoulos, K. The multilayered structure of ultrathin amorphous carbon films synthesized by filtered cathodic vacuum arc deposition. Journal of Materials Research 28, 2124–2131 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.206
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.206