Abstract
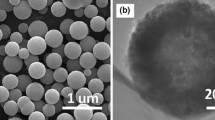
A one-step wet chemistry route has been explored to synthesize hollow hydroxyl titanium oxalate nanoscale spheres under mild experimental conditions. The hollow spheres were ∼200 nm in diameter, with a shell thickness of ∼30 nm. The nanospheres were formed by smaller aggregated colloidal subunits. The influence of temperature and solvent on the structure of the nanospheres was investigated. The formation of hollow interiors in the nanospheres may be rationalized by Ostwald ripening mechanism. Simple thermal treatment topotactically transformed the chemical composition into anatase TiO2. The high-order hollow porous spherical structure was preserved, with smaller crystalline anatase TiO2 nanoparticles as building units. Dense hydroxyl titanium oxalate nanospheres and their corresponding non-hollow porous anatase TiO2 nanospheres were also successfully achieved in suitable reaction conditions. The method and procedure reported herein may be extended in principle for the fabrication of other functional materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Caruso, R.A. Caruso, and H. Mohwald: Nanoengineering of inorganic and hybrid hollow spheres by colloidal templating. Science 282, 1111 (1998).
X.W. Lou, L.A. Archer, and Z.C. Yang: Hollow micro-/nanostructures: Synthesis and applications. Adv. Mater. 20, 3987 (2008).
Z.W. Shan, G. Adesso, A. Cabot, M.P. Sherburne, S.A.S. Asif, O.L. Warren, D.C. Chrzan, A.M. Minor, and A.P. Alivisatos: Ultrahigh stress and strain in hierarchically structured hollow nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 7, 947 (2008).
J. Goldberger, R.R. He, Y.F. Zhang, S.W. Lee, H.Q. Yan, H.J. Choi, and P.D. Yang: Single-crystal gallium nitride nanotubes. Nature 422, 599 (2003).
D. Deng and J.Y. Lee: A family of aligned C-curved nanoarches. ACS Nano 3, 1723 (2009).
A.D. Dinsmore, M.F. Hsu, M.G. Nikolaides, M. Marquez, A.R. Bausch, and D.A. Weitz: Colloidosomes: Selectively permeable capsules composed of colloidal particles. Science 298, 1006 (2002).
H. Strohm and P. Lobmann: Porous TiO2 hollow spheres by liquid phase deposition on polystyrene latex-stabilised Pickering emulsions. J. Mater. Chem. 14, 2667 (2004).
F.Q. Guo, Z.F. Zhang, H.F. Li, S.L. Meng, and D.Q. Li: A solvent extraction route for CaF2 hollow spheres. Chem. Commun. 46, 8237 (2010).
J. Li and H.C. Zeng: Hollowing Sn-doped TiO2 nanospheres via Ostwald ripening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 15839 (2007).
W. Cheng, K.B. Tang, Y.X. Qi, J. Sheng, and Z.P. Liu: One-step synthesis of superparamagnetic monodisperse porous Fe3O4 hollow and core-shell spheres. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 1799 (2010).
X.M. Yin, C.C. Li, M. Zhang, Q.Y. Hao, S. Liu, L.B. Chen, and T.H. Wang: One-step synthesis of hierarchical SnO2 hollow nanostructures via self-assembly for high power lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 8084 (2010).
R.B. Zheng, X.W. Meng, F.Q. Tang, L. Zhang, and J. Ren: A general, one-step and template-free route to rattle-type hollow carbon spheres and their application in lithium battery anodes. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 13065 (2009).
H.G. Yang and H.C. Zeng: Preparation of hollow anatase TiO2 nanospheres via Ostwald ripening. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 3492 (2004).
X.W. Lou, D. Deng, J.Y. Lee, J. Feng, and L.A. Archer: Self-supported formation of needlelike Co3O4 nanotubes and their application as lithium-ion battery electrodes. Adv. Mater. 20, 258 (2008).
D. Deng and J.Y. Lee: Hollow core-shell mesospheres of crystalline SnO2 nanoparticle aggregates for high capacity Li+ ion storage. Chem. Mater. 20, 1841 (2008).
Y.X. Li, G. Chen, Q. Wang, X. Wang, A.K. Zhou, and Z.Y. Shen: Hierarchical ZnS-In2S3-CuS nanospheres with nanoporous structure: Facile synthesis, growth mechanism, and excellent photocatalytic activity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 3390 (2010).
F.H. Liu, G.J. Xu, J.H. Wu, Y.C. Cheng, J.J. Guo, and P. Cui: Preparation and electrorheological properties of a hydroxyl titanium oxalate suspension. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 125015 (2009).
W.J. Wen, X.X. Huang, S.H. Yang, K.Q. Lu, and P. Sheng: The giant electrorheological effect in suspensions of nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2, 727 (2003).
D. Zhang, H.D. Su, and H. Gao: Study on adsorption behavior of nanosized barium-strontium titanate powder for lead ion in water using FAAS. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 28, 218 (2008).
X. Chen and S.S. Mao: Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 107, 2891 (2007).
D. Deng, M.G. Kim, J.Y. Lee, and J. Cho: Green energy storage materials: Nanostructured TiO2 and Sn-based anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2, 818 (2009).
C.W. Peng, M. Richard-Plouet, T.Y. Ke, C.Y. Lee, H.T. Chiu, C. Marhic, E. Puzenat, F. Lemoigno, and L. Brohan: Chimie douce route to sodium hydroxo titanate nanowires with modulated structure and conversion to highly photoactive titanium dioxides. Chem. Mater. 20, 7228 (2008).
H.L. Choi and C. Park: Effect of ultrasonic treatment on ripening of titanium oxalate salt from solution. J. Mater. Sci. 34, 3591 (1999).
J.H. Choy, Y.S. Han, and S.J. Kim: Oxalate coprecipitation route to the piezoelectric Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 oxide. J. Mater. Chem. 9, 1807 (1997).
T. Berger, A. Rodes, and R. Gomez: Oxalic acid photooxidation on rutile nanowire electrodes. PCCP 12, 10503 (2010).
J. Fang, F. Wang, K. Qian, H.Z. Bao, Z.Q. Jiang, and W.X. Huang: Bifunctional N-doped mesoporous TiO2 photocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 18150 (2008).
T. Thongtem and S. Thongtem: Characterization of Bi4Ti3O12 powder prepared by the citrate and oxalate coprecipitation processes. Ceram. Int. 30, 1463 (2004).
X. Feng, L. Yang, and Y. Liu: A simple one-step fabrication of micrometer-scale hierarchical TiO2 hollow spheres. Mater. Lett. 64, 2688 (2010).
S. Zhang, C. Liu, Y. Liu, Z. Zhang, and G. Li: Fabrication of micrometer-scale anatase-phase TiO2 congeries assembled with hollow spheres. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 2067 (2008).
J. Yu and J. Zhang: A simple template-free approach to TiO2 hollow spheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Dalton Trans. 39, 5860 (2010).
G. Madras and B.J. McCoy: Temperature effects during Ostwald ripening. J. Chem. Phys. 119, 1683 (2003).
B. Liu and H.C. Zeng: Symmetric and asymmetric Ostwald ripening in the fabrication of homogeneous core-shell semiconductors. Small 1, 566 (2005).
K.L. Roberts and E.J. Markel: Generation of Mo2N nanoparticles from topotactic Mo2N crystallites. J. Phys. Chem. 98, 4083 (1994).
A. Kolmakov, Y.X. Zhang, and M. Moskovits: Topotactic thermal oxidation of Sn nanowires: Intermediate suboxides and core-shell metastable structures. Nano Lett. 3, 1125 (2003).
S.M. Liu, L.M. Gan, L.H. Liu, W.D. Zhang, and H.C. Zeng: Synthesis of single-crystalline TiO2 nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 14, 1391 (2002).
L. Liu, J.S. Qian, B. Li, Y.M. Cui, X.F. Zhou, X.F. Guo, and W.P. Ding: Fabrication of rutile TiO2 tapered nanotubes with rectangular cross-sections via anisotropic corrosion route. Chem. Commun. 46, 2402 (2010).
B. Liu and E.S. Aydil: Growth of oriented single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanorods on transparent conducting substrates for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 3985 (2009).
Z.Y. Zhong, Y.D. Yin, B. Gates, and Y.N. Xia: Preparation of mesoscale hollow spheres of TiO2 and SnO2 by templating against crystalline arrays of polystyrene beads. Adv. Mater. 12, 206 (2000).
V.G. Erkov, S.F. Devyatova, E.L. Molodstova, T.V. Malsteva, and U.A. Yanovskii: Si-TiO2 interface evolution at prolonged annealing in low vacuum or N2O ambient. Appl. Surf. Sci. 166, 51 (2000).
J.Y. Zhang, I.W. Boyd, B.J. O’Sullivan, P.K. Hurley, P.V. Kelly, and J.P. Senateur: Nanocrystalline TiO2 films studied by optical, XRD and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 303, 134 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, D., Martin, S.T. & Ramanathan, S. Synthesis of hollow porous nanospheres of hydroxyl titanium oxalate and their topotactic conversion to anatase titania. Journal of Materials Research 26, 1545–1551 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.149
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.149