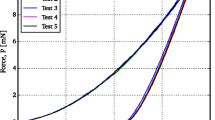
Abstract
Finite element analysis is used to simulate cone indentation creep in materials across a wide range of hardness, strain rate sensitivity, and work-hardening exponent. Modeling reveals that the commonly held assumption of the hardness strain rate sensitivity (mH) equaling the flow stress strain rate sensitivity (ms) is violated except in low hardness/modulus materials. Another commonly held assumption is that for self-similar indenters the indent area increases in proportion to the (depth)2 during creep. This assumption is also violated. Both violations are readily explained by noting that the proportionality “constants” relating (i) hardness to flow stress and (ii) area to (depth)2 are, in reality, functions of hardness/modulus ratio, which changes during creep. Experiments on silicon, fused silica, bulk metallic glass, and poly methyl methacrylate verify the breakdown of the area-(depth)2 relation, consistent with the theory. A method is provided for estimating area from depth during creep.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.G. Atkins, A. Silverio, D. Tabor Indentation hardness and creep of solids. J. Inst. Met. 94, (Part 11) 369 (1966)
S.N.G. Chu, J.C.M. Li Impression creep: A new creep test. J. Mater. Sci. 12, (11) 2200 (1977)
T.O. Mulhearn, D. Tabor Creep and hardness of metals: A physical study. J. Inst. Met. 89, 7 (1960)
Y-T Cheng, C-M Cheng Scaling, dimensional analysis, and indentation measurements. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44, (4–5) 91 (2004)
A.F. Bower, N.A. Fleck, A. Needleman, N. Ogbonna Indentation of a power law creeping solid. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 1993, (441) 97 (1911)
R. Hill Similarity analysis of creep indentation tests. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 1992, (436) 617 (1898)
U.F. Kocks, A.S. Argon, M.F. Ashby Thermodynamics and kinetics of slip Progress in Materials Science Vol. 19 (Pergamon Press, New York 1975)
D. Jang, M. Atzmon Grain-size dependence of plastic deformation in nanocrystalline Fe. J. Appl. Phys. 93, (11) 9282 (2003)
F. Wang, P. Huang, K.W. Xu Time dependent plasticity at real nanoscale deformation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, (16) 161921 (2007)
S.P. Hannula, D. Stone, C.Y. Li Determination of time-dependent plastic properties of metals by indentation load relaxation techniques Electronic Packaging Materials Science edited by E.A. Giess, K-N. Tu, and D.R. Uhlmann (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc 40, Pittsburgh, PA 1985) 217–224
D.S. Stone, K.B. Yoder Division of the hardness of molybdenum into rate-dependent and rate-independent components. J. Mater. Res. 9, (10) 2524 (1994)
B.N. Lucas, W.C. Oliver Time dependent indentation testing at non-ambient temperatures utilizing the high temperature mechanical properties microprobe Thin Films: Stresses and Mechanical Properties V edited by S.P. Baker, C.A. Ross, P.H. Townsend, C.A. Volkert, and P. Børgesen (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc 356, Pittsburgh, PA 1995) 645
M.F. Tambwe, D.S. Stone, A.J. Griffin, H. Kung, Y.C. Lu, M. Nastasi Haasen plot analysis of the Hall-Petch effect in Cu–Nb nanolayer composites. J. Mater. Res. 14, (2) 407 (1999)
A.A. Elmustafa, S. Kose, D.S. Stone The strain-rate sensitivity of the hardness in indentation creep. J. Mater. Res. 22, (4) 926 (2007)
W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19, (1) 3 (2004)
M.F. Doerner, W.D. Nix A method for interpreting the data from depth-sensing indentation instruments. J. Mater. Res. 1, (4) 601 (1986)
W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr Improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, (6) 1564 (1992)
A.A. Elmustafa, D.S. Stone Strain rate sensitivity in nanoindentation creep of hard materials. J. Mater. Res. 22, (10) 2912 (2007)
D.L. Goldsby, A. Rar, G.M. Pharr, T.E. Tullis Nanoindentation creep of quartz, with implications for rate- and state-variable friction laws relevant to earthquake mechanics. J. Mater. Res. 19, (1) 357 (2004)
A. Rar, S. Sohn, W.C. Oliver, D.L. Goldsby, T.E. Tullis, G.M. Pharr On the measurement of creep by nanoindentation with continuous stiffness techniques Fundamentals of Nanoindentation and Nanotribology III edited by K.J. Wahl, N. Huber, A.B. Mann, D.F. Bahr, and Y-T. Cheng (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc 841, Warrendale, PA 2005) R4.2
K.L. Johnson Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK 1985) 452
G. Kermouche, J.L. Loubet, J.M. Bergheau Cone indentation of time-dependent materials: The effects of the indentation strain rate. Mech. Mater. 39, (1) 24 (2007)
G. Kermouche, J.L. Loubet, J.M. Bergheau A new index to estimate the strain rate sensitivity of glassy polymers using conical/pyramidal indentation. Philos. Mag. 86, (33–35) 5667 (2006)
M. Sakai, T. Akatsu, S. Numata, K. Matsuda Linear strain hardening in elastoplastic indentation contact. J. Mater. Res. 18, (9) 2087 (2003)
D. Tabor The Hardness of Metals (Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK 1951)
A. Bolshakov, G.M. Pharr Influences of pileup on the measurement of mechanical properties by load and depth-sensing indentation techniques. J. Mater. Res. 13, (4) 1049 (1998)
R. Quinson, J. Perez, M. Rink, A. Pavan Yield criteria for amorphous glassy polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 32, (5) 1371 (1997)
C.A. Schuh, T.G. Nieh A survey of instrumented indentation studies on metallic glasses. J. Mater. Res. 19, (1) 46 (2004)
J.B. Puthoff, J.E. Jakes, H. Cao, D.S. Stone Investigation of thermally activated deformation in amorphous PMMA and Zr–Cu–Al bulk metallic glasses with broadband nanoindentation creep. J. Mater. Res. 24, (3) 1279 (2009)
S.A.S. Asif, K.J. Wahl, R.J. Colton, O.L. Warren Quantitative imaging of nanoscale mechanical properties using hybrid nanoindentation and force modulation. J. Appl. Phys. 90, (3) 1192 (2001)
J.E. Jakes, C.R. Frihart, J.F. Beecher, R.J. Moon, P.J. Resto, Z.H. Melgarejo, O.M. Suarez, H. Baumgart, A.A. Elmustafa, D.S. Stone Nanoindentation near the edge. J. Mater. Res. 24, (3) 1016 (2009)
J.E. Jakes, C.R. Frihart, J.F. Beecher, R.J. Moon, D.S. Stone Experimental method to account for structural compliance in nanoindentation measurements. J. Mater. Res. 23, (4) 1113 (2008)
M. Sakai, Y. Nakano Elastoplastic load–depth hysteresis in pyramidal indentation. J. Mater. Res. 17, (8) 2161 (2002)
J.H. Strader, S. Shim, H. Bei, W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr An experimental evaluation of the constant relating the contact stiffness to the contact area in nanoindentation. Philos. Mag. 86, (33–35) 5285 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Articles in this section are based on presentations that were selected by MRS Meeting Symposium Organizers as outstanding papers. Upon selection, authors are invited to submit their research results to Journal of Materials Research. These papers are subject to the same peer review and editorial standards as all other JMR papers. This is another way by which the Materials Research Society recognizes high quality papers presented at its meetings.
This paper was selected as an Outstanding Symposium Paper for the 2007 MRS Fall Meeting, Symposium AA Proceedings, Vol. 1049.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stone, D.S., Joseph, J.E., Puthoff, J. et al. Analysis of indentation creep. Journal of Materials Research 25, 611–621 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2010.0092
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2010.0092