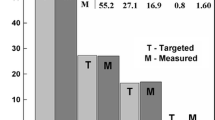
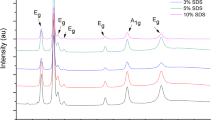
Abstract
Results of an investigation of the interaction potential of synthetic and pre-treated calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) [with hexadecyltrimethylammonium (HDTMA)] are reported. The effective and strong interaction of these molecules with the C-S-H surface was shown using 13C and 29Si cross polarization magic angle spinning (CP MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance, x-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis. The HDTMA–C-S-H interaction is influenced by the poorly crystallized layered structure of C-S-H. An indefinite number of layers and an irregular arrangement are confirmed by the SEM images. The position and shape of the 002 reflection of C-S-H are affected by drying procedures, chemical pre-treatment, and reaction temperature. Recovery of the initial 002 peak position after severe drying and rewetting with distilled water or interaction with HDTMA is incomplete but accompanied by an increase in intensity. It is inferred that the stability of C-S-H binders in concrete can be affected by a variation in nanostructure resulting from engineering variables such as curing temperature and use of chemical admixtures.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.W. Brown, H.F.W. Taylor: The role of ettringite in external sulfate attack in Materials Science of Concrete: Special Volume on Sulfate Attack Mechanisms edited by J. Marchand and J.P. Skalny American Ceramic Society Westerville, OH 2000 73
J. Marchand: Modeling the behavior of unsaturated cement systems exposed to aggressive chemical environments. Mater. Struct. 34, 195 2001
H.F.W. Taylor, C. Famy, K. Scrivener: Delayed ettringite formation. Cem. Concr. Res. 31, 683 2001
G.G. Litvan: Volume stability of porous solids. Part I in Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Chemistry of Cement, Paris, France 1980 3, VII–46–VII–50
J.A. Raussell-Colom, M.J. Serraiosa: in Chemistry of Clays and Clay Minerals edited by A.C.D. Newman Mineralogical Society London 1987 371
P.C. Lebaron, Z. Wang, T.J. Pinnavaia: Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: An overview. Appl. Clay Sci. 15, 11 1999
E.P. Giannelis: Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: Synthesis, properties and applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 12, 675 1998
R.K. Bharadwaj: Modeling the barrier properties of polymer layered silicate nanocomposites. Macromolecules 34, 1989 2001
J.W. Gilman, T. Kashiwagi, J.D. Lichtenhan: Flammability studies of polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites. SAMPE J. 33, 40 1997
R.S. Sinha, K. Yamada, M. Okamoto, K. Ueda: New polylactide/ layered silicate nanocomposite: A novel biodegradable material. Nano Lett. 2, 1093 2002
H. Van Olphen: Interaction of clays and organic compounds in An Introduction to Clay and Colloid Chemistry John Wiley & Sons New York 1977 318
J.J. Tunney, C. Detellier: Interlammellar covalent grafting of organic units on kaolinite. Chem. Mater. 5, 747 1993
J.J. Tunney, C. Detellier: Preparation and characterization of an 8.4 A hydrate kaolinite. Clays Clay Miner. 42, 552 1994
B. Velde: Clay structures in Introduction to Clay Minerals edited by B. Velde Chapman and Hall London, UK 1992 195
W. Dosch: Interlamellar reaction of tetracalcium aluminate hydrates with water and organic compounds in Proceedings of the 15th National Conference on Clay and Clay Minerals, edited by S.W. Bailey Pergamon Press NY 1966 273–292
V.H. Terisse, A. Nonat, C.J. Petit: Zeta potential study of calcium silicate hydrates interacting with alkaline cations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 244, 58 2001
I.G. Richardson: Tobermorite/jennite and tobermorite/calcium hydroxide-based models for the structure of C-S-H: Applicability to hardened pastes of tricalcium silicate, β-dicalcium silicate, Portland cement and blends of Portland cement with blast furnace slag, metakaolin or silica fume. Cement Concrete Res. 34, 1733 2004
I. Pointeau, B. Piriou, M. Fedoroff, G.M. Bartes, N. Marmier, F. Fromage: Sorption mechanisms of Eu3+ on C-S-H phases of hydrated cements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 236, 252 2001
A.J. Allen, J.J. Thomas, H. Jennings: Composition and density of nanoscale calcium-silicate-hydrate in cement. Nat. Mater. 6, 311 2007
R.F. Feldman, P.J. Sereda: The new model for hydrated Portland cement and its practical implications. Eng. J. 53, 53 1970
H.W. Taylor: Hydration of the calcium silicate phases in Cement Chemistry Academic Press London, UK 1990 475
S.A. Hamid: The crystal structure of the 11A tobermorite Ca2.25[Si3O7.5(OH)1.5] ⋅ 1H2O. Z. Kristallogr. 154, 189 1981
R.F. Feldman, P.J. Sereda: A model for hydrated Portland cement paste as deduced from sorption-length change and mechanical properties. Mater. Construct. 1, 509 1968
J.J. Beaudoin: Why engineers need materials science. Concrete Int. 21, 86 1999
L.B. Alemany, D.M. Grant, T.D. Alger, R.J. Pugmire: Cross-polarization and magic angle spinning NMR spectra of model organic compounds 3. Effect of 13C–1H dipolar interaction on cross-polarization and carbon proton dephasing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 6697 1983
S.J. Opella, M.H. Frey: Selection of protonated carbon resonances in solid state nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 101, 5954 1979
J.A. Ripmeester, N.E. Burlinson: Chiral discrimination and solid state 13C NMR. Application to tri-o-thymotide clathrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107, 3713 1985
H. Viallis, P. Faucon, J.C. Petit, A. Nonat: Interaction between salts (NaCl, CsCl) and calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H). J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 6697 1999
H. Matsuyama, J.F. Young: Intercalation of polymers in calcium silicate hydrate: A new synthetic approach to biocomposites. Chem. Mater. 11, 16 1999
A. Franceschini, S. Abramson, B. Bresson, H. Vandamme, N. Lequeux: Cement-silylated polymers nanocomposites in Proc. 12th Int. Cong. Chem. Cem., Theme ST5, edited by J.J. Beaudoin, J.M. Maker, and L. Raki, National Research Council Canada 2007
H.F.W. Taylor: Hydration of the calcium silicate phases in Cement Chemistry 2nd ed. Thomas Telford London, UK 1997 475
H. Drame, J.J. Beaudoin, L. Raki: Volume stability of hydrated calcium silicate systems exposed to aqueous salt solutions. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 6837 2007
R.F. Feldman, V.S. Ramachandran: Microstructure of calcium hydroxide depleted Portland cement paste. I: Density and helium flow measurements. Cem. Con. Res. 12, 179 1982
G.W. Brindley, R.W. Hoffman: Orientation and packing of aliphatic chain molecules on montmorillonite. Clays Clay Miner. 9, 546 1962
X. Cong, R.J. Kirkpatrick: Effects of the temperature and relative humidity on the structure of C-S-H gel. Cem. Concr. Res. 25, 1237 1995
A.H. Delgado, R.M. Paroli, J.J. Beaudoin: Comparison of IR techniques for the characterization of construction cement and hydrated products. Appl. Spec. 50, 970 1996
P. Yu, R.J. Kirkpatrick, B. Poe, P.F. Mcmillan: Structure of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H): Near-, mid-, and far-infrared spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 742 1999
H.F.W. Taylor, A.B. Turner: Reactions of tricalcium silicate paste with organic liquids. Cem. Concr. Res. 17, 613 1987
J.J. Beaudoin: Thermal analysis and IR spectroscopy in Handbook of analytical techniques in concrete science and technology edited by V.S. Ramachandran and J.J. Beaudoin William Andrew Publishers New York 2001 964
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beaudoin, J.J., Dramé, H., Raki, L. et al. Formation and characterization of calcium silicate hydrate–hexadecyltrimethylammonium nanostructure. Journal of Materials Research 23, 2804–2815 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0342
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0342