Abstract
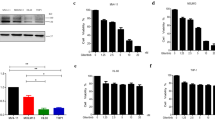
Flt3 internal tandem duplication (Flt3-ITD) is a prevalent mutation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Flt3-ITD constitutively activates various signaling pathways, including a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. Arsenic trioxide (ATO) and MEK inhibition were recently reported to interact synergistically to induce apoptosis in AML cells. In this study, we aimed to clarify whether ATO and Flt3 inhibition would be a mor specific and efficient therapy for Flt3-ITD cells.We demonstrate that the combination of ATO and an Flt3 inhibitor,AG1296, profoundly inhibits the growth of Flt3-ITD cells and induces their apoptosis. We further revealed that this combined treatment potently inhibits the ERK activity that might be responsible for cell growth. Moreover, using the Chou-Talalay method, we observed a synergistic growth-inhibitory effect for ATO and AG1296 in Flt3-ITD cells (BaF3-Flt3-ITD, MV4-11, and PL-21 cells), but not in Flt3 wild-type cells (RS4-11 and NB4 cells), for almost all dose ranges tested. Our results provide an experimental basis for a specific and efficient therapy for Flt3-ITD cells that involves combined treatment with Flt3 inhibitors and ATO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yokota S, Kiyoi H, Nakao M, et al. Internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 gene is preferentially seen in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome among various hematological malignancies: a study on a large series of patients and cell lines. Leukemia. 1997;11:1605–1609.
Gilliland DG, Griffin JD. The roles of FLT3 in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Blood. 2002;100:1532–1542.
Hayakawa F, Towatari M, Kiyoi H, et al. Tandem-duplicated Flt3 constitutively activates STAT5 and MAP kinase and introduces autonomous cell growth in IL-3-dependent cell lines. Oncogene. 2000;19:624–631.
Takahashi S, McConnell MJ, Harigae H, et al. The Flt3 internal tandem duplication mutant inhibits the function of transcriptional repressors by blocking interactions with SMRT. Blood. 2004;103:4650–4658.
Radomska HS, Basseres DS, Zheng R, et al. Block of C/EBP± function by phosphorylation in acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3 activating mutations. J Exp Med. 2006;203:371–381.
Stone RM, DeAngelo DJ, Klimek V, et al. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia and an activating mutation in FLT3 respond to a small-molecule FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, PKC412. Blood. 2005;105:54–60.
Fiedler W, Serve H, Dohner H, et al. A phase 1 study of SU11248 in the treatment of patients with refractory or resistant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or not amenable to conventional therapy for the disease. Blood. 2005;105:986–993.
Levis M, Pham R, Smith BD, Small D. In vitro studies of a FLT3 inhibitor combined with chemotherapy: sequence of administration is important to achieve synergistic cytotoxic effects. Blood. 2004;104:1145–1150.
Yee KW, Schittenhelm M, O’Farrell AM, et al. Synergistic effect of SU11248 with cytarabine or daunorubicin on FLT3 ITD-positive leukemic cells. Blood. 2004;104:4202–4209.
Miranda MB, McGuire TF, Johnson DE. Importance of MEK-1/-2 signaling in monocytic and granulocytic differentiation of myeloid cell lines. Leukemia. 2002;16:683–692.
Kelly LM, Liu Q, Kutok JL, Williams IR, Boulton CL, Gilliland DG. FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutations associated with human acute myeloid leukemias induce myeloproliferative disease in a murine bone marrow transplant model. Blood. 2002;99:310–318.
Milella M, Kornblau SM, Estrov Z, et al. Therapeutic targeting of the MEK/MAPK signal transduction module in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest. 2001;108:851–859.
Lunghi P, Tabilio A, Lo-Coco F, Pelicci PG, Bonati A. Arsenic trioxide (ATO) and MEK1 inhibition synergize to induce apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2005;19:234–244.
Lunghi P, Costanzo A, Salvatore L, et al. MEK1 inhibition sensitizes primary acute myelogenous leukemia to arsenic trioxideinduced apoptosis. Blood. 2006;107:4549–4553.
Takahashi S, Harigae H, Kameoka J, Sasaki T, Kaku M. AML1B transcriptional repressor function is impaired by the Flt3-internal tandem duplication. Br J Haematol. 2005;130:428–436.
Takahashi S, Harigae H, Kaku M, Sasaki T, Licht JD. Flt3 mutation activates p21WAF1/CIP1 gene expression through the action of STAT5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;316:85–92.
Takahashi S. Inhibition of the MEK/MAPK signal transduction pathway strongly impairs the growth of Flt3-ITD cells. Am J Hematol. 2006;81:154–155.
Takahashi S, Furuyama K, Kobayashi A, et al. Cloning of a coproporphyrinogen oxidase promoter regulatory element binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;273:596–602.
Inomata M, Takahashi S, Harigae H, Kameoka J, Kaku M, Sasaki T. Inverse correlation between Flt3 and PU.1 expression in acute myeloblastic leukemias. Leuk Res. 2006;30:659–664.
Takahashi S, Harigae H, Ishii KK, et al. Over-expression of Flt3 induces NF-kB pathway and increases the expression of IL-6. Leuk Res. 2005;29:893–899.
Tse KF, Allebach J, Levis M, Smith BD, Bohmer FD, Small D. Inhibition of the transforming activity of FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutants from AML patients by a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Leukemia. 2002;16:2027–2036.
Simbulan-Rosenthal CM, Rosenthal DS, Iyer S, Boulares AH, Smulson ME. Transient poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of nuclear proteins and role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in the early stages of apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13703–13712.
Yang X, Liu L, Sternberg D, et al. The FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutation prevents apoptosis in interleukin-3-deprived BaF3 cells due to protein kinase A and ribosomal S6 kinase 1-mediated BAD phosphorylation at serine 112. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7338–7347.
Zhang TD, Chen GQ, Wang ZG, Wang ZY, Chen SJ, Chen Z. Arsenic trioxide, a therapeutic agent for APL. Oncogene. 2001;20:7146–7153.
George P, Bali P, Cohen P, et al. Cotreatment with 17-allylaminodemethoxygeldanamycin and FLT-3 kinase inhibitor PKC412 is highly effective against human acute myelogenous leukemia cells with mutant FLT-3. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3645–3652.
Yao Q, Nishiuchi R, Kitamura T, Kersey JH. Human leukemias with mutated FLT3 kinase are synergistically sensitive to FLT3 and Hsp90 inhibitors: the key role of the STAT5 signal transduction pathway. Leukemia. 2005;19:1605–1612.
Lopes de Menezes DE, Peng J, Garrett EN, et al. CHIR-258: a potent inhibitor of FLT3 kinase in experimental tumor xenograft models of human acute myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5281–5291.
Kubonishi I, Machida K, Niiya K, et al. Establishment of a new peroxidase-positive human myeloid cell line, PL-21. Blood. 1984;63:254–259.
Quentmeier H, Reinhardt J, Zaborski M, Drexler HG. FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines. Leukemia. 2003;17:120–124.
Lanotte M, Martin-Thouvenin V, Najman S, Balerini P, Valensi F, Berger R. NB4, a maturation inducible cell line with t(15;17) marker isolated from a human acute promyelocytic leukemia (M3). Blood. 1991;77:1080–1086.
Cavigelli M, Li WW, Lin A, Su B, Yoshioka K, Karin M. The tumor promoter arsenite stimulates AP-1 activity by inhibiting a JNK phosphatase. EMBO J. 1996;15:6269–6279.
Ludwig S, Hoffmeyer A, Goebeler M, et al. The stress inducer arsenite activates mitogen-activated protein kinases extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 via a MAPK kinase 6/p38-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1917–1922.
Huang C, Ma WY, Li J, Goranson A, Dong Z. Requirement of Erk, but not JNK, for arsenite-induced cell transformation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:14595–14601.
Baines P, Fisher J, Truran L, et al. The MEK inhibitor, PD98059, reduces survival but does not block acute myeloid leukemia blast maturation in vitro. Eur J Haematol. 2000;64:211–218.
Lunghi P, Tabilio A, DallAglio PP, et al. Downmodulation of ERK activity inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of primary acute myelogenous leukemia blasts. Leukemia. 2003;17:1783–1793.
Morgan MA, Dolp O, Reuter CW. Cell-cycle-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK-1/2) in myeloid leukemia cell lines and induction of growth inhibition and apoptosis by inhibitors of RAS signaling. Blood. 2001;97:1823–1834.
Lowenberg B, Downing JR, Burnett A. Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1051–1062.
Douer D, Tallman MS. Arsenic trioxide: new clinical experience with an old medication in hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2396–2410.
Hunter HM, Pallis M, Seedhouse CH, Grundy M, Gray C, Russell NH. The expression of P-glycoprotein in AML cells with FLT3 internal tandem duplications is associated with reduced apoptosis in response to FLT3 inhibitors. Br J Haematol. 2004;127:26–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, S., Harigae, H., Yokoyama, H. et al. Synergistic Effect of Arsenic Trioxide and Flt3 Inhibition on Cells with Flt3 Internal Tandem Duplication. Int J Hematol 84, 256–261 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.06076
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.06076