Abstract
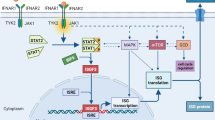
Interferon ζ (IFN-ζ)/limitin has been regarded as a novel type IIFN by the Nomenclature Committee of the International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research. IFN-ζ/limitin, which has some sequence homology with IFN-α and IFN-ß, has a globular structure with 5 α helices and 4 loops and recognizes IFN-α/ß receptor. Although it displays antiviral, immunomodulatory, and antitumor effects, IFN-ζ/limitin has much less lymphomyelosuppressive activity than IFN-α. Unique interactions between IFN-ζ/limitin and the receptor probably led to the narrow range of signals and biological activities. A human homologue of IFN-ζ/limitin may be clinically more effective than IFN-α and IFN-ß because it has fewer adverse effects. Moreover, further analysis of the structure-function relationship may establish an engineered cytokine with the useful features of IFN-ζ/ limitin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maeyer E, Maeyer-Guignard J. Type I interferon. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;17:53–73.
Pfeffer LM, Dinarello CA, Herberman RB, et al. Biological properties of recombinant α-interferons: 40th anniversary of the discovery of interferons. Cancer Res. 1998;58:2489–2499.
LaFleur DW, Nardelli B, Tsareva T, et al. Interferon-kappa, a novel type I interferon expressed in human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:39765–39771.
Kotenko SV, Gallagher G, Baurin VV, et al. IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:69–77.
Sheppard P, Kindsvogel W, Xu W, et al. IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:63–68.
Kincade PW, Medina K, Pietrangeli CE, Hayashi S-I, Naemen AE. Stromal cell lines which support lymphocyte growth II: characteristics of a suppressive subclone. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;292:227–234.
Oritani K, Medina KL, Tomiyama Y, et al. Limitin: an interferon- like cytokine that preferentially influences B-lymphocyte precursors. Nat Med. 2000;6:659–666.
Kawamoto S, Oritani K, Asada H, et al. Antiviral activity of limitin against encephalomyocarditis virus, herpes simplex virus, and mouse hepatitis virus: diverse requirements by limitin and alpha interferon for interferon regulatory factor 1. J Virol. 2003;77:9622–9631.
Takahashi I, Kosaka H, Oritani K, et al. A new IFN-like cytokine, limitin, modulates the immune response without influencing thymocyte development. J Immunol. 2001;167:3156–3163.
Domanski P, Colamonici OR. The type-I interferon receptor: the long and short of it. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1996;7:143–151.
Cohen B, Novick D, Barak S, Rubinstein M. Ligand-induced association of the type I interferon receptor components. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:4208–4214.
Yan H, Krishnan K, Lim JT, Contillo LG, Krolewski JJ. Molecular characterization of an alpha interferon receptor 1 subunit (IFNaR1) domain required forTYK2 binding and signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:2074–2082.
Leung S, Qureshi SA, Kerr IM, Darnell JE Jr, Stark GR. Role of STAT2 in the alpha interferon signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:1312–1317.
Improta T, Schindler C, Horvath CM, et al. Transcription factor ISGF-3 formation requires phosphorylated Stat91 protein, but Stat113 protein is phosphorylated independently of Stat91 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:4776–4780.
Haque SJ, Williams BR. Identification and characterization of an interferon (IFN)-stimulated response element-IFN-stimulated gene factor 3-independent signaling pathway for IFN-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:19523–19529.
Taniguchi T, Ogasawara K, Takaoka A, Tanaka N. IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:623–655.
Ahmad S, Alsayed YM, Druker BJ, Platanias LC. The type I interferon receptor mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of the CrkL adaptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29991–29994.
Shimoda K, Kamesaki K, Numata A, et al. Cutting edge: tyk2 is required for the induction and nuclear translocation of Daxx which regulates IFN-alpha-induced suppression of B lymphocyte formation. J Immunol. 2002;169:4707–4711.
Muller U, Steinhoff U, Reis LF, et al. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science. 1994;264:1918–1921.
Gribaudo G, Lembo D, Cavallo G, Landolfo S, Lengyel P. Interferon action: binding of viral RNA to the 40-kilodalton 2’-5’- oligoadenylate synthetase in interferon-treated Hela cells infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1991;65:1748–1757.
Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282.
Samuel CE, Duncan GS, Knutson GS, Hershey JWB. Mechanisms of interferon action. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:13451–13457.
Pavlovic J, Zurcher T, Haller O, Staeheli P. Resistance to influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus conferred by expression of human MxA protein. J Virol. 1990;64:3370–3375.
Ortaldo JR, Mantovani A, Hobbs D, et al. Effects of several species of human leukocyte interferon on cytotoxic activity of NK cells and monocytes. Int J Cancer. 1983;31:285–289.
Blackman MJ, Morris AG. The effect of interferon treatment of targets on susceptibility to cytotoxic T-lymphocyte killing: augmentation of allogenic killing and virus specific killing relative to viral antigen expression. Immunology. 1985;56:451–457.
Fellous M, Nir U, Wallach D, et al. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA for the major histocompatibility antigens in human fibro- blasts and lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79:3082–3086.
Yamada G, Ogawa M, Akagi K, et al. Specific depletion of the pre B-cell population induced by aberrant expression of human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A. 1991;88:532–536.
Holtschke T, Lohler J, Kanno Y, et al: Immunodeficiency and chronic myelogenous leukemia-like syndrome in mice with a targeted mutation of the ICSBP gene. Cell. 1996;87:307–317.
Koromilas AE, Roy S, Barber GN, Katze MG, Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-inducible dsRNA- dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992;257:1685–1689.
Rysiecki G, Gewert DR, Williams BRG. Constitutive expression of a 2’,5’-oligoadenylate synthetase cDNA results in increased antiviral activity and growth suppression. J Interferon Res. 1989;9:649–657.
Tamura T, Ishihara M, Lamphier MS, et al. An IRF-1-dependent pathway of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in mitogen activated T lymphocytes. Nature. 1995;376:596–599.
Takaoka A, Hayakawa S, Yanai H, et al. Integration of inter- feron-α/ß signaling to p53 responses in tumor suppression and antiviral defence. Nature. 2003;424:516–523.
Platanias LC, Uddin S, Bruno E, et al. CrkL and CrkII participate in the generation of the growth inhibitory effects of interferons on pri- mary hematopoietic progenitors. Exp Hematol. 1999;27:1315–1321.
Gongora R, Stephan RP, Zhang Z, Cooper MD. An essential role for Daxx in the inhibition of B lymphopoiesis by type I interferons. Immunity. 2001;14:727–737.
Jonasch E, Haluska FG. Interferon in oncological practice: review of interferon biology, clinical applications, and toxicities. Oncologist 2001;6:34–55.
Shaw GD, Boll W, Taira H, et al. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983;11:555–573.
Higashi Y, Sokawa Y, Watanabe Y, et al. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983; 258:9522–9529.
Oritani K, Kincade PW, Zhang C, Tomiyama Y, Matsuzawa Y. Type I interferons and limitin: a comparison of structures, recep- tors, and functions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001;12:337–348.
Uze G, Lutfalla G, Mogensen KE. α and ß interferons and their receptor and their friends and relations. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995;15:3–26.
Oritani K, Kincade PW, Tomiyama Y. Limitin: an interferon-like cytokine without myeloerythroid suppressive properties. J Mol Med.2001;79:168–174.
Oritani K, Hirota S, Nakagawa T, et al. T lymphocytes constitu- tively produce an interferonlike cytokine limitin characterized as a heat- and acid-stable and heparin-binding glycoprotein. Blood. 2003;101:178–185.
Takaoka A, Taniguchi T. New aspects of IFN-alpha/beta signalling in immunity, oncogenesis and bone metabolism. Cancer Sci. 2003; 94:405–411.
Kawamoto S, Oritani K, Asakura E, et al. A new interferon, limitin displays equivalent immunomodulatory and antitumor activities without myelosuppressive properties as compared with interferon- alpha. Exp Hematol. 2004;32:797–805.
Sperber S, Hunger S, Schwartz B, Pestka S. Anti-rhinoviral activity of recombinant and hybrid species of interferon alpha. Antiviral Res. 1993;22:121–129.
Foster GR, Finter NB. Are all type I human interferons equivalent? J Viral Hepat. 1998;5:143–152.
Rani SMR, Foster GR, Leung S, et al. Characterization of beta-R1, a gene that is selectively induced by interferon-beta (IFN-beta) compared with IFN-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:22878–22884.
Abramovich C, Shulman LM, Ratovitski E, et al. Differential tyro- sine phosphorylation of the IFNAR chain of the type I interferon receptor and an associated surface protein in response to IFN alpha and IFN beta. EMBO J. 1994;13:5871–5877.
Cebrian M, Yague E, Landazuri MO, et al. Different functional sites on rIFN-alpha 2 and their relation to the cellular binding site. J Immunol. 1987;138:484–490.
Kontsek P, Borecky L, Kontsekova E, et al. Mapping of two immunodominant structures on human interferon alpha 2c and their role in binding to cells. Mol Immunol. 1991;28:1289–1297.
Uze G, Di Marco S, Mouchel-Vielh E, et al. Domains of interaction between alpha interferon and its receptor components. J Mol Biol. 1994;243:245–257.
Runkel L, Pfeffer L, Lewerenz M, et al. Differences in activity between alpha and beta type I interferons explored by mutational analysis. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:8003–8008.
Shorts LH, Dancz CE, Shupp JW, Pontzer CH. Characterization of N-terminal interferon tau mutants: P26L affords enhanced activity and lack of toxicity. Exp Biol Med. 2004;229:194–202.
Bascosi M, Russo F, D'Innocenzo S, et al. Amantadine and inter- feron in the combined treatment of hepatitis C virus in elderly patients. Hepatol Res. 2002;22:231–239.
Reddy KR, Wright TL, Pockros PJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of pegylated (40-kd) interferon alpha-2a compared with interferon alpha-2a in noncirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2001;33:433–438.
Melian EB, Plosker GL. Interferon alphacon-1: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Drugs. 2001;61:1661–1691.
Weiss K. Safety profile of interferon-α therapy. Semin Oncol. 1998; 25:9–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Oritani, K., Tomiyama, Y. Interferon- ζ/Limitin: Novel Type I Interferon That Displays a Narrow Range of Biological Activity. Int J Hematol 80, 325–331 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.04087
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.04087