Abstract
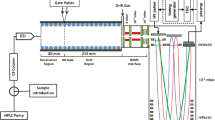
We recently developed a quantitative peptidomics method using stable isotopic labels and mass spectrometry to both quantify and identify a large number of peptides. To test this approach and screen for peptides regulated by cocaine administration, 32 Cpe fat/fat mice and 16 wild-type mice were treated twice daily for 5 d either with saline or 10 mg/kg cocaine. Peptides were extracted from striatum, hypothalamus, hippocampus, and trimethylammonium butyrate containing either nine deuterium or nine hydrogen atoms. Pools of heavy- and light-labeled peptides were combined, purified on an anhydrotrypsin affinity column, and analyzed on a reverse-phase column coupled to an electrospray ionization quadrapole time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Changes in peptide levels upon cocaine treatment were determined from the relative peak intensities of the cocaine versus saline peaks, and peptides were identified from collision-induced dissociation spectra. Ten peptides were found to increase or decrease in each of two separate analyses from distinct groups of mice. Peptides found to increase corresponded to fragments of proenkephalin, prothyrotropin-releasing hormone, provasopressin, proSAAS, secretogranin II, chromogranin B, and peptidyl-glycine-α-amidating mono-oxygenase in the hypothalamus. The same peptidyl-glycine-α-amidating mono-oxygenase peptide decreased in the prefrontal cortex, along with striatal neurokinin B and two unidentified peptides. Thirty other peptides were not substantially affected by cocaine treatment in both replicates. Taken together, the quantitative peptidomics approach provides an efficient method to screen for changes in a large number of peptides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams D. H., Hanson G. R., and Keefe K. A. (2001) Differential effects of cocaine and methamphetamine on neurotensin/neuromedin N and preprotachykinin messenger RNA expression in unique regions of the striatum. Neuroscience 102, 843–851.
Adams D. H., Hanson G. R., and Keefe K. A. (2003) Distinct effects of methamphetamine and cocaine on preprodynorphin messenger RNA in rat striatal patch and matrix. J. Neurochem. 84, 87–93.
Aebersold R. and Mann M. (2003) Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422, 198–207.
Alburges M. E., Ramos B. P., Bush L., and Hanson G. R. (2000) Responses of the extrapyramidal and limbic substance P systems to ibogaine and cocaine treatments. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 390, 119–126.
Arroyo M., Baker W. A., and Everitt B. J. (2000) Cocaine self-administration in rats differentially alters mRNA levels of the monoamine transporters and striatal neuropeptides. Mol. Brain Res. 83, 107–120.
Baggerman G., Verleyen P., Clynen E., Huybrechts J., De Loof A., and Schoofs L. (2004) Peptidomics. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 803, 3–16.
Blouin R. A., Kolpek J. H., and Mann H. J. (1987) Influence of obesity on drug disposition. Clin. Pharmacol. 6, 706–714.
Branch A. D., Unterwald E. M., Lee S. E., and Kreek M. J. (1992) Quantitation of preproenkephalin mRNA levels in brain regions from male Fischer rats following chronic cocaine treatment using a recently developed solution hybridization assay. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 14, 231–238.
Cain B. M., Wang W., and Beinfeld, M. C. (1997) Cholecystokinin (CCK) levels are greatly reduced in the brains but not the duodenums of Cpe fat/Cpefat mice: a regional difference in the involvement of carboxypeptidase E (Cpe) in pro-CCK processing. Endocrinology 138, 4034–4037.
Chard T. (1987) An Introduction to Radioimmunoassay and Related Techniques. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Che F.-Y. and Fricker L. D. (2002) Quantitation of neuropeptides in Cpe fat/Cpefat mice using differential isotopic tags and mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 74, 3190–3198.
Che F.-Y. and Fricker L. D. (2005) Quantitative peptidomics of mouse pituitary: Comparison of different stable isotopic tags. J. Mass Spectrom. 40, 238–249.
Che F.-Y., Biswas R., and Fricker L. D. (2005a) Relative quantitation of peptides in wild type and Cpe fat/fat mouse pituitary using stable isotopic tags and mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 40, 227–237.
Che F.-Y., Eipper B. A., Mains R. E., and Fricker L. D. (2003) Quantitative peptidomics of pituitary glands from mice deficient in copper transport. Cell. Mol. Biol. 49, 713–722.
Che F.-Y., Lim J., Biswas R., Pan H., and Fricker L. D. (2005b) Quantitative neuropeptidomics of microwave-irradiated mouse brain and pituitary. Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 4, 1391–1405.
Che F.-Y., Yan L., Li H., Mzhavia N., Devi L., and Fricker L. D. (2001) Identification of peptides from brain and pituitary of Cpe fat/Cpefat mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 9971–9976.
Che F.-Y., Yuan Q., Kalinina E., and Fricker L. D. (2005c) Peptidomics of Cpe fat/fat mouse hypothalamus: effect of food deprivation and exercise on peptide levels. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 4451–4461.
Cheymol G. (2000) Effects of obesity on pharmacokinetics implications for drug therapy. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 39, 215–231.
Douglass J., McKinzie A. A., and Couceyro P. (1995) PCR differential display identifies a rat brain mRNA that is transcriptionally regulated by cocaine and amphetamine. J. Neurosci. 15, 2471–2481.
Erstad B. L. (2004) Dosing of medications in morbidly obese patients in the intensive care unit setting. Intensive Care Med. 30, 18–32.
Eugene P. A., Senanayake S., and Sattin A. (2002) Cocaine regulates TRH-related peptides in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 41, 415–428.
Fricker L. D., Berman Y. L., Leiter E. H., and Devi L. A. (1996) Carboxypeptidase E activity is deficient in mice with the fat mutation: effect on peptide processing. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 30,619–30,624.
Fricker L. D., McKinzie A. A., Sun J., Curran E., Qian Y., Yan L., et al. (2000) Identification and characterization of proSAAS, a granin-like neuroendocrine peptide precursor that inhibits prohormone processing. J. Neurosci. 20, 639–648.
Gygi S. P. and Aebersold R. (2000) Mass spectrometry and proteomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 4, 489–494.
Hanson G. R., Midgley L. P., Bush L. G., Johnson M., and Gibb J. W. (1989) Comparison of responses by neuropeptide systems in rat to the psychotropic drugs, methamphetamine, cocaine and PCP. NIDA Res. Monogr. 95, 348.
Julka S. and Regnier F. E. (2004) Quantification in proteomics through stable isotope coding: a review. J. Proteome Res. 3, 350–363.
Kuzmin A. and Johansson B. (1999) Expression of c-fos, NGFI-A and secretogranin II mRNA in brain regions during initiation of cocaine self-administration in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11, 3694–3700.
Maj M., Turchan J., Smialowska M., and Przewlocka B. (2003) Morphine and cocaine influence on CRF biosynthesis in the rat central nucleus of amygdala. Neuropeptides 37, 105–110.
Mathieu-Kia A. M. and Besson M. J. (1998) Repeated administration of cocaine, nicotine and ethanol: effects on preprodynorphin, preprotachykinin A and preproenkephalin mRNA expression in the dorsal and the ventral striatum of the rat. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 54, 141–151.
Naggert J. K., Fricker L. D., Varlamov O., Nishina P. M., Rouille Y., Steiner D. F., et al. (1995) Hyperproinsulinemia in obese fat/fat mice associated with a point mutation in the carboxypeptidase E gene and reduced carboxypeptidase E activity in the pancreatic islets. Nat. Genet. 10, 135–142.
Rovere C., Viale A., Nahon J., and Kitabgi P. (1996) Impaired processing of brain proneurotensin and promelanin-concentrating hormone in obese fat/fat mice. Endocrinology 137, 2954–2958.
Schrader M. and Schulz-Knappe P. (2001) Peptidomics technologies for human body fluids. Trends Biotechnol. 19, S55-S60.
Skold K., Svensson M., Kaplan A., Bjorkesten L., Astrom J., and Andren P.E. (2002) A neuroproteomic approach to targeting neuropeptides in the brain. Proteomics 2, 447–454.
Smiley P. L., Johnson M., Bush L., Gibb J. W., and Hanson G. R. (1990) Effects of cocaine on extrapyramidal and limbic dynorphin systems. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 253, 938–943.
Spangler R., Unterwald E. M., and Kreek M. J. (1993) ‘Binge’ cocaine administration induces a sustained increase of prodynorphin mRNA in rat caudateputamen. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 19, 323–327.
Svensson M., Skold K., Svenningsson P., and Andren P. F. (2003) Peptidomics-based discovery of novel neuropeptides. J. Proteome Res. 2, 213–219.
Turchan J., Maj M., Przewlocka B., and Przewlocki R. (2002) Effect of cocaine and amphetamine on biosynthesis of proenkephalin and prodynorphin in some regions of the rat limbic system. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 54, 367–372.
Varlamov O. and Fricker L. D. (1998) Intracellular trafficking of metallocarboxypeptidase D in AtT-20 cells: localization to the trans-Golgi network and recycling from the cell surface. J. Cell Sci. 111, 877–885.
Varlamov O., Eng F. J., Novikova E. G., and Fricker L. D. (1999a) Localization of metallocarboxypeptidase D in AtT-20 cells: Potential role in prohormone processing. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 14,759–14,767.
Varlamov O., Leiter E. H., and Fricker L. D. (1996) Induced and spontaneous mutations at Ser202 of carboxypeptidase E: Effect on enzyme expression, activity, and intracellular routing. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 13,981–13,986.
Varlamov O., Wu F., Shields D., and Fricker L. D. (1999b) Biosynthesis and packaging of carboxypeptidase D into nascent secretory vesicles in pituitary cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 14,040–14,045.
Wahlestedt C., Karoum F., Jaskiw G., Wyatt R. J., Larhammar D., Ekman R., and Reis D. J. (1991) Cocaine-induced reduction of brain neuropeptide Y synthesis dependent on medial prefrontal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 88, 2078–2082.
Westwood S. C. and Hanson G. R. (1999) Effects of stimulants of abuse on extrapyramidal and limbic neuropeptide Y systems. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 288, 1160–1166.
Yuferov V., Nielsen D., Butelman E., and Kreek M. J. (2005) Microarray studies of psychostimulant-induced changes in gene expression. Addict. Biol. 10, 101–118.
Zhang R., Sioma C. S., Thompson R. A., Xiong L., and Regnier F. E. (2002) Controlling deuterium isotope effects in comparative proteomics. Anal. Chem. 74, 3662–3669.
Zhou Y., Spangler R., Schlussman S. D., Yuferov V. P., Sora I., Ho A., et al. (2002) Effects of acute “binge” cocaine on preprodynorphin, preproenkephalin, proopiomelanocortin, and corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor mRNA levels in the striatum and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis of mu-opioid receptor knockout mice. Synapse 45, 220–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Che, FY., Vathy, I. & Fricker, L.D. Quantitative peptidomics in mice. J Mol Neurosci 28, 265–275 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:28:3:265
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:28:3:265