Abstract
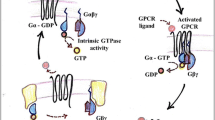
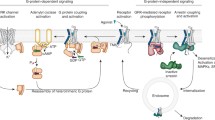
Seven membrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) function as ligand-activated guanine nucleotide exchange factors for heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding (G) proteins that relay extracellular stimuli by activating intracellular effector enzymes or ion channels. Recent work, however, has shown that GPCRs also participate in numerous other protein-protein interactions that generate intracellular signals in conjunction with, or even independent of, G-protein activation. Nowhere has the importance of protein complex assembly in GPCR signaling been demonstrated more clearly than in the control of the spatial and temporal activity of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade. ERK1/2 activation by GPCRs often involves cross talk with classical receptor tyrosine kinases or focal adhesion complexes, which scaffold the assembly of a Ras activation complex. Even more surprising is the phenomenon of G protein-independent signaling using β-arrestins, proteins originally characterized for their role in homologous GPCR desensitization, as scaffolds for the assembly of a multiprotein signalsome directly upon the GPCR. Although both forms of signaling lead to MAP kinase activation, the pathways appear to be functionally, as well as mechanistically, distinct. Transactivated receptor tyrosine kinase mediate rapid and transient MAP kinase activation that favors nuclear translocation of the kinases and transcriptional activation. In contrast, β-arrestin-dependent signaling produces a slower and more sustained increase in MAP kinase activity that is often restricted to the cytosol. Together, these highly organized signaling complexes dictate the location, duration, and ultimate function of GPCR-stimulated MAP kinase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed I., Gesty-Palmer D., Drezner M. K., and Luttrell L. M. (2003) Transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor mediates parathyroid hormone and prostaglandin F2β-stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in cultured transgenic murine osteoblasts. Mol. Endocrinol. 17, 1607–1621.
Ahn S., Nelson C. D., Garrison T. R., Miller W. E., and Lefkowitz R. J. (2003) Desensitization, internalization, and signaling functions of beta-arrestins demonstrated by RNA interference. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 1740–1744.
Ahn S., Wei H., Garrison T. R., and Lefkowitz R. J. (2004a) Reciprocal regulation of angiotensin receptor-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinases by beta-arrestins 1 and 2. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 7807–7811.
Ahn S., Shenoy S. K., Wei H., and Lefkowitz R.J. (2004b) Differential kinetic and spatial patterns of β-arrestin and G protein-mediated ERK activation by the angiotensin II receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 35518–35525.
Asakura M., Kitakaze M., Takashima S., Liao Y., Ishikura F., Yoshinaka T., et al. (2002) Cardiac hypertrophy is inhibited by antagonism of ADAM12 processing of HB-EGF: metalloproteinase inhibitors as a new therapy. Nat. Med. 8, 35–40.
Azzi M., Charest P. G., Angers S., Rousseau G., Kohout T., Bouvier M., and Pinyero G. (2003) Beta-arrestinmediated activation of MAPK by inverse agonists reveals distinct active conformations for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 11406–11411.
Bockaert J., Marin P., Dumuis A., and Fagni L. (2003) The ‘magic tail’ of G protein-coupled receptors: An anchorage for functional protein networks. FEBS Lett. 546, 65–72.
Brady A. E. and Limbird L. E. (2002) G protein-coupled receptor interacting proteins: Emerging roles in localization and signal transduction. Cell. Signal. 14, 297–309.
Daub H., Wallash C., Lankenau A., Herrlich A., and Ullrich A. (1997) Signal characteristics of G protein-transactivated EGF receptor.EMBO J. 16 , 7032–7044.
Daub H., Weiss F. U., Wallasch C., and Ullrich A. (1996) Role of transactivation of the EGF receptor in signalling by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 379, 557–560.
DeFea K. A., Vaugh Z. D., O’Bryan E. M., Nishijima D., Dery O., and Bunnett N. W. (2000a) The proliferative and antiapoptotic effects of substance P are facilitated by formation of a β-arrestin-dependent scaffolding complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 11086–11091.
DeFea K. A., Zalevsky J., Thoma M. S., Dery O., Mullins R. D., and Bunnett N. W. (2000b) β-Arrestin-dependent endocytosis of proteinase-activated receptor 2 is required for intracellular targeting of activated ERK1/2. J. Cell Biol. 148, 1267–1281.
Della Rocca G. J., Maudsley S., Daaka Y., Lefkowitz R. J., and Luttrell L. M. (1999) Pleiotropic coupling of G-protein-coupled receptors to the MAP kinase cascade: role of focal adhesions and receptor tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 13978–13984.
Dhanasekaran N., Heasley L. E., and Johnson G. L. (1995) G protein-coupled receptor systems involved in cell growth and oncogenesis. Endocr. Rev. 16, 259–270.
Dikic I., Tokiwa G., Lev S., Courtneidge S. A., and Schlessinger J. (1996) A role for PYK2 and Src in linking G-protein-coupled receptors with MAP kinase activation. Nature 383, 547–550.
Eguchi S., Numaguchi K., Iwasaki H., Matsumoto T., Yamakawa T., Utsunomiya H., et al. (1998) Calcium-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation mediates the angiotensin II-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8890–8896.
Elorza A., Penela P., Sarnago S., and Mayor F. Jr. (2003) MAPK-dependent degradation of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 29164–29173.
Fan H. and Derynck R. (1999) Ectodomain shedding of TGF-α and other transmembrane proteins is induced by receptor tyrosine kinase activation and MAP kinase signaling cascades. EMBO J. 18, 6962–6972.
Ferguson S. S. (2001) Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: the role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 1–24.
Fong A. M., Premont R. T., Richardson R. M., Yu Y. R., Lefkowitz R. J., and Patel D. D. (2002) Defective lymphocyte chemotaxis in beta-arrestin 2- and GRK6-deficientmice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 7478–7483.
Fredriksson R., Lagerstrom M. C., Lundin L. G., and Schioth H. B. (2003) The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol. Pharmacol. 63, 1256–1272.
Freedman N. J. and Lefkowitz R. J. (1996) Desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 51, 319–351.
Ge L., Ly Y., Hollenberg M., and DeFea K. (2003) A beta-arrestin-dependent scaffold is associated with prolonged MAPK activation in pseudopodia during protease-activated receptor-2-induced chemotaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 34418–34426.
Goodman O. B. Jr., Krupnick J. G., Santini F., Gurevich V. V., Penn R. B., Gagnon A. W., et al. (1996) Beta-arrestin acts as a clathrin adaptor in endocytosis of the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Nature 383, 447–450.
Gutkind J. S. (1998) The pathways connecting G protein-coupled receptors to the nucleus through divergent mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 1839–1842.
Hall R. A. and Lefkowitz R. J. (2002) Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling by scaffold proteins. Circ. Res. 91, 672–680.
Hawes B. E., Luttrell L. M., van Biesen T., and Lefkowitz R. J. (1996) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is an early intermediate in the Gβγ-mediated mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 12133–12136.
Herrlich A., Daub H., Knebel A., Herrlich P., Ullrich A., Schultz G., and Gudermann T. (1998) Ligand-independent activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor is a necessary intermediate in lysophosphatidic acid-stimulated mitogenic activity in L cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95, 8985–8990.
Kohout T. A., Nicholas S. L., Perry S. J., Reinhart G., Junger S., and Struthers R. S. (2004) Differential desensitization, receptor phosphorylation, β-arrestin recruit ment, and ERK1/2 activation by the two endogenous ligands for the CC chemokine receptor 7. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 23214–23222.
Laporte S. A., Oakley R. H., Zhang J., Holt J. A., Ferguson S. S., Caron M. G., and Barak L. S. (1999) The beta2-adrenergic receptor/beta-arrestin complex recruits the clathrin adaptor AP-2 during endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 3712–3717.
Lev S., Moreno H., Martinez R., Canoll P., Peles E., Musacchio J. M., et al. (1995) Protein tyrosine kinase PYK2 involved in Ca(2+)-induced regulation of ion channel and MAP kinase functions. Nature 376, 737–745.
Linseman D. A., Benjamin C. W., and Jones D. A. (1995) Convergence of angiotensin II and platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling cascades in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 12563–12568.
Luttrell L. M. and Lefkowitz R. J. (2002) The role of beta-arrestins in the termination and transduction of G-protein-coupled receptor signals. J. Cell. Sci. 115, 455–465.
Luttrell L. M., Della Rocca G. J., van Biesen T., Luttrell D. K., and Lefkowitz R. J. (1997) Gβγ subunits mediate Src-dependent phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 4637–4644.
Luttrell L. M., Ferguson S. S. G., Daaka Y., Miller W. E., Maudsley S., Della Rocca G. J., et al. (1999) β-Arrestin-dependent formation of β2 adrenergic receptor/Src protein kinase complexes. Science 283, 655–661.
Luttrell L. M., Roudabush F. L., and Choy E. W., Miller W. E., Field M. E., Pierce K. L., and Lefkowitz R. J. (2001) Activation and targeting of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by β-arrestin scaffolds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 2449–2454.
Maudsley S., Pierce K. L., Zamah A. M., Miller W. E., Ahn S., Daaka Y., et al. (2000) The {ie262-1}adrenergic receptor mediates extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation via assembly of a multi-receptor complex with the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 9572–9580.
McDonald P. H., Chow C.-W., Miller W. E., LaPorte S. A., Field M. E., Lin F.-T., et al. (2000) β-Arrestin 2: a receptor-regulated MAPK scaffold for the activation of JNK3. Science 290, 1574–1577.
Miranti C. K. and Brugge J. S. (2002) Sensing the environment: a historical perspective on integrin signal transduction. Nat. Cell. Biol. 4, E83–90.
Oakley R. H., Laporte S. A., Holt J. A., Caron M. G., and Barak L. S. (2000) Differential affinities of visual arrestin, β-arrestin1, and β-arrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 17201–17210.
Oakley R. H., Laporte S. A., Holt J. A., Barak L. S., and Caron M. G. (2001) Molecular determinants underlying the formation of stable intracellular G protein-coupled receptor-β-arrestin complexes after receptor endocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 19452–19460.
Parsons J. T. (2003) Focal adhesion kinase: the first ten years. J. Cell Sci. 116, 1409–1416.
Pierce K. L., Luttrell L. M., and Lefkowitz R. J. (2001a) New mechanisms in heptahelical receptor signaling to mitogen activated protein kinase cascades. Oncogene 20, 1532–1539.
Pierce K. L., Tohgo A., Ahn S., Field M. E., Luttrell L. M., and Lefkowitz R. J. (2001b) Epidermal growth factor receptor dependent ERK activation by G protein-coupled receptors: a co-culture system for identifying intermediates upstream and downstream of HB-EGF shedding. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 23155–23165.
Prenzel N., Zwick E., Daub H., Leserer M., Abraham R., Wallasch C., and Ullrich A. (1999) EGF receptor transactivation by G-protein-coupled receptors requires metalloproteinase cleavage of proHB-EGF. Nature 402, 884–888.
Scott M. G., Le Rouzic E., Perianin A., Pierotti V., Enslen H., Benichou S., et al. (2002) Differential nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of β-arrestins. Characterization of a leucine-rich nuclear export sequence in β-arrestin2. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 37693–37701.
Shah B. H., Yesilkaya A., Olivares-Reyes J. A., Chen H. D., Hunyady L., and Catt K. J. (2004) Differential pathways of angiotensin II-induced extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation in specific cell types: role of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor. Mol. Endocrinol. 18, 2035–2048.
Shenoy S. K. and Lefkowitz R. J. (2003). Multifaceted roles of beta-arrestins in the regulation of seven-membrane-spanning receptor trafficking and signalling. Biochem. J. 375, 503–515.
Tohgo A., Pierce K. L., Choy E. W., Lefkowitz R. J., and Luttrell L. M. (2002) β-Arrestin scaffolding of the ERK cascade enhances cytosolic ERK activity but inhibits ERK-mediated transcription following angiotensin AT1a receptor stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 9429–9436.
Tohgo A., Choy E. W., Gesty-Palmer D., Pierce K. L., Laporte S., Oakley R. H., et al. (2003) The stability of the G protein-coupled receptor-beta-arrestin interaction determines the mechanism and functional consequence of ERK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 6258–6267.
van Biesen T., Hawes B. E., Luttrell D. K., Krueger K. M., Touhara K., Porfiri E., et al. (1995) Receptor-tyrosine-kinase-and Gβγ-mediated MAP kinase activation by a common signalling pathway. Nature 376, 781–784.
van Biesen T., Luttrell L. M., Hawes B. E., and Lefkowitz R. J. (1996) Mitogenic signaling via G protein-coupled receptors. Endocr. Rev. 17, 698–714.
Wang P., Wu Y., Ge X., Ma L., and Pei G. (2003) Subcellular localization of beta-arrestins is determined by their intact N domain and the nuclear export signal at the C terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11648–11653.
Wei H., Ahn S., Shenoy S. K., Karnik S. S., Hunyady L., Luttrell L. M., and Lefkowitz R. J. (2003) Independent beta-arrestin 2 and G protein-mediated pathways for angiotensin II activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 10782–10787.
Yart A., Roche S., Wetzker R., Laffargue M., Tonks N., Mayeux P., Chap H., and Raynal P. (2002) A function for phosphoinositide 3-kinase beta lipid products in coupling beta gamma to Ras activation in response to lysophosphatidic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 21167–21178.
Zhang J., Barak L. S., Anborgh P. H., Laporte S. A., Caron M. G., and Ferguson S. S. (1999) Cellular trafficking of G protein-coupled receptor/β-arrestin endocytic complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 10999–11006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luttrell, L.M. Composition and function of G protein-coupled receptor signalsomes controlling mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. J Mol Neurosci 26, 253–264 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:26:2-3:253
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:26:2-3:253