Abstract
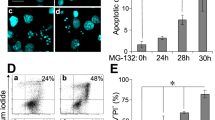
To understand the role of Ras-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) in trophic factor withdrawal- and oxidative stress-induced apoptotic cell death processes, undifferentiated rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells and a PC12 variant cell line stably expressing the Ras dominant-negative mutant (M-M17-26) were subjected to serum withdrawal in the absence or presence of H2O2 treatment. The extent of cell death was analyzed by lactate dehydrogenase release, internucleosomal DNA fragmentation, and caspase-3 assays. Both serum with-drawal and H2O2 treatment induced apoptotic cell death in PC12 cells, and the extent of cell death was greatly enhanced in M-M17-26 cells. DNA fragmentation induced by serum withdrawal or H2O2 treatment was blocked completely by a general caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-FMK. A selective MAPK kinase inhibitor, U0126, blocked the H2O2-induced phosphorylation of Erk1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) in PC12 cells and increased the levels of active caspase-3 in M-M17-26 under serum withdrawal or H2O2 treatment. In addition, the short-term H2O2 treatment (5–30 min) was sufficient to cause DNA fragmentation in M-M17-26 cells even though H2O2 was removed and cells were incubated in regular growth medium with complete serum for 24 h. However, similar, short-term H2O2 treatment of PC12 cells did not induce DNA fragmentation 24 h later. These results suggest that the Ras-Erk pathway is critical in mediating protection against apoptotic cell death induced by either trophic factor withdrawal or increased oxidative stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe J., Okuda M., Huang Q., Yoshizumi M., and Berk B. C. (2000) Reactive oxygen species activate P90 ribosomal S6 kinase via Fyn and Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 1739–1748.
Abe M. K., Kartha S., Karpova A. Y., Li J., Liu P. T., Kuo W. L., and Hershenson M. B. (1998) Hydrogen peroxide activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase via protein kinase C, Raf-1, and MEK1. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 18, 562–569.
Anastasiadis P.Z., Jiang H., Bezin L., Kuhn D. M., and Levine R. A. (2001) Tetrahydrobiopterin enhances apoptotic PC12 cell death following withdrawal of trophic support. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 9050–9058.
Bains J. S. and Shaw C. A. (1997) Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: the role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death. Brain Res. Rev. 25, 335–358.
Crossthwaite A. J., Hasan S., and Williams R. J. (2002) Hydrogen peroxide-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2, Akt/PKB and JNK in cortical neurones: dependence on Ca(2+) and PI3-kinase. J. Neurochem. 80, 24–35.
Favata M. F., Horiuchi K. Y., Manos E. J., Daulerio A. J., Stradley D. A., Feeser W. S., et al. (1998) Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 18,623–18,632.
Greene L. A. (1978) Nerve growth factor prevents the death and stimulates the neuronal differentiation of clonal PC12 pheochromocytoma cells in serum-free medium. J. Cell Biol. 78, 747–755.
Guyton K. Z., Liu Y., Gorospe M., Xu Q., and Holbrook N. J. (1996) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by H2O2. Role in cell survival following oxidant injury. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 4138–4142.
Ishikawa Y. and Kitamura M. (1999) Dual potential of extra-cellular signal-regulated kinase for the control of cell survival. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 264, 696–701.
Jacobson M. D. (1996) Reactive oxygen species and programmed cell death. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 83–86.
Jiang H., Movsesyan V., Fink D. W. Jr., Fasler M., Whalin M., Katagiri Y., et al. (1997a) Expression of human P140trk receptors in P140trk-deficient, PC12/endothelial cells results in nerve growth factor-induced signal transduction and DNA synthesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 66, 229–244.
Jiang H., Ulme D. S., Dickens G., Chabuk A., Lavarreda M., Lazarovici P., and Guroff G. (1997b) Both P140(Trk) and P75(NGFR) nerve growth factor receptors mediate nerve growth factor-stimulated calcium uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 6835–6837.
Kamata H., Tanaka C., Yagisawa H., and Hirata H. (1996) Nerve growth factor and forskolin prevent H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by glutathione independent mechanism. Neurosci. Lett. 212, 179–182.
Kurland J. F., Voehringer D. W., and Meyn R. E. (2003) The MEK/ERK pathway acts upstream of NF-kappa B1 (P50) homodimer activity and Bcl-2 expression in a murine B-cell lymphoma cell line: MEK inhibition restores radiation-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 32,465–32,470.
Kyriakis J. M. (1999) Making the connection: coupling of stress-activated ERK/MAPK (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase) core signalling modules to extracellular stimuli and biological responses. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 64, 29–48.
Lazarovici P., Jiang H., and Fink D. Jr. (1998) The 38-amino-acid form of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide induces neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells that is dependent on protein kinase C and extracellular signal-regulated kinase but not on protein kinase a, nerve growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, P21(Ras) G protein, and Pp60(c-Src) cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase. Mol. Pharmacol. 54, 547–558.
Lazarovici P., Oshima M., Shavit D., Shibutani M., Jiang H., Monshipouri M., et al. (1997) Down-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptors by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells is P140(Trk)-, Ras-, and Src-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11,026–11,034.
Lee S. D., Lee B. D., Han J. M., Kim J. H., Kim Y., Suh P. G., and Ryu S. H. (2000) Phospholipase D2 activity suppresses hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 75, 1053–1059.
Lindenboim L., Haviv R., and Stein R. (1995) Inhibition of drug-induced apoptosis by survival factors in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 64, 1054–1063.
Maroto R. and Perez-Polo J. R. (1997) Bcl-2-related protein expression in apoptosis: oxidative stress versus serum deprivation in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 69, 514–523.
Mori M., Uchida M., Watanabe T., Kirito K., Hatake K., Ozawa K., and Komatsu N. (2003) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1 and ERK2 induces Bcl-XL up-regulation via inhibition of caspase activities in erythropoietin signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 195, 290–297.
Okuda S. Nishiyama N., Saito H., and Katsuki H. (1996) Hydrogen peroxide-mediated neuronal cell death induced by an endogenous neurotoxin, 3-hydroxykynurenine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93, 12,553–12,558.
Olanow C. W. and Arendash G. W. (1994) Metals and free radicals in neurodegeneration. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 7, 548–558.
Park D. S., Stefanis L., Yan C. Y. I., Farinelli S. E., and Greene L. A. (1996) Ordering the cell death pathway. Differential effects of Bcl2, an interleukin-1-converting enzyme family protease inhibitor, and other survival agents on JNK activation in serum/nerve growth factor-deprived PC12 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 21,898–21,905.
Robinson M. J. and Cobb M. H. (1997) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 180–186.
Rukenstein A., Rydel R. E., and Greene L. A. (1991) Multiple agents rescue PC12 cells from serum-free cell death by Transla. J. Neurosci. 11, 2552–2563.
Sakamoto T., Repasky W. T., Uchida K., Hirata A., and Hirata F. (1996) Modulation of cell death pathways to apoptosis and necrosis of H2O2-treated rat thymocytes by lipocortin I. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 220, 643–647.
Salh B. S., Martens J., Hundal R. S., Yoganathan N., Charest D., Mui A., and Gomez-Munoz A. (2000) PD98059 attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death through inhibition of Jun N-terminal kinase in HT29 cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. Res. Commun. 4, 158–165.
Satoh T., Sakai N., Enokido Y., Uchiyama Y., and Hatanaka H. (1996) Free radical-independent protection by nerve growth factor and Bcl-2 of PC12 cells from hydrogen peroxide-triggered apoptosis. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 120, 540–546.
Szeberenyi J., Cai H., and Cooper G. M. (1990) Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on neuronol differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10, 5324–5332.
Tabakman R., Jiang H., Levine R. A., Kohen R., and Lazarovici P. (2004) Apoptotic characteristics of cell death and the neuroprotective effect of homocarnosine on pheochromocytoma PC12 cells exposed to ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 75, 499–507.
Tischler A. S. and Greene L. A. (1978) Morphologic and cytochemical properties of a clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Lab. Invest. 39, 77–89.
Vaudry D., Chen Y., Hsu C. M., and Eiden L. E. (2002a) PC12 cells as a model to study the neurotrophic activities of PACAP. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 971, 491–496.
Vaudry D., Stork P. J., Lazarovici P., and Eiden L. E. (2002b) Signaling pathways for PC12 cell differentiation: making the right connections. Science 296, 1648–1649.
Yamakawa H., Ito Y., Naganawa T., Banno Y., Nakashima S., Yoshimura S., et al. (2000) Activation of caspase-9 and -3 during H2O2-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells independent of ceramide formation. Neurol. Res. 22, 556–564.
Zhang X. D., Borrow J. M., Zhang X. Y., Nguyen T., and Hersey P. (2003) Activation of ERK1/2 protects melanoma cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis by inhibiting Smac/DIABLO release from mitochondria. Oncogene 22, 2869–2881.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Zhang, L., Koubi, D. et al. Roles of Ras-Erk in apoptosis of PC12 cells induced by trophic factor withdrawal or oxidative stress. J Mol Neurosci 25, 133–140 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:25:2:133
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:25:2:133