Abstract
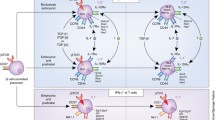
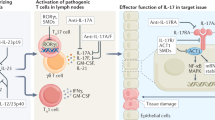
The proinflammatory cytokine IL-17A, mainly produced by specialized T cells, plays an important homeostatic role in regulating neutrophil production and blood neutrophil counts. This review will assemble and discuss the evidence for this function of IL-17A-producing cells, which are collectively called neutrophil-regulatory T cells or Tn cells. IL-17A-producing lymphocytes are most abundant in the mesenteric lymph node, where they account for 0.15% of all lymphocytes. About 60% of the Tn cells are γδ T cells, about 25% NKT-like cells, and less than 15% are CD4 T cells. These latter cells are also known as T-17 or ThIL-17 cells, a subset of Tn cells that also plays an important role in autoimmune diseases. IL-17A produced by Tn cells regulates the production of G-CSF, which in turn promotes the proliferation of promyelocytes and maturation of neutrophils. This homeostatic mechanism plays an important role in normal physiology and in host defense against bacterial infections. This review is aimed at highlighting the important role of IL-17A-producing T cells at the interface between the adaptive and innate immune system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stark MA, Huo Y, Burcin TL, Morris MA, Olson TS, Ley K: Phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils regulates granulopoiesis via IL-23 and IL-17. Immunity 2005; 22(3):285–294.
Demetri GD, Griffin JD: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and its receptor. Blood 1991; 78(11): 2791–2808.
Nathan C. Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol 2006;6(3):173–182.
Becker C, Wirtz S, Blessing M, et al: Constitutive p40 promoter activation and IL-23 production in the terminal ileum mediated by dendritic cells. J Clin Invest 2003;112(5):693–706.
Forlow SB, Schurr JR, Kolls JK, Bagby GJ, Schwarzenberger PO, Ley K: Increased granulopoiesis through interleukin-17 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in leukocyte adhesion molecule-deficient mice. Blood 2001;98(12):3309–3314.
Koury MJ. Erythropoietin: the story of hypoxia and a finely regulated hematopoietic hormone Exp Hematol 2005;33(11):1263–1270.
Yao Z, Painter SL, Fanslow WC, et al.: Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J Immunol 1995;155(12):5483–5486.
Li H, Chen J, Huang A, et al: Cloning and characterization of IL-17B and IL-17C, two new members of the IL-17 cytokine family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97(2):773–778.
Lee J, Ho WH, Maruoka M, et al: IL-17E, a novel proinflammatory ligand for the IL-17 receptor homolog IL-17Rh1. J Biol Chem 2001;276(2):1660–1664.
Starnes T, Robertson MJ, Sledge G, et al: Cutting edge: IL-17F, a novel cytokine selectively expressed in activated T cells and monocytes, regulates angiogenesis and endothelial cell cytokine production. J Immunol 2001;167(8):4137–4140
Hurst SD, Muchamuel T, Gorman DM, et al: New IL-17 family members promote Th1 or Th2 responses in the lung: in vivo function of the novel cytokine IL-25. J Immunol 2002;169(1):443–453.
Starnes T, Broxmeyer HE, Robertson MJ, Hromas R. Cutting edge: IL-17D, a novel member of the IL-17 family, stimulates cytokine production and inhibits hemopoiesis. J Immunol 2002;169(2):642–646.
Fossiez F, Djossou O, Chomarat P, et al: T cell interleukin-17 induces stromal cells to produce proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines. J Exp Med 1996;183(6):2593–2603.
Hymowitz SG, Filvaroff EH, Yin JP, et al: IL-17s adopt a cystine knot fold: structure and activity of a novel cytokine, IL-17F, and implications for receptor binding. EMBO J 2001;20(19):5332–5341.
Ziolkowska M, Koc A, Luszczykiewicz G, et al: High levels of IL-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients: IL-15 triggers in vitro IL-17 production via cyclosporin A-sensitive mechanism. J Immunol 2000;164(5): 2832–2838.
Fujino S, Andoh A, Bamba S, et al.: Increased expression of interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2003;52(1):65–70.
Yao Z, Spriggs MK, Derry JM, et al.: Molecular characterization of the human interleukin (IL)-17 receptor. Cytokine 1997;9(11):794–800.
Novatchkova M, Leibbrandt A, Werzowa J, Neubuser A, Eisenhaber F. The STIR-domain superfamily in signal transduction, development and immunity. Trends Biochem Sci 2003;28(5):226–229.
Kolls JK, Linden A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity 2004;21(4):467–476.
Kramer JM, Yi L, Shen F, et al: Cutting edge: evidence for ligand-independent multimerization of the IL-17 receptor. J Immunol 2006;176(2):711–715.
Laan M, Lotvall J, Chung KF, Linden A: IL-17-induced cytokine release in human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro: role of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases. Br J Pharmacol 2001;133(1):200–206.
Kehlen A, Thiele K, Riemann D, Langner J: Expression, modulation and signalling of IL-17 receptor in fibrob-last-like synoviocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 2002;127(3):539–546.
Lomaga MA, Yeh WC, Sarosi I, et al.: TRAF6 deficiency results in osteopetrosis and defective interleukin-1, CD40, and LPS signaling. Genes Dev 199913(8):1015–1024.
Naito A, Azuma S, Tanaka S, et al.: Severe osteopetrosis, defective interleukin-1 signalling and lymph node organogenesis in TRAF6-deficient mice. Genes to Cells 1999;4(6):353–362.
Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, et al: A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol 2005;6(11):1133–1141.
Aggarwal S, Ghiladi N, Xie MH, de Sauvage FJ, Gurney AL, Interleukin-23 promotes a distinct CD4 T cell activation state characterized by the production of interleukin-17. J Biol Chem 2003;278(3):1910–1914.
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, et al: IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp. med 2005;20(2): 233–240.
Harrington LE, hatton RD, Mangan PR, et al.: Inteleukin 17-producing CD4+effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages Nat Immunol 2005;6(11):1123–1132.
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, et al: Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat. Immunol. 2005;6(11):1123–1132.
Langrish CL, McKenzie BS, Wilson NJ, de Waal MR, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ: IL-12 and IL-23: master regulators of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 2004;202:96–105.
Ferretti S, Bonneau O, Dubois GR, Jones CE, Trifilieff A: IL-17, produced by lymphocytes and neutrophils, is necessary for lipopolysaccharide-induced airway neutrophilia: IL-15 as a possible trigger. J Immunol 2003;170(4):2106–2112.
Happel KI, Zheng M, Young E, et al: Clutting edge: roles of toll-like receptor 4 and IL-23 in IL-17 expression in response to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. J Immunol 2003;170(9):4432–4436.
Monteiro JP, Benjamin A, Costa ES, Barcinski MA, Bonomo A: Normal hematopoiesis is maintained by activated bone row CD4+ T cells. Blood 2005;105(4): 1484–1491.
Schwarzenberger P, La Russa V, Miller A, et al: IL-17 stimulates granulopoiesis in mice: use of an alternate, novel gene therapy-derived method for in vivo evaluation of cytokines. J Immunol 1998;161(11): 6383–6389.
Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Lu H, Norman K, et al: Spontaneous skin ulceration and defective T cell function in CD18 null mice. J. Exp Med 1998;188(1):119–131.
Forlow SB, White, EJ, Barlow SC et al: Severe inflammatory defect and reduced viability in CD18 and E-selectin double mutant mice. J Clin Invest 2000; 106:1457–1466.
Forlow SB, Foley PL, Ley K. Severely reduced neutrophil adhesion and impaired host defense against fecal and commensal bacteria in CD18−/−P-selectin−/−double null mice. FASEB J 2002;16(12): 1488–1496.
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B: TGFbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 2006;24(2):179–189.
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, et al: Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 2000;13(5):715–725.
Liu W, Kurlander RJ: Analysis of the interrelationship between IL-12, TNF-alpha, and IFN-gamma production during murine listeriosis. Cell Immunol 1995;163(2): 260–267.
Ozenci V, Kouwenhoven M, Press R, Link H, Huang YM: IL-12 elispot assays to detect and enumerate IL-12 secreting cells. Cytokine 2000;12(8):1218–1224.
McKenzie BS, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ: Understanding the IL-23-IL-17 immune pathway. Trends Immunol 2006;27(1):17–23.
Murphy CA, Langrish CL, Chen Y, et al: Divergent pro-and antiinflammatory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 2003;198(12): 1951–1957.
Napolitani G, Rinaldi A, Bertoni F, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A: Selected Toll-like receptor agonist combinations synergistically trigger a T helper type 1-polarizing program in dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 2005; 6(8):769–776.
Li J, Gran B, Zhang GX et al: Differential expression and regulation of IL-23 and IL-12 subunits and receptors in adult mouse microglia. J Neurol Sci 2003;215(1–2): 95–103.
Vanden ES, Goriely S, De WD, Goldman M, Willems F: Preferential production of the IL-12(p40)/IL-23(p19) heterodimer by dendritic cells from human newborns. Eur J Immunol 2006;36(1):21–26.
Kidoya H, Umemura M, Kawabe T et al: Fas ligand induces cell-autonomous IL-23 production in dendritic cells, a mechanism for Fas ligand-induced IL-17 production. J Immunol 2005;175(12):8024–8031.
Wiekowski MT, Leach MW, Evans EW, et al: Ubiquitous transgenic expression of the IL-23 subunit p19 induces multiorgan inflammation, runting, infertility, and premature death. J Immunol 2001;166(12):7563–7570.
Parham C, Chirica M, Timans J et al: A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12R{beta} 1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J Immunol 2002;168(11):5699–5708.
Ziolkowska M, Koc A, Luszczykiewicz G, et al: High levels of IL-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients: IL-15 triggers in vitro IL-17 production via cyclosporin A-sensitive mechanism. J Immunol 2000;164(5):2832–2838.
Ferretti S, Bonneau O, Dubois GR, Jones CE, Trifilieff A: IL-17, produced by lymphocytes and neutrophils, is necessary for lipopolysaccharide-induced airway neutrophilia: IL-15 as a possible trigger. J Immunol 2003;170(4):2106–2112.
Tsuchiya M, Asano S, Kaziro Y, Nagata S. Isolation and characterization of the cDNA for murine granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Proc. Natl Acad USA 1986;83(20):7633–7637.
Larsen A, Davis T, Curtis BM et al: Expression cloning of a human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor: a structural mosaic of hematopoietin receptor, immunoglobulin, and fibronectin domains. J Exp Med 1990;172(6):1559–1570.
Ye P, Rodriguez FH, Kanaly S et al.: Requirement of interleukin 17 receptor signaling for lung CXC chemokine and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor expression, neutrophil recruitment, and host defense. J Exp Med 2001;194(4):519–528.
Niess JH, Brand S, Gu X, et al: CX3CR1-mediated dendritic cell access to the intestinal lumen and bacterial clearance. Science 2005;307(5707):254–258.
Ohkubo T, Tsuda M, Suzuki S, El BN, Yamamura M. Peripheral blood neutrophils of germ-free rats modified by in vivo granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor and exposure to natural environment. Scand J Immunol 1999;49(1):73–77.
Lieschke GJ, Grail D, Hodgson G, et al: Mice lacking granulocyte colony-stimulating factor have chronic neutropenia, granulocyte and macrophage progenitor cell deficiency, and impaired neutrophil mobilization. Blood 1994;84(6):1737–1746.
Liu F, Wu HY, Wesselschmidt R, Kornaga T, Link DC: Impaired production and increased apoptosis of neutrophils in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor-deficient mice. Immunity 1996;5(5):491–501.
Nakae S, Komiyama Y, Nambu A, et al: Antigen-specific T cell sensitization is impaired in IL-17-deficient mice, causing suppression of allergic cellular and humoral responses. Immunity 2002;17(3):375–387.
Ghilardi N, Kljavin N, Chen Q, Lucas S, Gurney AL, de Sauvage FJ. Compromised humoral and delayed-type hypersensitivity responses in IL-23-deficient mice. J Immunol 2004;172(5):2827–2833.
Horwitz BH, Mizgerd JP, Scott ML, Doerschuk CM: Mechanisms of granulocytosis in the absence of CD18. Blood 2001;97(6):1578–1583.
Ren Y, Stuart L, Lindberg FP et al: Nonphologistic clearance of late apoptotic neutrophils by macrophages: efficient phagocytosis independent of {{beta}{ 2 integrins. J Immunol 2001;166(7):4743–4750.
Savill JS, Wyllie AH, Henson JE, Walport MJ, Henson PM, Haslett C. Macrophage phagocytosis of aging neutrophils in inflammation. Programmed cell death in the neutrophil leads to its recognition by macrophages. J Clin Invest 1989;83(3):865–875.
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Konowal A, Freed PW, Westcott JY, Henson PM: Macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells in vitro inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production through autocrine/paracrine mechanisms involving TGF-beta, PGE2, and PAF. J Clin Invest 1998;101(4):890–898.
Savill J, Fadok V. Corpse clearance defines the meaning of cell death. Nature 2000;407(6805):784–788.
Hoffmann PR, Kench JA, Vondracek A, et al: Interaction between phosphatidylserine and the phosphatidylserine receptor inhibits immune responses in vivo. J Immunol 2005;174(3):1393–1404.
Stuart LM, Lucas M, Simpson C, Lamb J, Savill J, Lacy-Hulbert A Inhibitory effects of apoptotic cell ingestion upon endotoxin-driven myeloid dendritic cell maturation. J Immunol 2002:168(4):1627–1635
Huynh ML, Fadok VA, Henson PM: Phosphatidylserine-dependent ingestion of apoptotic cells promotes TGF-{beta{ 1 secretion and the resolution of inflammation. J Clin Invest 2002;109(1):41–50.
Demetri GD, Zenzie BW, Rheinwald JG, Griffin JD: Expression of colony-stimulating factor genes by normal human mesothelial cells and human malignant mesothelioma cells lines in vitro. Blood 1989;74(3):940–946.
Zsebo KM, Yuschenkoff VN, Schiffer S, et al: Vascular endothelial cells and granulopoiesis: interleukin-1 stimulates release of G-CSF and GM-CSF. Blood 1988;71(1):99–103.
Suzuki A, Takahashi T, Okuno Y et al: IL-1 production as a regulator of G-CSF and IL-6 production in CSF-producing cell lines. Br J Cancer 1992;65(4):515–518.
Lenhoff S, Olofsson T. Cytokine regulation of GM-CSF and G-CSF secretion by human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Cytokine 1996;8(9): 702–709.
Ernst TJ, Ritchie AR, Demetri GD, Griffin JD: Regulation of granulocyte- and monocyte-colony stimulating factor mRNA levels in human blood monocytes is mediated primarily at a post- transcriptional level. J Biol Chem 1989;264(10):5700–5703.
Vellenga E, Dokter W, de Wolf JT, van de Vinne B, Esselink MT, Halie MR. Interleukin-4 prevents the induction of G-CSF mRNA in human adherent monocytes in response to endotoxin and IL-1 stimulation. Br J Haematol 1991;79(1):22–26.
Wieser M, Bonifer R, Oster W, Lindemann A, Mertelsmann R, Herrmann F: Interleukin-4 induces secretion of CSF for granulocytes and CSF for macrophages by peripheral blood monocytes. Blood 1989;73(5): 1105–1108.
Koeffler HP, Gasson J, Tobler A: Transcriptional and posttranscriptional modulation of myeloid colony-stimulating factor expression by tumor necrosis factor and other agents. Mol Cell Biol 1988;8(8):3432–3438.
Demetri GD, Zenzie BW, Rheinwald JG, Griffin JD: Expression of colony-stimulating factor genes by normal human mesothelial cells and human malignant mesothelioma cells lines in vitro. Blood 1989;74(3): 940–946.
Lu L, Srour EF, Warren DJ, et al: Enhancement of release of granulocyte- and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated sorted subsets of human T lymphocytes by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Synergism with recombinant human IFN-gamma. J Immunol 1988;141(1):201–207.
Oster W, Lindemann A, Mertelsmann R, Herrmann F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF) and multilineage CSF recruit human monocytes to express granulocyte CSF. Blood 1989;73(1):64–67.
Collins RG, Jung U, Ramirez M, et al: Dermal and pulmonary inflammatory disease in E-selectin and P-selectin double-null mice is reduced in triple-selectin-null mice. Blood 2001;98(3):727–735.
Spreandio M, Thatte A, Foy D, Ellies LG, Marth JD, Ley K. Severe impairment of leukocyte rolling in venules of core 2 glucosaminyltransferase-deficient mice. Blood 2001;97(12):3812–3819.
Novatchkova M, Leibbrandt A, Werzowa J, Neubuser A, Eisenhaber F. The STIR-domain superfamily in singal transduction, development and immunity. Trends Biochem Sci, 2003;28(5):226–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ley, K., Smith, E. & Stark, M.A. IL-17A-producing neutrophil-regulatory Tn lymphocytes. Immunol Res 34, 229–242 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:34:3:229
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:34:3:229