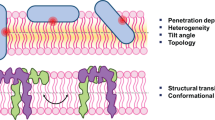
Abstract
A large number of transmembrane proteins form aqueous pores or channels in the phospholipid bilayer, but the structural bases of pore formation and assembly have been determined experimentally for only a few of the proteins and protein complexes. The polypeptide segments that form the transmembrane pore and the secondary structure that creates the aqueous-lipid interface can be identified using multiple independent fluorescence techniques (MIFT). The information obtained from several different, but complementary, fluorescence analyses, including measurements of emission intensity, fluorescence lifetime, accessibility to aqueous and to lipophilic quenching agents, and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) can be combined to characterize the nature of the protein-membrane interaction directly and unambiguously. The assembly pathway can also be determined by measuring the kinetics of the spectral changes that occur upon pore formation. The MIFT approach therefore allows one to obtain structural information that cannot be obtained easily using alternative techniques such as crystallography. This review briefly outlines how MIFT can reveal the identity, location, conformation, and topography of the polypeptide sequences that interact with the membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schirmer, T. (1998) General and specific porins from bacterial outer membranes. J. Struct. Biol. 121, 101–109.
Johnson, A. E. and van Waes, M. A. (1999) The translocon: a dynamic gateway at the ER membrane. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 15, 799–842.
Rassow, J. and Pfanner, N. (2000) The protein import machinery of the mitochondrial membranes. Traffic 1, 457–464.
Alouf, J. E. and Freer, J. H. (1999) The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins, 2nd ed., Academic, London.
Heuck, A. P., Tweten, R. K., and Johnson, A. E. (2001) β-Barrel pore forming toxins: intriguing dimorphic proteins. Biochemistry 40, 9065–9073.
Lakey, J. H. and Slatin, S. L. (2001) Pore-forming colicins and their relatives, in Pore-Forming Toxins (van der Goot, F. G., ed.), Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology Series, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 131–161.
Hamman, B. D., Chen, J.-C., Johnson, E. E., and Johnson, A. E. (1997) The aqueous pore through the translocon has a diameter of 40–60 Å during cotranslational protein translocation at the ER membrane. Cell 89, 535–544.
Hamman, B. D., Hendershot, L. M., and Johnson, A. E. (1998) BiP maintains the permeability barrier of the ER membrane by sealing the lumenal end of the translocon pore before and early in translocation. Cell 92, 747–758.
Gabriel, K., Buchanan, S. K., and Lithgow, T. (2001) The alpha and the beta: protein translocation across mitochondrial and plastid outer membranes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26, 36–40.
White, S. H. and Wimley, W. C. (1999) Membrane protein folding and stability: physical principles. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 28, 319–365.
Baleja, J. D. (2001) Structure determination of membrane-associated proteins from nuclear magnetic resonance data. Anal. Biochem. 288, 1–15.
White, S. H., Ladokhin, A. S., Jayasinghe, S., and Hristova, K. (2001) How membranes shape protein structure. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 32,395–32,398.
Hubbell, W. L., Gross, A., Langen, R., and Lietzow, M. A. (1998) Recent advances in sitedirected spin labeling of proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8, 649–656.
Vigano, C., Manciu, L., Buyse, F., Goormaghtigh, E. and Ruysschaert, J.-M. (2000) Attenuated total reflection IR spectroscopy as a tool to investigate the structure, orientation and tertiary structure changes in peptides and membrane proteins. Biopolymers 55, 373–380.
Chen, Y. and Barkley, M. D. (1998) Toward understanding tryptophan fluorescence in proteins. Biochemistry 37, 9976–9982.
Johnson, A. E., Esmon, N. L., Laue, T. M., and Esmon, C. T. (1983) Structural changes required for activation of protein C are induced by Ca2+ binding to a high affinity site that does not contain γ-carboxyglutamic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 5554–5560.
Soulages, J. L. and Arrese, E. L. (2000) Fluorescence spectroscopy of single tryptophan mutants of apolipophorin-III in discoidal lipopoproteins of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry 39, 10,574–10,580.
Nakamura, M., Sekino-Suzuki, N., Mitsui, K.-I., and Ohno-Iwashita, Y. (1998) Contribution of tryptophan residues to the structural changes in perfringolysin O during interaction with liposomal membranes J. Biochem. 123, 1145–1155.
Shepard, L. A., Heuck, A. P., Hamman, B. D., Rossjohn, J., Parker, M. W., Ryan, K. R., et al. (1998) Identification of a membrane-spanning domain of the thiol-activated pore-forming toxin Clostridium perfringens perfringolysin O: an α-helical to β-sheet transition identified by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry 37, 14,563–14,574.
Ye, J., Esmon, N. L., Esmon, C. T., and Johnson, A. E. (1991) The active site of thrombin is altered upon binding to thrombomodulin: two distinct structural changes are detected by fluorescence, but only one correlates with protein C activation. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 23,016–23,021.
Hotze, E. M., Wilson-Kubalek, E. M., Rossjohn, J., Parker, M. W., Johnson, A. E. and Tweten, R. K. (2001) Arresting pore formation of a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin by disulfide trapping synchronizes the insertion of the transmembrane β-sheet from a prepore intermediate. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 8261–8268.
Arai, K.-I., Kawakita, M., Nakamura, S., Ishikawa, I. and Kaziro, Y. (1974) Studies on the polypeptide elongation factors from E. coli. IV. Characterization of sulfhydryl groups in EF-Tu and EF-Ts. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 76, 523–534.
Mansoor, S. E., Mchaourab, H. S. and Farrens, D. L. (1999) Determination of protein secondary structure and solvent accessibility using sitedirected fluorescence labeling. Studies of T4 lysozyme using the fluorescent probe monobromobimane. Biochemistry 38, 16,383–16,393.
Crowley, K. S., Liao, S., Worrell, V. E., Reinhart, G. D., and Johnson, A. E. (1994) Secretory proteins move through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane via an aqueous, gated pore. Cell 78, 461–471.
Liao, S., Lin, J., Do, H. and Johnson, A. E. (1997) Both lumenal and cytosolic gating of the aqueous ER translocon pore is regulated from inside the ribosome during membrane protein integration. Cell 90, 31–41.
Husten, E. J., Esmon, C. T. and Johnson, A. E. (1987) The active site of blood coagulation factor Xa. Its distance from the phospholipid surface and its conformational sensitivity to components of the prothrombinase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 12,953–12,961.
Yegneswaran, S., Smirnov, M. D., Safa, O., Esmon, N. L., Esmon, C. T. and Johnson, A. E. (1999) Relocating the active site of activated protein C eliminates the need for its protein S cofactor. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer study. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 5462–5468.
Heuck, A. P., Hotze, E. M., Tweten, R. K., and Johnson, A. E. (2000) Mechanism of membrane insertion of a multimeric β-barrel protein: perfringolysin O creates a pore using ordered and coupled conformational changes. Mol. Cell 6, 1233–1242.
MacDonald, R. C., MacDonald, R. I., Menco, B. P. M., Takeshita, K., Subbarao, N. K. and Hu, L. (1991) Small-volume extrusion apparatus for preparation of large, unilamellar vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1061 297–303.
Mayer, L. D., Hope, M. J. and Cullis, P. R. (1986) Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 858, 161–168.
Weber, G. and Farris, F. J. (1979) Synthesis and spectral properties of a hydrophobic fluorescent probe: 6-propionyl-2-(dimethylamino)naphthalene. Biochemistry 18, 3075–3078.
Prendergast, F. G., Meyer, M., Carlson, G. L., Iida, S., and Potter, J. D. (1983) Synthesis, spectral properties, and use of 6-acryloyl-2-dimethylaminonaphthalene (acrylodan). A thiol-selective, polarity-sensitive fluorescent probe. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 7541–7544.
Valeva, A., Weisser, A., Walker, B., Kehoe, M., Bayley, H., Bhakdi, S., et al. (1996) Molecular architecture of a toxin pore: a 15-residue sequence lines the transmembrane channel of staphylococcal α-toxin. EMBO J. 15, 1857–1864.
Schindel, C., Zitzer, A., Schulte, B., Gerhards, A., Stanley, P., Hughes, C., et al. (2001) Interaction of Escherichia coli hemolysin with biological membranes. A study using cysteine scanning mutagenesis. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 800–808.
Kenner, R. A. and Aboderin, A. A. (1971) A new fluorescent probe for protein and nucleoprotein conformation. Binding of 7-(p-methoxybenzylamino)-4-nitrobenzoxadiazole to bovine trypsinogen and bacterial ribosomes. Biochemistry 10, 4433–4440.
Crowley, K., Reinhart, G. D. and Johnson, A. E. (1993) The signal sequence moves through a ribosomal tunnel into a noncytoplasmic aqueous environment at the ER membrane early in translocation. Cell 73, 1101–1115.
Kosower, E. M. and Kosower, N. S. (1995) Bromobimane probes for thiols. Methods Enzymol. 251, 133–148.
Wang, Y., Malenbaum, S. E., Kachel, K., Zhan, H., Collier, R. J. and London, E. (1997) Identification of shallow and deep membranepenetrating forms of diphtheria toxin T domain that are regulated by protein concentration and bilayer width. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 25,091–25,098.
Shatursky, O., Heuck, A. P., Shepard, L. A., Rossjohn, J., Parker, M. W., Johnson, A. E., et al. (1999) The mechanism of membrane insertion for a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin: a novel paradigm for pore-forming toxins. Cell 99, 293–299.
Chattopadhyay, A. and London, E. (1987) Parallax method for direct measurement of membrane penetration depth utilizing fluorescence quenching by spin-labeled phospholipids. Biochemistry 26, 39–45.
Mutucumarana, V. P., Duffy, E. J., Lollar, P., and Johnson, A. E. (1992) The active site of factor IXa is located far above the membrane surface and its conformation is altered upon association with factor VIIIa. A fluorescence study. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 17,012–17,021.
McCallum, C. D., Hapak, R. C., Neuenschwander, P. F., Morrissey, J. H., and Johnson, A. E. (1996) The location of the active site of blood coagulation factor VIIa above the membrane surface and its reorientation upon association with tissue factor. A fluorescence energy transfer study. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 28,168–28,175.
Yegneswaran, S., Wood, G. M., Esmon, C. T., and Johnson, A. E. (1997) Protein S alters the active site location of activated protein C above the membrane surface. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer study of topography. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 25,013–25,021.
Armstrong, S. A., Husten, E. J., Esmon, C. T., and Johnson, A. E. (1990) The active site of membrane-bound meizothrombin: a fluorescence determination of its distance from the phospholipid surface and its conformational sensitivity to calcium and factor Va. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 6210–6218.
Lu, R., Esmon, N. L., Esmon, C. T. and Johnson, A. E. (1989) The active site of the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex: a fluorescence energy transfer measurement of its distance above the membrane surface. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 12,956–12,962.
Duffy, E. J., Parker, E. T., Mutucumarana, V. P., Johnson, A. E. and Lollar, P. (1992) Binding of factor VIIIa and factor VIII to factor IXa on phospholipid vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 17,006–17,011.
Harris, R. W., Sims, P. J. and Tweten, R. K. (1991) Kinetic aspects of the aggregation of Clostridium perfringens θ-toxin on erythrocyte membranes. A fluorescence energy transfer study. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 6936–6941.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heuck, A.P., Johnson, A.E. Pore-forming protein structure analysis in membranes using multiple independent fluorescence techniques. Cell Biochem Biophys 36, 89–101 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:36:1:89
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:36:1:89