Abstract
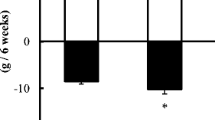
In this study, we investigated the effects of acute exercise on tissue levels of iron, magnesium, and uric acid of rats. Twenty adult Wistar albino rats were used for the study. They were divided into two groups: controls (n=10) and the study group (n=10). The study group was left into a small water pool and allowed to do swimming exercise for 30 min while controls rested. All of the animals were sacrificed, and their livers and spleens removed and homogenized immediately. The iron, magnesium, and uric acid levels of the homogenates were measured by an autoanalyzer (ILAB 900, Italy) with commercial kits from the same company. Results were evaluated by the Mann-Whitney U-test. According to our results, the liver iron levels increased significantly with exercise, whereas spleen iron levels decreased significantly (p<0.05) compared to controls. We found no significant differences in the levels of the other two parameters with exercise. These results show that the iron distribution in organs changes with exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Turgut, O. Genç, and B. Kaptanoğlu, Investigation of serum calcium, phosphorus, albumine, uric acid and lipid parameters in sportsmen and sedanters, Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Ther. Latinoam. 49, 184–188 (1999).
A. Haskell, E. R. Nadel, N. S. Stachenfeld, et al., Transcapillary escape rate of albumin in humans during exercise-induced hypervolemia, J. Appl. Physiol. 83, 407–413 (1997).
E. Bonora, G. Targher, M. B. Zenere, et al., Relationship of uric acid concentration to cardiovascular risk factors in young men, Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 20, 975–980 (1996).
A. Sedgwick, D. Thomas, and M. Davies, Relationships between change in aerobic fitness and changes in blood pressure and plasma lipids in men and women, J. Clin. Epidemiol. 46, 141–151 (1993).
A. Sedgwick, D. Thomas, M. Davies, et al., Cross-sectional and longitudinal relationships between physical fitness and risk factors for coronary heart disease in men and women, J. Clin. Epidemiol. 42, 189–200 (1989).
W. Ming, A. M. Caroline, A. H. Carlton, et al., Changes in lipids associated with change in regular exercise in free-living men, J. Clin. Epidemiol. 50, 1137–1142 (1997).
F. J. Navas, J. F. Martin, and A. Cordova, Compartmental shifts of calcium and magnesium as a result of swimming and swimming training in rats, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 29, 882–891 (1997).
P. M. Clarkson, Minerals: Exercise performance and supplementation in athletes, J. Sports Sci. 9, 91–116 (1991).
A. Magazanik, Y. Weinstein, R. A. Dlin, et al., Iron deficiency caused by 7 weeks of intensive physical exercise, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 57, 198–202 (1988).
Y. Rayssiguier, C. Y. Guezennecc, and J. Durlach, New experimental and clinical data on the relationship between magnesium and sport, Magnesium Res. 3, 93–102 (1990).
S. Demir, G. Turgut, Ö. Yurtseven, et al., Effect of exercise on lipid peroxidation, Acta Med. 44, 41–42 (2001).
J. M. McBride, W. J. Kraemer, T. M. Triplett, et al., Effect of resistance exercise on free radical production, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 30, 67–72 (1998).
B. Halliwell and J. Gutteridge, Lipid peroxidation, oxygen radicals, cell damage, and antioxidant therapy, Lancet 23, 1396–1398 (1984).
E. Witt, A. Reznick, C. Viguie, et al., Exercise, oxidative damage and effects of antioxidant manipulation, J. Nutr. 122, 766–773 (1992).
M. F. Waller and E. M. Haymes, The effects of heat and exercise on sweat iron loss, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 28, 197–203 (1996).
K. Sakurada and J. Tanaka, Sport-anemia: studies on hematological status in high school boy athletes, Rinsho Byori 44, 616–621 (1996).
J. F. Escanero, J. Villanueva, and A. Rojo, Iron stores in professional athletes throughout the sports season, Physiol. Behav. 62, 811–814 (1997).
C. M. Weaver and S. Raaram, Exercise and iron status, J. Nutr. 122, 782–787 (1992).
F. J. Navas and A. Cordova, Iron distribution in different tissues in rats following exercise, Biol. Trace Element Res. 73, 259–268 (2000).
L. Strause, J. Hegenauer, and P. Saltman, Effects of exercise on iron metabolism in rats, Nutr. Res. 3, 79–89 (1983).
M. K. Prasad and C. Pratt, The effects of exercise and two levels of dietary iron on iron status, Nutr. Res. 10, 1273–1283 (1990).
Y. Hellsten-Westing, L. Kaijser, B. Ekblom, et al., Exchange of purines in human liver and skeletal muscle with short-term exhaustive exercise, Am. J. Physiol. 266, 81–86 (1994).
K. Koyama, M. Kaya, T. Ishigaki, et al., Role of xanthine oxidase in delayed lipid peroxidation in rat liver induced by acute exhausting exercise, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 80, 28–33 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaptanoğlu, B., Turgut, G., Genç, O. et al. Effects of acute exercise on the levels of iron, magnesium, and uric acid in liver and spleen tissues. Biol Trace Elem Res 91, 173–177 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:91:2:173
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:91:2:173