Abstract
Purpose
Current evidence regarding salvage resection for recurrent retroperitoneal (RP) sarcomas generally lacks detailed histology-specific analyses, but the aggressiveness of these tumors varies widely by histology. We investigated associations between timing and extent of salvage surgery and survival outcomes in patients with recurrent RP well-differentiated liposarcoma (WDLPS).
Methods
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Surgical Oncology sarcoma database was reviewed to identify patients with RP WDLPS who underwent surgical resection for first recurrent disease (salvage surgery) in 1995–2015. Medical records were retrospectively reviewed to identify factors associated with overall survival and disease-free survival.
Results
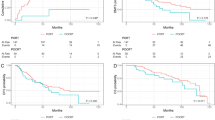
We identified 52 patients who underwent salvage surgery for RP WDLPS for first local recurrence; 28 (54%) underwent salvage surgery within 6 months after recurrence. Concomitant organ resections were performed in 32 (62%) patients, 4 (13%) of whom had pathologic invasion of resected organs. After R0/R1 resections (n = 45), 38 (84%) experienced a second local recurrence. Multivariable analyses revealed that organ invasion at the primary surgery [hazard ratio (HR) 13.08; p = 0.005] and disease-free interval < 1 year (HR 3.64; p = 0.044) were associated with shorter overall survival. Recurrence-to-salvage interval < 6 months was associated with shorter disease-free survival (HR 2.18; p = 0.025). Concomitant organ resection was associated with a longer hospital stay: ≥ 14 days (odds ratio 21.58; p = 0.007).
Conclusions
Early salvage surgery may not always be the best approach for recurrent RP WDLPS patients. Because organ invasion is rare among recurrent RP WDLPS patients and concomitant organ resection is associated with a longer hospital stay, preservation of uninvolved organs should be considered.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kotilingam D, Lev DC, Lazar AJ, Pollock RE. Staging soft tissue sarcoma: evolution and change. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56(5):282-91; quiz 314.
Crago AM, Brennan MF. Principles in management of soft tissue sarcoma. Adv Surg. 2015;49:107–22.
Tseng W, Martinez SR, Tamurian RM, Borys D, Canter RJ. Histologic type predicts survival in patients with retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma. J Surg Res. 2012;172(1):123–30.
Gronchi A, Strauss DC, Miceli R, et al. Variability in patterns of recurrence after resection of primary retroperitoneal sarcoma (RPS): A Report on 1007 Patients From the Multi-institutional Collaborative RPS Working Group. Ann Surg. 2016;263(5):1002–9.
Tan MC, Brennan MF, Kuk D, et al. Histology-based classification predicts pattern of recurrence and improves risk stratification in primary retroperitoneal sarcoma. Ann Surg. 2016;263(3):593–600.
Anaya DA, Lahat G, Wang X, et al. Establishing prognosis in retroperitoneal sarcoma: a new histology-based paradigm. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(3):667–75.
Lewis JJ, Leung D, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF. Retroperitoneal soft-tissue sarcoma: analysis of 500 patients treated and followed at a single institution. Ann Surg. 1998;228(3):355–65.
Hamilton TD, Cannell AJ, Kim M, et al. Results of resection for recurrent or residual retroperitoneal sarcoma after failed primary treatment. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24(1):211–8.
van Dalen T, Hoekstra HJ, van Geel AN, et al. Locoregional recurrence of retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma: second chance of cure for selected patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2001;27(6):564–8.
Hassan I, Park SZ, Donohue JH, et al. Operative management of primary retroperitoneal sarcomas: a reappraisal of an institutional experience. Ann Surg. 2004;239(2):244–50.
Gronchi A, Miceli R, Allard MA, et al. Personalizing the approach to retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma: histology-specific patterns of failure and postrelapse outcome after primary extended resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(5):1447–54.
Anaya DA, Lahat G, Liu J, et al. Multifocality in retroperitoneal sarcoma: a prognostic factor critical to surgical decision-making. Ann Surg. 2009;249(1):137–42.
Park JO, Qin LX, Prete FP, Antonescu C, Brennan MF, Singer S. Predicting outcome by growth rate of locally recurrent retroperitoneal liposarcoma: the one centimeter per month rule. Ann Surg. 2009;250(6):977–82.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240(2):205–13.
Feig B, Benjamin R. Guidelines for the treatment of recurrent retroperitoneal sarcoma: are we trying to fit a square peg into a round hole? Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(11):3440–3.
Lochan R, French JJ, Manas DM. Surgery for retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcomas: aggressive re-resection of recurrent disease is possible. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2011;93(1):39–43.
MacNeill AJ, Miceli R, Strauss DC, et al. Post-relapse outcomes after primary extended resection of retroperitoneal sarcoma: a report from the Trans-Atlantic RPS Working Group. Cancer. 2017;123(11):1971–8.
Grobmyer SR, Wilson JP, Apel B, et al. Recurrent retroperitoneal sarcoma: impact of biology and therapy on outcomes. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210(5):602–8, 608–10.
Laroche A, Chaire V, Algeo MP, Karanian M, Fourneaux B, Italiano A. MDM2 antagonists synergize with PI3 K/mTOR inhibition in well-differentiated/dedifferentiated liposarcomas. Oncotarget. 2017;8(33):53968.
Gronchi A, Lo Vullo S, Fiore M, et al. Aggressive surgical policies in a retrospectively reviewed single-institution case series of retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma patients. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(1):24–30.
Bonvalot S, Rivoire M, Castaing M, et al. Primary retroperitoneal sarcomas: a multivariate analysis of surgical factors associated with local control. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(1):31–7.
Pisters PW. Resection of some—but not all—clinically uninvolved adjacent viscera as part of surgery for retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(1):6–8.
Acknowledgment
Supported in part by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute under award number P30CA016672 (used the Clinical Trials Support Resource). The authors thank Sunita Patterson, Department of Scientific Publications, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, for editorial assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikoma, N., Roland, C.L., Torres, K.E. et al. Salvage Surgery for Recurrent Retroperitoneal Well-Differentiated Liposarcoma: Early Reoperation may not Provide Benefit. Ann Surg Oncol 25, 2193–2200 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-018-6417-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-018-6417-6