Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the prognostic value of concomitant seminal vesicle invasion (cSVI) in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (UCB) and contiguous prostatic stromal infiltration in a large cystectomy series.
Methods
A total of 385 patients with UCB and contiguous prostatic infiltration comprised our study. Patients were divided in two groups according to cSVI. Median follow-up was 36 months (interquartile range 11–74); the primary end point was cancer-specific mortality. The prognostic impact of cSVI was evaluated using multivariable Cox regression analysis. The predictive accuracy was assessed by a receiver operating characteristic analysis.
Results
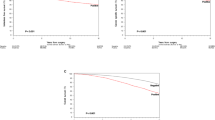
A total of 229 patients (59.5 %) without cSVI comprised group A, and 156 patients (40.5 %) with cSVI comprised group B. Positive lymph nodes (63 vs. 44 %, p < 0.001) and positive surgical margins (34 % vs. 14 %, p < 0.001) were more common in patients with cSVI. The 5- and 10-year cancer-specific survival rates were 41 % and 32 % (group A) and 21 and 17 % (group B) (p < 0.001). In multivariable analysis, pathological nodal stage (hazard ratio [HR] 2.19, p < 0.001), soft tissue surgical margin (HR 1.57, p = 0.010), clinical tumor stage (HR 1.46, p = 0.010), adjuvant chemotherapy (HR 0.40, p < 0.001), and cSVI (HR 1.69, p < 0.001) independently impacted cancer-specific mortality. The c-indices of the multivariable models with and without inclusion of cSVI were 0.658 (95 % confidence interval 0.60–0.71) and 0.635 (95 % confidence interval 0.58–0.69), respectively, resulting in a predictive accuracy gain of 2.3 % (p = 0.002).
Conclusions
In patients with UCB and prostatic stromal invasion, cSVI adversely affected cancer-specific survival compared to patients without cSVI. The inclusion of cSVI significantly improved the predictive accuracy of our multivariable model regarding survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witjes JA, Compérat E, Cowan NC, et al. EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2013 guidelines. Eur Urol. 2014;65:778–92.
Niegisch G, Albers P. Which patients benefit the most from neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced bladder cancer? Curr Opin Urol. 2011;21:434–9.
Feifer AH, Taylor JM, Tarin TV, Herr HW. Maximizing cure for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: integration of surgery and chemotherapy. Eur Urol. 2011;59:978–84.
Nuhn P, May M, Sun M, et al. External validation of postoperative nomograms for prediction of all-cause mortality, cancer-specific mortality, and recurrence in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol. 2012;61:58–64.
Tilki D, Svatek RS, Karakiewicz PI, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with pT4 urothelial carcinoma at radical cystectomy: a retrospective international study of 583 patients. J Urol. 2010;183:1757–63.
Liberman D, Alasker A, Sun M, et al. Radical cystectomy for patients with pT4 urothelial carcinoma in a large population-based study. BJU Int. 2011;107:905–11.
Greene FL, Gospodarowicz M, Wittekend C. American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging manual. 7th ed. Philadalphia: Springer; 2009.
Volkmer BG, Küfer R, Maier S, et al. Outcome in patients with seminal vesicle invasion after radical cystectomy. J Urol. 2003;169:1299–302.
Daneshmand S, Stein JP, Lesser T, et al. Prognosis of seminal vesicle involvement by transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol. 2004;172:81–4.
You D, Kim SC, Jeong IG, et al. Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder with seminal vesicle invasion: prognostic significance. BJU Int. 2010;106:1657–61.
Harrell FE Jr, Lee KL, Mark DB. Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med. 1996;15:361–87.
May M, Bastian PJ, Brookman-May S, et al. Gender-specific differences in cancer-specific survival after radical cystectomy for patients with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder in pathologic tumor stage T4a. Urol Oncol. 2011;31:1141–7.
Donat SM, Genega EM, Herr HW, Reuter VE. Mechanisms of prostatic stromal invasion in patients with bladder cancer: clinical significance. J Urol. 2001;165:1117–20.
Ro JY, Ayala AG, el-Naggar A, Wishnow KI. Seminal vesicle involvement by in situ and invasive transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987;11:951–8.
Montie JE, Wojno K, Klein E, Pearsall C, Levin H. Transitional cell carcinoma in situ of the seminal vesicles: 8 cases with discussion of pathogenesis, and clinical and biological implications. J Urol. 1997;158:1895–8.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Matthias May and Sabine Brookman-May contributed equally to this article, and both should be considered first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
May, M., Brookman-May, S., Burger, M. et al. Concomitant Seminal Vesicle Invasion in pT4a Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder with Contiguous Prostatic Infiltration is an Adverse Prognosticator for Cancer-Specific Survival after Radical Cystectomy . Ann Surg Oncol 21, 4034–4040 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3827-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3827-y