Abstract
Background
The prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and portal vein tumor thrombus remains poor. We previously reported the beneficial effects of interferon alpha (IFN) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) combination therapy for these patients. We showed that the mechanism of therapy was regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Here, we combined IFN/5-FU therapy with the VEGF receptor–selective inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584 (PTK/ZK) and examined the antitumor effects and the mechanism of action.
Methods
We studied two HCC cell lines, PLC/PRF/5 and HuH7, and a human umbilical vein endothelial cell line, HUVEC. We studied the effects of IFN/5-FU with or without PTK/ZK in growth inhibition assays, immunohistochemistry, Western blot analysis, and immunocytochemistry.
Results
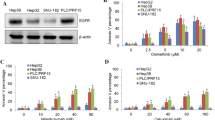
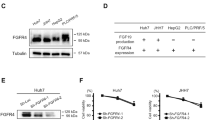
In a HuH7 xenograft model, the combination of PTK/ZK and IFN/5-FU significantly inhibited proliferation, induced apoptosis, decreased microvessel density, reduced the number of tumor cells that expressed VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR-2), and repressed the phosphorylation of Akt in vivo. In HCC cells and HUVECs in vitro, IFN/5-FU plus PTK/ZK repressed the expression of VEGFR-2 and repressed the phosphorylation of VEGFR, Akt, Erk, and p38MAPK.
Conclusions
VEGF signaling inhibition enhanced the antitumor effects of IFN/5-FU therapy on HCC cells and endothelial cells via Erk, Akt, and p38MAPK pathways.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362(9399):1907–17.
Lee HS, Kim JS, Choi IJ, Chung JW, Park JH, Kim CY. The safety and efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and main portal vein obstruction. A prospective controlled study. Cancer. 1997;79:2087–94.
Bruix J, Llovet JM. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. HePatology. 2002;35:519–24.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–90.
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Wada H, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 alters the sensitivity to interferon-based anticancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:1483–90.
Eguchi H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Augmentation of antitumor activity of 5-fluorouracil by interferon alpha is associated with up-regulation of p27Kip1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2881–90.
Yamamoto T, Nagano H, Sakon M, et al. Partial contribution of tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/TRAIL receptor pathway to antitumor effects of interferon-alpha/5-fluorouracil against hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7884–95.
Murakami M, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK/ZK enhances the antitumor effects of interferon-alpha/5-fluorouracil therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:589–96.
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Combination of interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil inhibits endothelial cell growth directly and by regulation of angiogenic factors released by tumor cells. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:361.
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Combination therapy of interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil inhibits tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins. Oncol ReP. 2007;18:801–9.
Li XM, Tang ZY, Zhou G, Lui YK, Ye SL. Significance of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA expression in invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J ExP Clin Cancer Res. 1998;17:13–7.
Yamaguchi R, Yano H, Iemura A, Ogasawara S, Haramaki M, Kojiro M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. HePatology. 1998;28:68–77.
Yamaguchi R, Yano H, Nakashima Y, et al. Expression and localization of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in human hepatocellular carcinoma and non-HCC tissues. Oncol ReP. 2000;7:725–9.
Evans IM, Britton G, Zachary IC. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces heat shock protein (HSP) 27 serine 82 phosphorylation and endothelial tubulogenesis via protein kinase D and independent of p38 kinase. Cell Signal. 2008;20:1375–84.
Liu Y, Poon RT, Li Q, Kok TW, Lau C, Fan ST. Both antiangiogenesis- and angiogenesis-independent effects are responsible for hepatocellular carcinoma growth arrest by tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584. Cancer Res. 2005;65:3691–9.
Damdinsuren B, Nagano H, Wada H, et al. Stronger growth-inhibitory effect of interferon-beta compared to IFN-alpha is mediated by IFN signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2007;30:201–8.
Tomokuni A, Eguchi H, Tomimaru Y, et al. miR-146a suppresses the sensitivity to interferon-alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem BioPhys Res Commun. 2011;414:675–80.
Miyoshi N, Ishii H, Nagai K, et al. Defined factors induce reprogramming of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:40–5.
Abe T, Yamaguchi Y, Izumino K, et al. Evaluation of insulin response in glucose tolerance test in a patient with Werner’s syndrome: a 16-year follow-up study. Diabetes Nutr Metab. 2000;13:113–8.
A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. HePatology. 1998;28:751–5.
Kondo M, Nagano H, Wada H, et al. Combination of IFN-alpha and 5-fluorouracil induces apoptosis through IFN-alpha/beta receptor in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1277–86.
Zhao L, Wientjes MG, Au JL. Evaluation of combination chemotherapy: integration of nonlinear regression, curve shift, isobologram, and combination index analyses. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7994–8004.
Wang L, Jia D, Duan F, et al. Combined anti-tumor effects of IFN-α and sorafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Biochem BioPhys Res Commun. 2012;422:687–92.
Ota H, Nagano H, Sakon M, et al. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein thrombosis by combined therapy with subcutaneous interferon-alpha and intra-arterial 5-fluorouracil; role of type 1 interferon receptor expression. Br J Cancer. 2005;93:557–64.
Nagano H, Miyamoto A, Wada H, et al. Interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil combination therapy after palliative hepatic resection in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, portal venous tumor thrombus in the major trunk, and multiple nodules. Cancer. 2007;110:2493–501.
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia–Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34.
Yau T, Chan P, Pang R, Ng K, Fan ST, Poon RT. Phase 1–2 trial of PTK787/ZK222584 combined with intravenous doxorubicin for treatment of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: implication for antiangiogenic approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2010;116:5022–9.
Wood JM, Bold G, Buchdunger E, et al. PTK787/ZK 222584, a novel and potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, impairs vascular endothelial growth factor-induced responses and tumor growth after oral administration. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2178–89.
Nakamura M, Nagano H, Sakon M, et al. Role of the Fas/FasL pathway in combination therapy with interferon-alpha and fluorouracil against hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro. J HePatol. 2007;46:77–88.
Brogi E, Schatteman G, Wu T, et al. Hypoxia-induced paracrine regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression. J Clin Invest. 1996;97:469–76.
von Marschall Z, Scholz A, Cramer T, et al. Effects of interferon alpha on vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription and tumor angiogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:437–48.
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Expression pattern of angiogenic factors and prognosis after hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma: importance of angiopoietin-2 and hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha. Liver Int. 2006;26:414–23.
Yano S, Herbst RS, Shinohara H, et al. Treatment for malignant pleural effusion of human lung adenocarcinoma by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:957–65.
Ng IO, Poon RT, Lee JM, Fan ST, Ng M, Tso WK. Microvessel density, vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1/KDR in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2001;116:838–45.
Yang ZF, Poon RT, Liu Y, et al. High doses of tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787 enhance the efficacy of ischemic hypoxia for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: dual effects on cancer cell and angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:2261–70.
Liu Y, Lui EL, Friedman SL, et al. PTK787/ZK22258 attenuates stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrosis in vivo by inhibiting VEGF signaling. Lab Invest. 2009;89:209–21.
Takahashi T, Shibuya M. The 230 kDa mature form of KDR/Flk-1 (VEGF receptor-2) activates the PLC-gamma pathway and partially induces mitotic signals in NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1997;14:2079–89.
Keyt BA, Nguyen HV, Berleau LT, et al. Identification of vascular endothelial growth factor determinants for binding KDR and FLT-1 receptors. Generation of receptor-selective VEGF variants by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:5638–46.
Fong GH, Zhang L, Bryce DM, Peng J. Increased hemangioblast commitment, not vascular disorganization, is the primary defect in flt-1 knock-out mice. DeveloPment. 1999;126:3015–25.
Jia H, Bagherzadeh A, Bicknell R, Duchen MR, Liu D, Zachary I. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D and VEGF-A differentially regulate KDR-mediated signaling and biological function in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:36148–57.
Wu WZ, Sun HC, Shen YF, et al. Interferon alpha 2a down-regulates VEGF expression through PI3Kinase and MAP kinase signaling pathways. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005;131:169–78.
Koike K, Takaki A, Tatsukawa M, et al. Combination of 5-FU and IFNalpha enhances IFN signaling pathway and caspase-8 activity, resulting in marked apoptosis in hepatoma cell lines. Int J Oncol. 2006;29:1253–61.
Sakon M, Nagano H, Dono K, et al. Combined intraarterial 5-fluorouracil and subcutaneous interferon-alpha therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the major portal branches. Cancer. 2002;94:435–42.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsura, Y., Wada, H., Murakami, M. et al. PTK787/ZK222584 Combined with Interferon Alpha and 5-Fluorouracil Synergistically Inhibits VEGF Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 20 (Suppl 3), 517–526 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-2948-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-2948-z