Abstract
Background
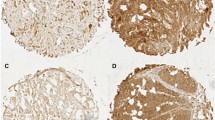
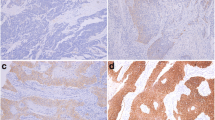
CD151 is a member of the tetraspanins and has recently been reported as a promoter of the malignant progression of cancer. The purpose of this study was to clarify the clinicopathological outcome and prognostic significance of the immunohistochemical expression of CD151 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Methods
We evaluated the significance of CD151 expression by immunohistochemistry in 138 surgically resected ESCC and the association of CD151 expression with clinicopathological features.
Results
Seventy-five (51.7%) ESCC showed a positive expression of CD151, which indicated a significant association with tumor depth (P = 0.004), lymph node metastasis (P = 0.002), distant metastasis (P = 0.025), and lymphatic invasion (P = 0.046), as well as the Ki-67 labeling index (P = 0.011). The 5-year survival rate of ESCC patients with CD151-positive expression was significantly lower than with CD151-negative expression (positive, 43.1%; negative, 63.8%; P = 0.003). Multivariate analysis showed that positive CD151 expression was not an independent factor for poor survival (P = 0.096).
Conclusions
CD151 expression is associated with tumor proliferation and invasiveness in ESCC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kato H, Fukuchi M, Miyazaki T, et al. Surgical treatment for esophageal cancer. Current issues. Dig Surg. 2007;24:88–95.
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241–52.
Stipp CS, Kolesnikova TV, Hemler ME. Functional domains in tetraspanin proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:106–12.
Yunta M, Lazo PA. Tetraspanin proteins as organisers of membrane microdomains and signalling complexes. Cell Signal. 2003;15:559–64.
Hemler ME. Tetraspanin functions and associated microdomains. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:801–11.
Berditchevski F, Gilbert E, Griffiths MR, Fitter S, Ashman L, Jenner SJ. Analysis of the CD151-alpha3beta1 integrin and CD151-tetraspanin interactions by mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41165–74.
Sridhar SC, Miranti CK. Tetraspanin KAI1/CD82 suppresses invasion by inhibiting integrin-dependent crosstalk with c-Met receptor and Src kinases. Oncogene. 2006;25:2367–78.
Hemler ME. Tetraspanin proteins mediate cellular penetration, invasion, and fusion events and define a novel type of membrane microdomain. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003;19:397–422.
Maecker HT, Todd SC, Levy S. The tetraspanin superfamily: molecular facilitators. FASEB J. 1997;11:428–42.
Fitter S, Tetaz TJ, Berndt MC, Ashman LK. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a novel platelet-endothelial cell tetra-span antigen, PETA-3. Blood. 1995;86:1348–55.
Testa JE, Brooks PC, Lin JM, Quigley JP. Eukaryotic expression cloning with an antimetastatic monoclonal antibody identifies a tetraspanin (PETA-3/CD151) as an effector of human tumor cell migration and metastasis. Cancer Res. 1999;59:3812–20.
Yauch RL, Berditchevski F, Harler MB, Reichner J, Hemler ME. Highly stoichiometric, stable, and specific association of integrin alpha3beta1 with CD151 provides a major link to phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase, and may regulate cell migration. Mol Biol Cell. 1998;9:2751–65.
Sterk LM, Geuijen CA, van den Berg JG, Claessen N, Weening JJ, Sonnenberg A. Association of the tetraspanin CD151 with the laminin-binding integrins alpha3beta1, alpha6beta1, alpha6beta4 and alpha7beta1 in cells in culture and in vivo. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:1161–73.
Takeda Y, Kazarov AR, Butterfield CE, et al. Deletion of tetraspanin Cd151 results in decreased pathologic angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Blood. 2007;109:1524–32.
Ke AW, Shi GM, Zhou J, et al. Role of overexpression of CD151 and/or c-Met in predicting prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2009;49:491–503.
Yang XH, Richardson AL, Torres-Arzayus MI, et al. CD151 accelerates breast cancer by regulating alpha 6 integrin function, signaling, and molecular organization. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3204–13.
Gesierich S, Paret C, Hildebrand D, et al. Colocalization of the tetraspanins, CO-029 and CD151, with integrins in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma: impact on cell motility. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2840–52.
Hashida H, Takabayashi A, Tokuhara T, et al. Clinical significance of transmembrane 4 superfamily in colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:158–67.
Ang J, Lijovic M, Ashman LK, Kan K, Frauman AG. CD151 protein expression predicts the clinical outcome of low-grade primary prostate cancer better than histologic grading: a new prognostic indicator? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13:1717–21.
Tokuhara T, Hasegawa H, Hattori N, et al. Clinical significance of CD151 gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:4109–14.
Sakai M, Kato H, Sano A, et al. Expression of lysyl oxidase is correlated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:2494–501.
Sadej R, Romanska H, Baldwin G, et al. CD151 regulates tumorigenesis by modulating the communication between tumor cells and endothelium. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:787–98.
Sano A, Kato H, Sakurai S, et al. CD24 expression is a novel prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:506–14.
Zoller M. Gastrointestinal tumors: metastasis and tetraspanins. Z Gastroenterol. 2006;44:573–86.
Kuwano H, Nakajima M, Miyazaki T, Kato H. Distinctive clinicopathological characteristics in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;9:6–13.
Youssef EM, Matsuda T, Takada N, et al. Prognostic significance of the MIB-1 proliferation index for patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer. 1995;76:358–66.
Klosek SK, Nakashiro K, Hara S, Shintani S, Hasegawa H, Hamakawa H. CD151 forms a functional complex with c-Met in human salivary gland cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;336:408–16.
Bussolino F, Di Renzo MF, Ziche M, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol. 1992;119:629–41.
Saeki H, Oda S, Kawaguchi H, et al. Concurrent overexpression of Ets-1 and c-Met correlates with a phenotype of high cellular motility in human esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2002;98:8–13.
Yang XH, Flores LM, Li Q, et al. Disruption of laminin-integrin-CD151-focal adhesion kinase axis sensitizes breast cancer cells to ErbB2 antagonists. Cancer Res. 2010;70:2256–63.
Gibault L, Metges JP, Conan-Charlet V, et al. Diffuse EGFR staining is associated with reduced overall survival in locally advanced oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005;93:107–15.
Mimura K, Kono K, Hanawa M, et al. Trastuzumab-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:4898–904.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, S., Miyazaki, T., Tanaka, N. et al. Prognostic Significance of CD151 Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Aggressive Cell Proliferation and Invasiveness. Ann Surg Oncol 18, 888–893 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1387-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1387-3